Abstract
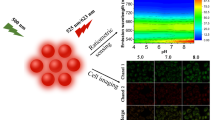
p-Aminothiophenol (pATP) functionalized multi-walled carbon nanotubes (MWCNTs) have been demonstrated as an efficient pH sensor for living cells. The proposed sensor employs gold/silver core-shell nanoparticles (Au@Ag NPs) functionalized MWCNTs hybrid structure as the surface-enhanced Raman scattering (SERS) substrate and pATP molecules as the SERS reporters, which possess a pH-dependent SERS performance. By using MWCNTs as the substrate to be in a state of aggregation, the pH sensing range could be extended to pH 3.0∼14.0, which is much wider than that using unaggregated Au@Ag NPs without MWCNTs. Furthermore, the pH-sensitive performance was well retained in living cells with a low cytotoxicity. The developed SERS-active MWCNTs-based nanocomposite is expected to be an efficient intracellular pH sensor for bio-applications.










Similar content being viewed by others
References
Hoyt KR, Reynolds IJ (1998) Alkalinization prolongs recovery from glutamate-induced increases in intracellular Ca2+ concentration by enhancing Ca2+ efflux through the mitochondrial Na+/Ca2+ exchanger in cultured rat forebrain neurons. J Neurochem 71(3):1051–1058
Speake T, Elliott AC (1998) Modulation of calcium signals by intracellular pH in isolated rat pancreatic acinar cells. J Physiol-Lond 506(2):415–430. doi:10.1111/j.1469-7793.1998.415bw.x
Gottlieb RA, Dosanjh A (1996) Mutant cystic fibrosis transmembrane conductance regulator inhibits acidification and apoptosis in C127 cells: possible relevance to cystic fibrosis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 93(8):3587–3591. doi:10.1073/pnas.93.8.3587
Gottlieb RA, Nordberg J, Skowronski E, Babior BM (1996) Apoptosis induced in Jurkat cells by several agents is preceded by intracellular acidification. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 93(2):654–658. doi:10.1073/pnas.93.2.654
Andresen TL, Jensen SS, Jorgensen K (2005) Advanced strategies in liposomal cancer therapy: problems and prospects of active and tumor specific drug release. Prog Lipid Res 44(1):68–97. doi:10.1016/j.plipres.2004.12.001
Chacko VP, Weiss RG (1993) Intracellular pH determination by C-13-NMR spectroscopy. Am J Physiol 264(3):C755–C760
Dennis AM, Rhee WJ, Sotto D, Dublin SN, Bao G (2012) Quantum dot-fluorescent protein FRET probes for sensing intracellular pH. ACS Nano 6(4):2917–2924. doi:10.1021/nn2038077
Kneen M, Farinas J, Li YX, Verkman AS (1998) Green fluorescent protein as a noninvasive intracellular pH indicator. Biophys J 74(3):1591–1599
Kneipp K, Wang Y, Kneipp H, Perelman LT, Itzkan I, Dasari R, Feld MS (1997) Single molecule detection using surface-enhanced Raman scattering (SERS). Phys Rev Lett 78(9):1667–1670. doi:10.1103/PhysRevLett.78.1667
Nie SM, Emery SR (1997) Probing single molecules and single nanoparticles by surface-enhanced Raman scattering. Science 275(5303):1102–1106. doi:10.1126/science.275.5303.1102
Porter MD, Lipert RJ, Siperko LM, Wang G, Narayanana R (2008) SERS as a bioassay platform: fundamentals, design, and applications. Chem Soc Rev 37(5):1001–1011. doi:10.1039/b708461g
Charan S, Chien FC, Singh N, Kuo CW, Chen PL (2011) Development of lipid targeting Raman probes for in vivo imaging of Caenorhabditis elegans. Chem-A Eur J 17(18):5165–5170. doi:10.1002/chem.201002896
Doering WE, Nie SM (2002) Single-molecule and single-nanoparticle SERS: examining the roles of surface active sites and chemical enhancement. J Phys Chem B 106(2):311–317. doi:10.1021/jp011730b
Wang YL, Seebald JL, Szeto DP, Irudayaraj J (2010) Biocompatibility and biodistribution of surface-enhanced Raman scattering nanoprobes in zebrafish embryos: in vivo and multiplex imaging. ACS Nano 4(7):4039–4053. doi:10.1021/nn100351h
Wang ZY, Bonoiu A, Samoc M, Cui YP, Prasad PN (2008) Biological pH sensing based on surface enhanced Raman scattering through a 2-aminothiophenol-silver probe. Biosens Bioelectron 23(6):886–891. doi:10.1016/j.bios.2007.09.017
Zong SF, Wang ZY, Yang J, Cui YP (2011) Intracellular pH sensing using p-aminothiophenol functionalized gold nanorods with low cytotoxicity. Anal Chem 83(11):4178–4183. doi:10.1021/ac200467z
Zhao L, Shingaya Y, Tomimoto H, Huang Q, Nakayama T (2008) Functionalized carbon nanotubes for pH sensors based on SERS. J Mater Chem 18(40):4759–4761. doi:10.1039/b809833f
Talley CE, Jusinski L, Hollars CW, Lane SM, Huser T (2004) Intracellular pH sensors based on surface-enhanced Raman scattering. Anal Chem 76(23):7064–7068. doi:10.1021/ac049093j
