Abstract
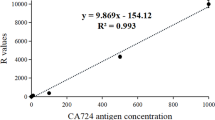
Rapid and quantitative detection of biomarkers with high sensitivity and specificity has become a common practice in the clinical diagnosis and treatment of cancer. Herein, a quantitative lateral flow immunoassay (LFIA) based on superparamagnetic nanoparticles (SPMNPs) was developed for detection of carbohydrate antigen 72-4 (CA72-4) in human serum. This direct and rapid method did not involve any sample preparation and was accomplished using a test strip in which a sandwich reaction was performed. Probes on the conjugate pad were prepared by coupling monoclonal antibody CC49 specific to CA72-4 onto SPMNPs. Coupled monoclonal antibody B72.3 and goat anti-mouse IgG were loaded onto a nitrocellulose (NC) membrane, serving as the test and control lines, respectively. Initially, results were evaluated by macroscopic observation. Afterwards, the magnetic signal strength of the reaction area was quantified using a magnetic assay reader (MAR). Several parameters that may influence the detection sensitivity were studied and optimized. Under optimal conditions, the proposed method was capable of detecting as low as 0.38 IU/mL of CA72-4 in 20 min and had a wide detection linearity range (0–100 IU/mL). We evaluated 100 clinical samples (70 positive and 30 negative) to assess the validity of these test strips, which exhibited high sensitivity (99 %) and specificity (97 %). The results indicated a high rate of accuracy (98.4–102 %) and a low relative standard deviation according to the average recovery test. In conclusion, the test strips based on SPMNP probes are a rapid, sensitive, and quantitative method for the detection of CA72-4 and possess great potential in point-of-care testing (POCT).

Schematic illustration of the strategy for CA72-4 detection and quantification using a superparamagnetic immunochromatographic strip






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Karimi P, Islami F, Anandasabapathy S, Freedman ND, Kamangar F. Gastric cancer: descriptive epidemiology, risk factors, screening, and prevention. Cancer Epidemiol Biomarkers Prev. 2014;23(5):700–13. doi:10.1158/1055-9965.epi-13-1057.
Ikeda A, Nishiumi S, Shinohara M, Yoshie T, Hatano N, Okuno T, et al. Serum metabolomics as a novel diagnostic approach for gastrointestinal cancer. Biomed Chromatogr. 2012;26(5):548–58. doi:10.1002/bmc.1671.
Shimada H, Noie T, Ohashi M, Oba K, Takahashi Y. Clinical significance of serum tumor markers for gastric cancer: a systematic review of literature by the Task Force of the Japanese Gastric Cancer Association. Gastric Cancer. 2014;17(1):26–33. doi:10.1007/s10120-013-0259-5.
Kim DH, Oh SJ, Oh CA, Choi MG, Noh JH, Sohn TS, et al. The relationships between perioperative CEA, CA 19-9, and CA 72-4 and recurrence in gastric cancer patients after curative radical gastrectomy. J Surg Oncol. 2011;104(6):585–91. doi:10.1002/jso.21919.
Gaspar MJ, Arribas I, Coca MC, Diez-Alonso M. Prognostic value of carcinoembryonic antigen, CA 19-9 and CA 72-4 in gastric carcinoma. Tumor Biol. 2001;22(5):318–22. doi:10.1159/000050633.
Chen X-Z, Zhang W-K, Yang K, Wang L-L, Liu J, Wang L, et al. Correlation between serum CA724 and gastric cancer: multiple analyses based on Chinese population. Mol Biol Rep. 2012;39(9):9031–9. doi:10.1007/s11033-012-1774-x.
Keller J, Reiss-Sklan E, Refael M, Andresen V, Levy-Herman Y, Ruvinsky I (2012) CA72-4 may contribute to real-time reconnaissance of gastric cancer. F1000 Res 1:33. doi:10.12688/f1000research.1-33.v1
Jin H, Wang X, Xin T, Gao P, Lin J-M, Liang S. Microplate chemiluminescence enzyme immunoassay for the quantitative evaluation of carbohydrate antigen 72-4 in human serum. Chin Sci Bull. 2008;53(19):2958–63. doi:10.1007/s11434-008-0428-9.
Gero EJ, Melsheimer R, Colcher D, Ferroni P, Giani S, Schlom J, et al. Ca 72-4 radioimmunoassay for the detection of the tag-72 carcinoma-associated antigen in serum of patients. J Clin Lab Anal. 1989;3(6):360–9. doi:10.1002/jcla.1860030609.
