Abstract
In this contribution, we propose a label-free immunosensor, based on a novel type of electrolyte-gated field-effect transistor (EGOFET), for ultrasensitive detection of the C-reactive protein (CRP). The recognition layer of the biosensor is fabricated by physical adsorption of the anti-CRP monoclonal antibody onto a poly-3-hexyl thiophene (P3HT) organic semiconductor surface. A supplementary nonionic hydrophilic polymer is used as a blocking agent preventing nonspecific interactions and allowing a better orientation of the antibodies immobilized onto the P3HT surface. The whole biomolecule immobilization procedure does not require any pretreatment of the organic semiconductor surface, and the whole functionalization process is completed in less than 30 min. Surface plasmon resonance (SPR) measurements were performed to assess the amount of biomolecules physisorbed onto the P3HT and to evaluate the CRP binding proprieties of the deposited anti-CRP layer. A partial surface coverage of about 23 % of adsorbed antibody molecules was found to most efficiently sense the CRP. The electrical performance of the EGOFET immunosensor was comparable to that of a bare P3HT EGOFET device, and the obtained CRP calibration curve was linear over six orders of magnitude (from 4 pM to 2 μM). The relative standard deviation of the individual calibration points, measured on immunosensors fabricated on different chips, ranged between 1 and 14 %, and a detection limit of 2 pM (220 ng/L) was established. The novel electronic immunosensor is compatible with low-cost fabrication procedures and was successfully employed for the detection of the CRP biomarker in the clinically relevant matrix serum.

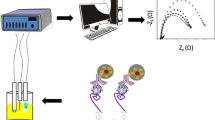
Schematic of the EGOFET immunosensor for CRP detection. The anti-CRP monoclonal antibody layer is physisorbed on the P3HT organic semiconductor and the CRP is directly measured by a label-free electronic EGOFET transducer






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Cramer T, Campana A, Leonardi F, Casalini S, Kyndiah A, Murgia M, et al. Water-gated organic field effect transistors—opportunities for biochemical sensing and extracellular signal transduction. J Mater Chem B. 2013;1(31):3728–41.
Kergoat L, Herlogsson L, Braga D, Piro B, Pham M-C, Crispin X, et al. A water-gate organic field-effect transistor. Adv Mater. 2010;22(23):2565–9.
Palazzo G, De Tullio D, Magliulo M, Mallardi A, Intranuovo F, Mulla MY, et al. Detection beyond Debye’s length with an electrolyte-gated organic field-effect transistor. Adv Mater. 2015;27:911–6.
Magliulo M, Mallardi A, Mulla MY, Cotrone S, Pistillo BR, Favia P, et al. Electrolyte-gated organic field-effect transistor sensors based on supported biotinylated phospholipid bilayer. Adv Mater. 2013;25(14):2090–4.
Magliulo M, Mallardi A, Gristina R, Ridi F, Sabbatini L, Cioffi N, et al. Part per trillion label-free electronic bioanalytical detection. Anal Chem. 2013;85(8):3849–57.
Kim SH, Hong K, Xie W, Lee KH, Zhang S, Lodge TP, et al. Electrolyte-gated transistors for organic and printed electronics. Adv Mater. 2013;25(13):1822–46.
Manoli K, Magliulo M, Mulla MY, Sing M, Sabbatini L, Palazzo G, et al. Printable bioelectronics to investigate functional biological interfaces. Angew Chem Int Ed. 2015;54:12562.
Mulla MY, Tuccori E, Magliulo M, Lattanzi G, Palazzo G, Persaud K, et al. Capacitance-modulated transistor detects odorant binding protein chiral interactions. Nat Commun. 2015;6:6010.
Casalini S, Leonardi F, Cramer T, Biscarini F. Organic field-effect transistor for label-free dopamine sensing. Org Electron. 2013;14(1):156–63.
Suspène C, Piro B, Reisberg S, Pham M-C, Toss H, Berggren M, et al. Copolythiophene-based water-gated organic field-effect transistors for biosensing. J Mater Chem B. 2013;1(15):2090.
Awsiuk K, Budkowski A, Marzec MM, Petrou P, Rysz J, Bernasik A. Effects of polythiophene surface structure on adsorption and conformation of bovine serum albumin: a multivariate and multitechnique study. Langmuir. 2014;30(46):13925–33.
Albers WM, Pelto JM, Suspène C, Määttä JA, Yassar A, Hytönen VP, et al. Structural and functional characteristics of chimeric avidins physically adsorbed onto functionalized polythiophene thin films. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces. 2012;4(8):4067–77.
Vikholm-Lundin I, Albers WM. Site-directed immobilisation of antibody fragments for detection of C-reactive protein. Biosens Bioelectron. 2006;21(7):1141–8.
Quershi A, Gurbuz Y, Kang WP, Davidson JL. A novel interdigitated capacitor based biosensor for detection of cardiovascular risk marker. Biosens Bioelectron. 2009;25(4):877–82.
Justino CIL, Freitas AC, Amaral JP, Rocha-Santos TAP, Cardoso S, Duarte AC. Disposable immunosensors for C-reactive protein based on carbon nanotubes field effect transistors. Talanta. 2013;108:165–70.
