Abstract
An LC-MS/MS-based method for determining d-serine (Ser), an endogenous co-agonist of the N-methyl-D-aspartate receptor, in human serum, was developed and validated using a triazole-bonded silica-packed column after pre-column fluorescence derivatization with a chiral labeling reagent, (S)-4-(3-isothiocyanatopyrrolidin-1-yl)-7-(N,N-dimethylaminosulfonyl)-2,1,3-benzoxadiazole. Enantiomeric separation of the d- and L-Ser derivatives occurred in the triazole-bonded column (R s: 1.85) with CH3CN/100 mM HCO2NH4 in H2O (95.5:4.5) as the mobile phase with isocratic elution. The ln(capacity factor of d-Ser) in the van’t Hoff plot gradually decreased with the inverse of temperature, suggesting enhanced hydrophilic interactions with the triazole-bonded stationary phase with increasing column temperature, owing to decrease in the partition coefficient to the mobile phase. Multiple reaction monitoring (m/z 457.10 > 409.00) by triple quadrupole mass spectrometry was used for quantifying d-Ser in human serum. The presence of d-Ser in the serum was confirmed by treatment with commercial d-amino acid oxidase. A linear calibration curve was constructed in the d-Ser concentration range of 0.5–5.0 μM (r 2 = 0.999, n = 3) using d-homoserine as the internal standard. The precision and recovery values were adequate for quantification. The detection limit for d-Ser was 1.1 fmol/injection (signal-to-noise ratio = 3), owing to the high CH3CN content in the mobile phase. The proposed LC-MS/MS method showed few fluctuations in the retention times of D- and L-Ser, and R s was stable until the 40th injection of serum without column washing, and thus can be useful for d-Ser determination in human serum in clinical research.

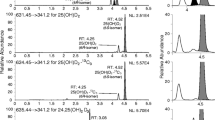
Multiple reaction monitoring chromatogram (left) and van't Hoff plot (right) of (S)-DBD-PyNCS-D- and L-serine on triazole-bonded column, obtained by LC-MS/MS






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Chouinard ML, Gaitan D, Wood PL (1993) Presence of the N-methyl-d-aspartate-associated glycine receptor agonist, d-serine, in human temporal cortex: comparison of normal, Parkinson, and Alzheimer tissues. J Neurochem 61:1561–1564
Wroblewski JT, Fadda E, Mazzetta J, Lazarewicz JW, Costa E (1989) Glycine and d-serine act as positive modulators of signal transduction at N-methyl-d-aspartate sensitive glutamate receptors in cultured cerebellar granule cells. Neuropharmacology 28:447–452
Schell MJ, Molliver ME, Snyder SH (1995) d-serine, an endogenous synaptic modulator-localization to astrocytes and glutamate-stimulated release. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 92:3948–3952
Schell M, Brady R, Molliver M, Snyder SH (1997) d-serine as a neuromodulator: regional and developmental localizations in rat brain glia resemble NMDA receptors. J Neurosci 17:1604–1615
Bardaweel SK, Alzweiri M, Ishaqat AA (2014) d-serine in neurobiology: CNS neurotransmission and neuromodulation. Can J Neurol Sci 41:164–176
Van Horn MR, Sild M, Ruthazer ES (2013) d-serine as a gliotransmitter and its roles in brain development and disease. Front Cell Neurosci 7:1–13
Madeira C, Freitas ME, Vargas-Lopes C, Wolosker H, Panizzutti R (2008) Increased brain d-amino acid oxidase (DAAO) activity in schizophrenia. Schizophr Res 101:76–83
Wu SZ, Bodles AM, Porter MM, Griffin WST, Basile AS, Barger SW (2004) Induction of serine racemase expression and d-serine release from microglia by amyloid beta-peptide. J Neuroinflammation 1:2
Wolosker H, Blackshaw S, Snyder SH (1999) Serine racemase: a glial enzyme synthesizing d-serine to regulate glutamate-N-methyl-d-aspartate neurotransmission. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 96:13409–13414
Khoronenkova SV, Tishkov VI (2008) d-Amino acid oxidase: physiological role and applications. Biochemistry (Moscow) 73:1511–1518
Pollegioni L, Piubelli L, Sacchi S, Piloni MS, Molla G (2007) Physiological functions of d-amino acid oxidases: from yeast to humans. Cell Mol Life Sci 64:1373–1394
Hashimoto K, Fukushima T, Shimizu E, Komatsu N, Watanabe H, Shinoda N, Nakazato M, Kumakiri C, Okada S, Hasegawa H, Imai K, Iyo M (2003) Decreased serum levels of d-serine in patients with schizophrenia—evidence in support of the N-methyl-d-aspartate receptor hypofunction hypothesis of schizophrenia. Arch Gen Psychiatry 60:572–576