Sheng SL, Wang Q, Huang G. Development of time-resolved immunofluorometric assays for CA 72-4 and application in sera of patients with gastric tumors. Clin Chim Acta. 2007;380(1–2):106–11. doi:10.1016/j.cca.2007.01.020.
Fan H, Guo Z, Gao L, Zhang Y, Fan D, Ji G, et al. Ultrasensitive electrochemical immunosensor for carbohydrate antigen 72-4 based on dual signal amplification strategy of nanoporous gold and polyaniline-Au asymmetric multicomponent nanoparticles. Biosens Bioelectron. 2015;64:51–6. doi:10.1016/j.bios.2014.08.043.
Tothill IE. Biosensors for cancer markers diagnosis. Semin Cell Dev Biol. 2009;20(1):55–62. doi:10.1016/j.semcdb.2009.01.015.
Ren M, Xu H, Huang X, Kuang M, Xiong Y, Xu H, et al. Immunochromatographic assay for ultrasensitive detection of aflatoxin B(1) in maize by highly luminescent quantum dot beads. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces. 2014;6(16):14215–22. doi:10.1021/am503517s.
Workman S, Wells SK, Pau C-P, Owen SM, Dong XF, LaBorde R, et al. Rapid detection of HIV-1 p24 antigen using magnetic immuno-chromatography (MICT). J Virol Methods. 2009;160(1–2):14–21. doi:10.1016/j.jviromet.2009.04.003.
Chamorro-Garcia A, Dela Escosura-Muniz A, Espinosa-Castaneda M, Rodriguez-Hernandez CJ, de Torres C, Arben M. Detection of parathyroid hormone-like hormone in cancer cell cultures by gold nanoparticle-based lateral flow immunoassays. Nanomedicine. 2015. doi:10.1016/j.nano.2015.09.012.
Wang C, Hou F, Ma Y. Simultaneous quantitative detection of multiple tumor markers with a rapid and sensitive multicolor quantum dots based immunochromatographic test strip. Biosens Bioelectron. 2015;68:156–62. doi:10.1016/j.bios.2014.12.051.
Xu QF, Xu H, Gu HC, Li JB, Wang YY, Wei M. Development of lateral flow immunoassay system based on superparamagnetic nanobeads as labels for rapid quantitative detection of cardiac troponin I. Mater Sci Eng C Biomim Supramol Syst. 2009;29(3):702–7. doi:10.1016/j.msec.2009.01.009.
Yager P, Edwards T, Fu E, Helton K, Nelson K, Tam MR, et al. Microfluidic diagnostic technologies for global public health. Nature. 2006;442(7101):412–8. doi:10.1038/nature05064.
Qi H, Zhong Z, Zhou H-X, Deng C-Y, Zhu H, Li J-F, et al. A rapid and highly sensitive protocol for the detection of Escherichia coli O157:H7 based on immunochromatography assay combined with the enrichment technique of immunomagnetic nanoparticles. Int J Nanomed. 2011;6:3033–9. doi:10.2147/ijn.s25684.
Liu C, Jia Q, Yang C, Qiao R, Jing L, Wang L, et al. Lateral flow immunochromatographic assay for sensitive pesticide detection by using Fe3O4 nanoparticle aggregates as color reagents. Anal Chem. 2011;83(17):6778–84. doi:10.1021/ac201462d.
Linares EM, Kubota LT, Michaelis J, Thalhammer S. Enhancement of the detection limit for lateral flow immunoassays: evaluation and comparison of bioconjugates. J Immunol Methods. 2012;375(1–2):264–70. doi:10.1016/j.jim.2011.11.003.
Posthuma-Trumpie GA, Korf J, van Amerongen A. Lateral flow (immuno) assay: its strengths, weaknesses, opportunities and threats. A literature survey. Anal Bioanal Chem. 2009;393(2):569–82. doi:10.1007/s00216-008-2287-2.
Sajid M, Kawde A-N, Daud M. Designs, formats and applications of lateral flow assay: a literature review. J Saudi Chem Soc. 2015. doi:10.1016/j.jscs.2014.09.001.
Barnett JM, Wraith P, Kiely J, Persad R, Hurley K, Hawkins P, et al. An inexpensive, fast and sensitive quantitative lateral flow magneto-immunoassay for total prostate specific antigen. Biosensors. 2014;4(3):204–20. doi:10.3390/bios4030204.