Gupta RK, Periyakaruppan A, Meyyappan M, Koehne JE. Label-free detection of C-reactive protein using a carbon nanofiber based biosensor. Biosens Bioelectron. 2014;59:112–9.
Qureshi A, Niazi JH, Kallempudi S, Gurbuz Y. Label-free capacitive biosensor for sensitive detection of multiple biomarkers using gold interdigitated capacitor arrays. Biosens Bioelectron. 2010;25(10):2318–23.
Kwon SM, Kang GB, Kim YT, Kim YH, Ju BK. In-situ detection of C-reactive protein using silicon nanowire field effect transistor. J Nanosci Nanotechnol. 2011;11(2):1511–4.
Urien M, Wantz G, Cloutet E, Hirsch L, Tardy P, Vignau L, et al. Field-effect transistors based on poly(3-hexylthiophene): effect of impurities. Org Electron. 2007;8(6):727–34.
Albers WM, Munter T, Laaksonen P, Vikholm-Lundin I. Improved functionality of antibody-colloidal gold conjugates with the aid of lipoamide-grafted N-[tris(hydroxymethyl)methyl]acrylamide polymers. J Colloid Interface Sci. 2010;348:1–8.
Dinelli F, Moulin JF, Loi MA, Da Como E, Massi M, Murgia M, et al. Effects of surface chemical composition on the early growth stages of alpha-sexithienyl films on silicon oxide substrates. J Phys Chem B. 2006;110(1):258–63.
Biacore 3000 instrument manual. Biacore AB, Uppsala, Sweden, 1999.
Braga D, Horowitz G. High-performance organic field-effect transistors. Adv Mater. 2009;21(14):1473–86.
Ishikawa FN, Curreli M, Chang H-K, Chen P-C, Zhang R, Cote RJ, et al. A calibration method for nanowire biosensors to suppress device-to-device variation. ACS Nano. 2009;3(12):3969–76.
Torsi L, Magliulo M, Manoli K, Palazzo G. Organic field-effect transistor sensors: a tutorial review. Chem Soc Rev. 2013;42:8612.
Cho S, Lee K, Yuen J, Wang G, Moses D, Heeger AJ, et al. Thermal annealing-induced enhancement of the field-effect mobility of regioregular poly(3-hexylthiophene) films. J Appl Phys. 2006;100(11):114503.
Casalini S, Dumitru AC, Leonardi F, Bortolotti CA, Herruzo ET, Campana A, et al. Multiscale sensing of antibody-antigen interactions by organic transistors and single-molecule force spectroscopy. ACS Nano. 2015;9(5):5051–62.
Mulla MY, Seshadri P, Torsi L, Manoli K, Mallardi A, Ditaranto N, et al. UV crosslinked poly(acrylic acid): a simple method to bio-functionalize electrolyte-gated OFET biosensors. J Mater Chem B. 2015;3:5049–57.
Harris LJ, Larson SB, Hasel KW, McPherson A. Refined structure of an intact IgG2a monoclonal antibody. Biochemistry. 1997;36:1581–97.
Algarra M, Gomes D, Esteves da Silva JCG. Current analytical strategies for C-reactive protein quantification in blood. Clin Chim Acta. 2013;415:1–9.
Lee WS, Sunkara V, Han JR, Park YS, Cho YK. Electrospun TiO2 nanofiber integrated lab-on-a-disc for ultrasensitive protein detection from whole blood. Lab Chip. 2015;15(2):478–85.
Aleeva Y, Pignataro B. Recent advances in upscalable wet methods and ink formulations for printed electronics. J Mater Chem C. 2014;2(32):6436.
Acknowledgments
The “Electrolyte-Gated Organic Field-Effect Biosensors—BioEGOFET” project FP7/2007-2013 under Grant agreement no. 248728, the “OFET biosensors for point-of-care applications–sense-of-care” project, FP7-People-ITN-EID-2012 under Grant Agreement 316845 and the PON project “Laboratorio per lo Sviluppo Integrato delle Scienze e delle Tecnologie dei Materiali Avanzati e per dispositivi innovativi-LABORATORIO SISTEMA,” and the PRIN 2010–2011 project no. 2010BJ23MN “Nanostructured Soft Matter” by the Italian MIUR (Ministry of Education, Universities and Research) are acknowledged for partial financial support of this work. Professor Gaetano Scamarcio is acknowledged for useful discussions. Dr. Cinzia Di Franco is acknowledged for her support in the realization of photo-lithographically patterned substrates.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
The study has been approved by the ethics committee of the University of Bari “Aldo Moro” and has been performed in accordance with the ethical standards.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Published in the topical collection featuring Young Investigators in Analytical and Bioanalytical Science with guest editors S. Daunert, A. Baeumner, S. Deo, J. Ruiz Encinar, and L. Zhang.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
ESM 1
(PDF 51 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Magliulo, M., De Tullio, D., Vikholm-Lundin, I. et al. Label-free C-reactive protein electronic detection with an electrolyte-gated organic field-effect transistor-based immunosensor. Anal Bioanal Chem 408, 3943–3952 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00216-016-9502-3
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00216-016-9502-3