Abstract
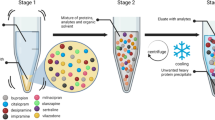
In the present study, a liquid chromatography–mass spectrometry (LC-MS/MS) multi-analyte approach based on a simple liquid–liquid extraction was developed for fast target screening and quantification of 33 antidepressants in whole blood, plasma, and serum. The method was validated with respect to selectivity, matrix effects, recovery, process efficiency, accuracy and precision, stabilities, and limits. In addition, cross-calibration between the three biosamples was done to assess the impact of the different matrices on the calibration. Whole blood, plasma, and serum (500 μL each) were extracted twice at pH 7.4 and at pH 10 with ether–ethyl acetate (1:1). Separation, detection, and quantification were performed using LC-MS/MS with electrospray ionization in positive mode. For accuracy and precision, full calibration was performed with ranges from subtherapeutic to toxic concentrations. The approach was sensitive and selective for 33 analytes in whole blood and 31 analytes in plasma and serum and accurate and precise for 30 of the 33 tested drugs in whole blood, 31 in plasma, and 28 in serum. Cross-calibration was successful only for 13 analytes in whole blood and 16 analytes in serum calculated over a calibration curve made in plasma, 12 analytes in whole blood and 15 analytes in plasma calculated over a calibration curve made in serum, and 10 analytes in plasma and 15 analytes in serum calculated over a calibration curve made in whole blood.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Maurer HH (2013) What is the future of (ultra) high performance liquid chromatography coupled to low and high resolution mass spectrometry for toxicological drug screening? J Chromatogr A 1292:19–24
Zheng MM, Wang ST, HU WK, Feng YO (2010) In-tube solid-phase microextraction based on hybrid silica monolith coupled to liquid chromatography-mass spectrometry for automated analysis of ten antidepressants in human urine and plasma. J Chromatogr A 1217:7493–7501
Silva BJG, Lancas FM, Queiroz MEC (2008) In-tube solid-phase microextraction coupled to liquid chromatography (in-tube SPME/LC) analysis of nontricyclic antidepressants in human plasma. J Chromatogr B 862:181–188
Schulz M, Iwersen-Bergmann S, Andresen H, Schmoldt A (2012) Therapeutic and toxic blood concentrations of nearly 1,000 drugs and other xenobiotics. Crit Care 16:R136
TIAFT blood level list. 2009. www.tiaft.org
Baumann P, Hiemke C, Ulrich S, Eckermann G, Gaertner I, Gerlach M, Kuss HJ, Laux G, Muller-Oerlinghausen B, Rao ML, Rieder P, Zernig G (2004) The AGNP-TDM expert group consensus guidelines: therapeutic drug monitoring in psychiatry. Pharmacopsychiatry 37:243–265
Brunner E, Dassinger M, Grohmann I, Jung B, Kuhlmann A, Loewe M, Pfleger A, Schwinn A, Selz C, Sieorath S, Sy K (2010) FachInfo-service. Rote Liste Service, Frankfurt, Available at http://www.fachinfo.de
Schweizerisches Zentrum für Qualitätskontrolle. Serum oder Plasma (2010) www.cscq.ch
Chae JW, Baek HM, Kim SK, Kang HI, Kwon KI (2013) Quantitative determination of duloxetine and its metabolite in rat plasma by HPLC-MS/MS. Biomed Chromatogr 27:953–200
Remane D, Meyer MR, Wissenbach DK, Maurer HH (2011) Full validation and application of an ultra high performance liquid chromatographic-tandem mass spectrometric procedure for target screening and quantification of 34 antidepressants in human blood plasma as part of a comprehensive multi-analyte approach. Anal Bioanal Chem 400:2093–2107
de Castro A, del Mar Ramírez Fernandez M, Laloup M, Samyn N, de Boeck G, Wood M, Maes V, López-Rivadulla M (2007) High-throughput on-line solid-phase extraction-liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry method for the simultaneous analysis of 14 antidepressants and their metabolites in plasma. J Chromatogr A 1160:3–12
Shinozuka T, Terada M, Tanaka E (2006) Solid-phase extraction and analysis of 20 antidepressant drugs in human plasma by LC/MS with SSI method. Forensic Sci Int 162:108–112
Juan H, Zhiling Z, Huande L (2005) Simultaneous determination of fluoxetine, citalopram, paroxetine, venlafaxine in plasma by high performance liquid chromatography-electrospray ionization mass spectrometry (HPLC-MS/ESI). J Chromatogr B 820:33–39