Yuan H, Yan F, Ma L, Wu F, Zhuang J, Yang W. Carboxyl-functionalized superparamagnetic Fe3O4/poly(St-co-MPS)/SiO2 composite particles for rapid and sensitive immunoassay. J Nanosci Nanotechnol. 2011;11(3):2232–6.
Goryacheva IY, Lenain P, Saeger SD. Nanosized labels for rapid immunotests. Trac Trends Anal Chem. 2013;46:30–43. doi:10.1016/j.trac.2013.01.013.
Wong RC, Tse HY. Lateral flow immunoassay. New York: Humana; 2010. doi:10.1007/978-1-59745-240-3.
Zhang XQ, Jiang L, Zhang CL, Li D, Wang C, Gao F, et al. A silicon dioxide modified magnetic nanoparticles-labeled lateral flow strips for HBs antigen. J Biomed Nanotechnol. 2011;7(6):776–81. doi:10.1166/jbn.2011.1352.
Xiao L, Li J, Brougham DF, Fox EK, Feliu N, Bushmelev A, et al. Water-soluble superparamagnetic magnetite nanoparticles with biocompatible coating for enhanced magnetic resonance imaging. ACS Nano. 2011;5(8):6315–24. doi:10.1021/nn201348s.
Kuo HT, Yeh JZ, Jiang CM, Wu MC. Magnetic particle-linked anti hCG beta antibody for immunoassay of human chorionic gonadotropin (hCG), potential application to early pregnancy diagnosis. J Immunol Methods. 2012;381(1–2):32–40. doi:10.1016/j.jim.2012.04.006.
Wang Y, Xu H, Wei M, Gu H, Xu Q, Zhu W. Study of superparamagnetic nanoparticles as labels in the quantitative lateral flow immunoassay. Mater Sci Eng C Biomim Supramol Syst. 2009;29(3):714–8. doi:10.1016/j.msec.2009.01.011.
Jans H, Liu X, Austin L, Maes G, Huo Q. Dynamic light scattering as a powerful tool for gold nanoparticle bioconjugation and biomolecular binding studies. Anal Chem. 2009;81(22):9425–32. doi:10.1021/ac901822w.
Liu X, Dai Q, Austin L, Coutts J, Knowles G, Zou JH, et al. A one-step homogeneous immunoassay for cancer biomarker detection using gold nanoparticle probes coupled with dynamic light scattering. J Am Chem Soc. 2008;130(9):2780–2. doi:10.1021/ja711298b.
Liu DF, Huang YM, Wang SY, Liu K, Chen MH, Xiong YH, et al. A modified lateral flow immunoassay for the detection of trace aflatoxin M1 based on immunomagnetic nanobeads with different antibody concentrations. Food Control. 2015;51:218–24. doi:10.1016/j.foodcont.2014.11.036.
Sheer DG, Schlom J, Cooper HL. Purification and composition of the human tumor-associated glycoprotein (TAG-72) defined by monoclonal antibodies CC49 and B72.3. Cancer Res. 1988;48(23):6811–8.
Zhang YP, Sun P, Zhang XR, Yang WL, Si CS (2013) Synthesis of CdTe quantum dot-conjugated CC49 and their application for in vitro imaging of gastric adenocarcinoma cells. Nanoscale Res Lett 8. doi:10.1186/1556-276x-8-294
Marrelli D, Roviello F, De Stefano A, Farnetani M, Garosi L, Messano A, et al. Prognostic significance of CEA, CA 19-9 and CA 72-4 preoperative serum levels in gastric carcinoma. Oncology. 1999;57(1):55–62. doi:10.1159/000012001.
Oh YK, Joung HA, Han HS, Suk HJ, Kim MG. A three-line lateral flow assay strip for the measurement of C-reactive protein covering a broad physiological concentration range in human sera. Biosens Bioelectron. 2014;61:285–9. doi:10.1016/j.bios.2014.04.032.
Acknowledgments
We are grateful for the financial support by the National Natural Scientific Foundation of China (Grant No. 81571835), the 863 High-Tech Project of China (2012AA022703 and 2014AA020700), Shanghai Science and Technology Fund (No. 13NM1401500), funding of SJTU No YG2012MS13, Shanghai Engineering Research Center for Intelligent diagnosis and treatment instrument Fund (No.15DZ2252000).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The author reports no conflicts of interest in this work.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Chen, Y., Wang, K., Liu, Z. et al. Rapid detection and quantification of tumor marker carbohydrate antigen 72-4 (CA72-4) using a superparamagnetic immunochromatographic strip. Anal Bioanal Chem 408, 2319–2327 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00216-016-9328-z
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00216-016-9328-z