Michaels AM, Jiang J, Brus L (2000) Ag nanocrystal junctions as the site for surface-enhanced Raman scattering of single Rhodamine 6G molecules. J Phys Chem B 104(50):11965–11971. doi:10.1021/jp0025476
Wang ZY, Zong SF, Yang J, Song CY, Li J, Cui YP (2010) One-step functionalized gold nanorods as intracellular probe with improved SERS performance and reduced cytotoxicity. Biosens Bioelectron 26(1):241–247. doi:10.1016/j.bios.2010.06.032
Song CY, Wang ZY, Zhang RH, Yang J, Tan XB, Cui YP (2009) Highly sensitive immunoassay based on Raman reporter-labeled immuno-Au aggregates and SERS-active immune substrate. Biosens Bioelectron 25(4):826–831. doi:10.1016/j.bios.2009.08.035
Yang J, Wang ZY, Zong SF, Song CY, Zhang RH, Cui YP (2012) Distinguishing breast cancer cells using surface-enhanced Raman scattering. Anal Bioanal Chem 402(3):1093–1100. doi:10.1007/s00216-011-5577-z
Wu L, Wang ZY, Zong SF, Huang Z, Zhang PY, Cui YP (2012) A SERS-based immunoassay with highly increased sensitivity using gold/silver core-shell nanorods. Biosens Bioelectron 38(1):94–99. doi:10.1016/j.bios.2012.05.005
Guo SJ, Li J, Ren W, Wen D, Dong SJ, Wang EK (2009) Carbon nanotube/silica coaxial nanocable as a three-dimensional support for loading diverse ultra-high-density metal nanostructures: facile preparation and use as enhanced materials for electrochemical devices and SERS. Chem Mater 21(11):2247–2257. doi:10.1021/cm900300v
Singhal R, Orynbayeva Z, Sundaram RVK, Niu JJ, Bhattacharyya S, Vitol EA, Schrlau MG, Papazoglou ES, Friedman G, Gogotsi Y (2011) Multifunctional carbon-nanotube cellular endoscopes. Nat Nanotechnol 6(1):57–64. doi:10.1038/nnano.2010.241
Lai GS, Wu J, Ju HX, Yan F (2011) Streptavidin-functionalized silver-nanoparticle-enriched carbon nanotube tag for ultrasensitive multiplexed detection of tumor markers. Adv Funct Mater 21(15):2938–2943. doi:10.1002/adfm.201100396
Zhou Q, Li XW, Fan Q, Zhang XX, Zheng JW (2006) Charge transfer between metal nanoparticles interconnected with a functionalized molecule probed by surface-enhanced Raman spectroscopy. Angew Chem-Int Ed 45(24):3970–3973. doi:10.1002/anie.200504419
Liu GK, Hu J, Zheng PC, Shen GL, Jiang JH, Yu RQ, Cui Y, Ren B (2008) Laser-induced formation of metal-molecule-metal junctions between Au nanoparticles as probed by surface-enhanced Raman spectroscopy. J Phys Chem C 112(16):6499–6508. doi:10.1021/jp709869f
Hill W, Wehling B (1993) Potential-dependent and ph-dependent surface-enhanced raman-scattering of p-mercaptoaniline on silver and gold substrates. J Phys Chem 97(37):9451–9455. doi:10.1021/j100139a032
Huang YF, Zhu HP, Liu GK, Wu DY, Ren B, Tian ZQ (2010) When the signal is not from the original molecule to be detected: chemical transformation of para-aminothiophenol on Ag during the SERS measurement. J Am Chem Soc 132(27):9244–9246
Huang YZ, Fang YR, Yang ZL, Sun MT (2010) Can p,p′-dimercaptoazobisbenzene be produced from p-aminothiophenol by surface photochemistry reaction in the junctions of a Ag nanoparticle-molecule-Ag (or Au) film? J Phys Chem C 114(42):18263–18269. doi:10.1021/jp107305z
Wu DY, Liu XM, Huang YF, Ren B, Xu X, Tian ZQ (2009) Surface catalytic coupling reaction of p-mercaptoaniline linking to silver nanostructures responsible for abnormal SERS enhancement: a DFT study. J Phys Chem C 113(42):18212–18222. doi:10.1021/jp9050929
Nitzan A, Brus LE (1981) Theoretical-model for enhanced photochemistry on rough surfaces. J Chem Phys 75(5):2205–2214. doi:10.1063/1.442333
Nitzan A, Brus LE (1981) Can photochemistry be enhanced on rough surfaces. J Chem Phys 74(9):5321–5322. doi:10.1063/1.441699
Hirsjarvi S, Peltonen L, Hirvonen J (2006) Layer-by-layer polyelectrolyte coating of low molecular weight poly(lactic acid) nanoparticles. Colloids Surf B: Biointerfaces 49(1):93–99. doi:10.1016/j.colsurfb.2006.03.009
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by the Natural Science Foundation of China (NSFC) (Nos. 61177033, 21104009, 61275182). Science Foundation for the Excellent Youth Scholars of Southeast University and the Fundamental Research Funds for the Central Universities.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
ESM 1
(PDF 162 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Chen, P., Wang, Z., Zong, S. et al. A wide range optical pH sensor for living cells using Au@Ag nanoparticles functionalized carbon nanotubes based on SERS signals. Anal Bioanal Chem 406, 6337–6346 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00216-014-8064-5
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00216-014-8064-5