Calcia MA, Madeira C, Alheira FV, Silva TC, Tannos FM, Vargas-Lopes C, Goldenstein N, Brasil MA, Ferreira ST, Panizzutti R (2012) Plasma levels of d-serine in Brazilian individuals with schizophrenia. Schizophr Res 142:83–87
Fukushima T, Iizuka H, Yokota A, Suzuki T, Ohno C, Kono Y, Nishikiori M, Seki A, Ichiba H, Watanabe Y, Hongo S, Utsunomiya M, Nakatani M, Sadamoto K, Yoshio T (2014) Quantitative analyses of schizophrenia-associated metabolites in serum: serum d-lactate levels are negatively correlated with gamma-glutamylcysteine in medicated schizophrenia patients. PLoS One 9, e101652
Ferraris D, Tsukamoto T (2011) Recent advances in the discovery of d-amino acid oxidase inhibitors and their therapeutic utility in schizophrenia. Curr Pharm Des 17:103–111
Sacchi S, Rosini E, Pollegioni L, Molla G (2013) d-Amino acid oxidase inhibitors as a novel class of drugs for schizophrenia therapy. Curr Pharm Des 19:2499–2511
Smith SM, Uslaner JM, Hutson PH (2010) The therapeutic potential of d-amino acid oxidase (DAAO) inhibitors. Open Med Chem J 4:3–9
Alt J, Rojas C, Wozniak K, Wu Y, Ferraris D, Tsukamoto T, Slusher B (2011) Development of a high-throughput method for the determination of pharmacological levels of plasma d-serine. Anal Biochem 419:106–109
Fukushima T, Kawai J, Imai K, Toyo'oka T (2004) Simultaneous determination of d- and l-serine in rat brain microdialysis sample using a column-switching HPLC with fluorimetric detection. Biomed Chromatogr 18:813–819
Miyoshi Y, Hamase K, Okamura T, Konno R, Kasai N, Tojo Y, Zaitsu K (2011) Simultaneous two-dimensional HPLC determination of free d-serine and d-alanine in the brain and periphery of mutant rats lacking d-amino-acid oxidase. J Chromatogr B 879:3184–3189
Miyoshi Y, Konno R, Sasabe J, Ueno K, Tojo Y, Mita M, Aiso S, Hamase K (2012) Alteration of intrinsic amounts of d-serine in the mice lacking serine racemase and d-amino acid oxidase. Amino Acids 43:1919–1931
Koga R, Miyoshi Y, Negishi E, Kaneko T, Mita M, Lindner W, Hamase K (2012) Enantioselective two-dimensional high-performance liquid chromatographic determination of N-methyl-d-aspartic acid and its analogues in mammals and bivalves. J Chromatogr A 1269:255–261
Miyoshi Y, Nagano M, Ishigo S, Ito Y, Hashiguchi K, Hishida N, Mita M, Lindner W, Hamase K (2014) Chiral amino acid analysis of Japanese traditional Kurozu and the developmental changes during earthenware jar fermentation processes. J Chromatogr B 966:187–192
Karakawa S, Shimbo K, Yamada N, Mizukoshi T, Miyano H, Mita M, Lindner W, Hamase K (2015) Simultaneous analysis of d-alanine, d-aspartic acid, and d-serine using chiral high-performance liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry and its application to the rat plasma and tissues. J Pharm Biomed Anal 115:123–129
Jin D, Nagakura K, Murofushi S, Toyo’oka T (1998) Total resolution of 17 DL-amino acids labeled with a fluorescent chiral reagent, R(-)-4-(3-isothiocyanatopyrrolidin-1-y1)-7-(N, N-dimethylaminosulfonyl)- 2,1,3-benzoxadiazole, by high-performance liquid chromatography. J Chromatogr A 822:215–224
Toyo’oka T, Jin D, Tomoi N, Oe T, Hiranuma H (2001) R(-)-4-(3-Isothiocyanatopyrrolidin-1-yl)-7-(N, N-dimethylaminosulfonyl)-2,1,3-benzoxadiazole, a fluorescent chiral tagging reagent: sensitive resolution of chiral amines and amino acids by reversed-phase liquid chromatography. Biomed Chromatogr 15:56–67
Visser WF, Verhoeven-Duif NM, Ophoff R, Bakker S, Klomp LW, Berger R, de Koning TJ (2011) A sensitive and simple ultra-high-performance-liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry based method for the quantification of d-amino acids in body fluids. J Chromatogr A 1218:7130–7136
Yamashita K, Fukushima T, Sasaki T, Arai K, Toyo’oka T (2009) Enantiomeric separation of d- and l-serine using high-performance liquid chromatography with electrochemical detection following pre-column diastereomer derivatization. Biomed Chromatogr 23:793–797
Min JZ, Hatanaka S, Yu HF, Higashi T, Inagaki S, Toyo’oka T (2011) Determination of DL-amino acids, derivatized with R(-)-4-(3-isothiocyanatopyrrolidin-1-yl)-7-(N, N-dimethylaminosulfonyl)-2,1,3-benzoxadiazole, in nail of diabetic patients by UPLC-ESI-TOF-MS. J Chromatogr B 879:3220–3228