Kollroser M, Schobert C (2002) Simultaneous determination of seven tricyclic antidepressant drugs in human plasma by direct-injection HPLC-APCI-MS-MS with an ion trap detector. Ther Drug Monit 24:537–544
Gutteck U, Rentsch KM (2003) Therapeutic drug monitoring of 13 antidepressant and five neuroleptic drugs in serum with liquid chromatography-electrospray ionization mass spectrometry. Clin Chem Lab 41:1571–1579
Kirchherr H, Kühn-Velten WN (2006) Quantitative determination of forty-eight antidepressants and antipsychotics in human serum by HPLC tandem mass spectrometry: a multi-level, single-sample approach. J Chromatogr B 843:100–113
Frahnert C, Rao ML, Grasmäder K (2003) Analysis of eighteen antidepressants, four atypical antipsychotics and active metabolites in serum by liquid chromatography: a simple tool for therapeutic drug monitoring. J Chromatogr B 794:35–47
Sauvage FL, Gaulier JM, Lachâtre G, Marquet P (2006) A fully automated turbulent-flow liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry technique for monitoring antidepressants in human serum. Ther Drug Monit 28:123–130
Castaing N, Titier K, Receveur-Daurel M, Le-Déodic M, Le-Bars D (2007) Quantification of eight new antidepressants and five of their active metabolites in whole blood by high-performance liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry. J Anal Toxicol 31:334–341
Vindenes V, Lund HME, Andresen W, Gjerde H, Ikdahle SE, Christophersen AS, Oiestad EL (2012) Detection of drugs of abuse in simultaneously collected oral fluid, urine and blood from Norwegian drug drivers. Forensic Sci Int 219:165–171
Amundsen I, Oiestad AM, Ekeberg D, Kristoffersen L (2013) Quantitative determination of fifteen basic pharmaceuticals in ante- and post-mortem whole blood by high pH mobile phase reversed phase ultra high performance liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry. J Chromatogr B 927:112–123
Wille SMR, de Letter EA, Piette MHA, van Overschelde LK, van Peteghem CH, Lambert WE (2009) Determination of antidepressants in human postmortem blood, brain tissue, and hair using gas chromatography-mass spectrometry. Int J Legal Med 123:451–458
Wille SMR, Maudens KE, van Peteghem CH, Lambert WEE (2005) Development of a solid phase extraction for 13 ‘new’ generation antidepressants and their active metabolites for gas chromatographic-mass spectrometric analysis. J Chromatogr A 1098:19–29
Maurer HH, Kratzsch C, Kraemer T, Peters FT, Weber AA (2002) Screening, library-assisted identification and validated quantification of oral antidiabetics of the sulfonylurea-type in plasma by atmospheric pressure chemical ionization liquid chromatography-mass spectrometry. J Chromatogr B Analyt Technol Biomed Life Sci 773:63–73
Montenarh D, Hopf M, Maurer HH, Schmidt P, Ewald AH (2014) Detection and quantification of benzodiazepines and Z-drugs in human whole blood, plasma, and serum samples as part of a comprehensive multi-analyte LC-MS/MS approach. Anal Bioanal Chem 406:803–818
Matuszewski BK, Constanzer ML, Chavez-Eng CM (2003) Strategies for the assessment of matrix effect in quantitative bioanalytical methods based on HPLC-MS/MS. Anal Chem 75:3019–3030
Remane D, Meyer MR, Wissenbach DK, Maurer HH (2010) Ion suppression and enhancement effects of co-eluting analytes in multi-analyte approaches: systematic investigation using ultra-high-performance liquid chromatography/mass spectrometry with atmospheric-pressure chemical ionization or electrospray ionization. Rapid Commun Mass Spectrom 24:3103–8
Peters FT, Paul LD, Musshoff F, Aebi B, Auwaerter V, Kraemer T, Skopp G (2009) Toxichem Krimtech 76:185–208
Montenarh D, Hopf M, Warth S, Maurer HH, Schmidt P, Ewald AH (2014) Drug Test Anal. doi:10.1002/dta.1657
Acknowledgments
The authors would like to thank Dr. Frank T. Peters for helpful discussion.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
ESM 1
(PDF 159 KB)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Montenarh, D., Wernet, M.P., Hopf, M. et al. Quantification of 33 antidepressants by LC-MS/MS—comparative validation in whole blood, plasma, and serum. Anal Bioanal Chem 406, 5939–5953 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00216-014-8019-x
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00216-014-8019-x