Hashimoto A, Nishikawa T, Oka T, Takahashi K, Hayashi T (1992) Determination of free amino-acid enantiomers in rat brain and serum by high-performance liquid-chromatography after derivatization with N-tert-butyloxycarbonyl-l-cysteine and o-phthaldialdehyde. J Chromatogr B 582:41–48
Toyo’oka T, Liu YM (1995) Development of optically-active fluorescent Edman-type reagents. Analyst 120:385–390
Buszewski B, Noga S (2012) Hydrophilic interaction liquid chromatography (HILIC)-a powerful separation technique. Anal Bioanal Chem 402:231–247
Isokawa M, Kanamori T, Funatsu T, Tsunoda M (2014) Recent advances in hydrophilic interaction chromatography for quantitative analysis of endogenous and pharmaceutical compounds in plasma samples. Bioanalysis 6:2421–2439
Jian WY, Edom RW, Xu YD, Weng N (2010) Recent advances in application of hydrophilic interaction chromatography for quantitative bioanalysis. J Sep Sci 33:681–697
Guo Y, Gaiki S (2011) Retention and selectivity of stationary phases for hydrophilic interaction chromatography. J Chromatogr A 1218:5920–5938
Huang ZY, Francis ZY, Ruan J (2015) Development of a simple method for quantitation of methanesulfonic acid at low ppm level using hydrophilic interaction chromatography coupled with ESI-MS. J Pharm Biomed Anal 102:17–24
Iwasaki M, Kashiwaguma Y, Nagashima C, Izumi M, Uekusa A, Iwasa S, Onozato M, Ichiba H, Fukushima T (2015) A high-performance liquid chromatography assay with a triazole-bonded column for evaluation of d-amino acid oxidase activity. Biomed Chromatogr. doi:10.1002/bmc.3559
Iizuka H, Ishii K, Hirasa Y, Kubo K, Fukushima T (2011) Fluorescence determination of d- and l-tryptophan concentrations in rat plasma following administration of tryptophan enantiomers using HPLC with pre-column derivatization. J Chromatogr B 879:3208–3213
Ohashi H, Iizuka H, Yoshihara S, Otani H, Kume M, Sadamoto K, Ichiba H, Fukushima T (2013) Determination of l-tryptophan and l-kynurenine in human serum by using LC-MS after derivatization with (R)-DBD-PyNCS. Int J Tryptophan Res 6:9–14
Song ZY, Ogaya T, Ishii K, Ichiba H, Iizuka H, Fukushima T (2010) Utilization of kynurenic acid produced from D-kynurenine in an in vitro assay of D-amino acid oxidase activity. J Health Sci 56:341–346
Iwasa S, Tabara H, Song Z, Nakabayashi M, Yokoyama Y, Fukushima T (2011) Inhibition of D-amino acid oxidase activity by antipsychotic drugs evaluated by a fluorometric assay using D-kynurenine as substrate. Yakugaku Zasshi 131:1111–1116
Christopherson MJ, Yoder KJ, Hill JT (2006) Hydrophilic interaction liquid chromatographic (HILIC)/ion exchange separation of picolinic and nicotinic acids. J Liq Chromatogr Relat Technol 29:2545–2558
Hao Z, Xiao B, Weng N (2008) Impact of column temperature and mobile phase components on selectivity of hydrophilic interaction chromatography (HILIC). J Sep Sci 31:1449–1464
Ikegami T, Tomomatsu K, Takubo H, Horie K, Nobuo T (2008) Separation efficiencies in hydrophilic interaction chromatography. J Chromatogr A 1184:474–503
Yoshihara S, Otani H, Tsunoda M, Ishii K, Iizuka H, Ichiba H, Fukushima T (2012) Alterations in extracellular tryptophan and dopamine concentrations in rat striatum following peripheral administration of D- and l-tryptophan: an in vivo microdialysis study. Neurosci Lett 526:74–78
Acknowledgments
The authors gratefully acknowledge Nacalai Tesque Co. Ltd. for valuable advice on the use of the triazole-bonded column, and Shimadzu Corporation for technical advice on the operation of LCMS-8040. The authors also thank Miss Megumi Iwasaki, Toho University, for her technical assistance. This study was partially supported by a Grant-in-Aid for Scientific Research (C) (no. 25460224) from the Japan Society for the Promotion of Science from the Ministry of Education, Culture, Sports, Science, and Technology. The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
ESM 1
(PDF 352 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sakamoto, T., Kuwabara, R., Takahashi, S. et al. Determination of d-serine in human serum by LC-MS/MS using a triazole-bonded column after pre-column derivatization with (S)-4-(3-isothiocyanatopyrrolidin-1-yl)-7- (N, N-dimethylaminosulfonyl)-2,1,3-benzoxadiazole. Anal Bioanal Chem 408, 517–526 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00216-015-9119-y
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00216-015-9119-y