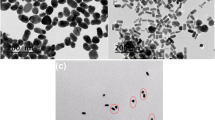
Abstract
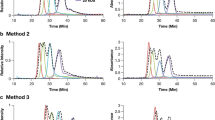
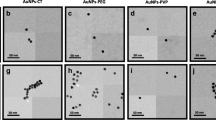
The development of highly efficient asymmetric-flow field flow fractionation (A4F) methodology for biocompatible PEGylated gold nanorods (GNR) without the need for surfactants in the mobile phase is presented. We report on the potential of A4F for rapid separation by evaluating the efficiency of functionalized surface coverage in terms of fractionation, retention time (t R ) shifts, and population analysis. By optimizing the fractionation conditions, we observed that the mechanism of separation for PEGylated GNRs by A4F is the same as that for CTAB stabilized GNRs (i.e., according to their AR) which confirms that the elution mechanism is not dependent on the surface charge of the analytes and/or the membrane. In addition, we demonstrated that A4F can distinguish different surface coverage populations of PEGylated GNRs. The data established that a change in Mw of the functional group and/or surface orientation can be detected and fractionated by A4F. The findings in this study provide the foundation for a complete separation and physicochemical analysis of GNRs and their surface coatings, which can provide accurate and reproducible characterization critical to advancing biomedical research.

A4F separation and elution of PEGylated gold nanorods (GNRs) are based on aspect ratio





Similar content being viewed by others
Notes
The identification of any commercial product or trade name does not imply endorsement or recommendation by the National Institute of Standards and Technology.
References
Sengupta S, Kulkarni A (2013) Design principles for clinical efficacy of cancer nanomedicine: a look into the basics. Acs Nano 7:2878–2882
Marchesano V, Hernandez Y, Salvenmoser W, Ambrosone A, Tino A, Hobmayer B, de la Fuente JM, Tortiglione C (2013) Imaging inward and outward trafficking of gold nanoparticles in whole animals. Acs Nano 7:2431–2442
Jin YD (2012) Engineering plasmonic gold nanostructures and metamaterials for biosensing and nanomedicine. Adv Mater 24:5153–5165
Mout R, Moyano DF, Rana S, Rotello VM (2012) Surface functionalization of nanoparticles for nanomedicine. Chem Soc Rev 41:2539–2544
Xiao YL, Jaskula-Sztul R, Javadi A, Xu WJ, Eide J, Dammalapati A, Kunnimalaiyaan M, Chen H, Gong SQ (2012) Co-delivery of doxorubicin and sirna using octreotide-conjugated gold nanorods for targeted neuroendocrine cancer therapy. Nanoscale 4:7185–7193
Huang XH, El-Sayed IH, Qian W, El-Sayed MA (2006) Cancer cell imaging and photothermal therapy in the near-infrared region by using gold nanorods. J Am Chem Soc 128:2115–2120
Charan S, Sanjiv K, Singh N, Chien FC, Chen YF, Nergui NN, Huang SH, Kuo CW, Lee TC, Chen PL (2012) Development of chitosan oligosaccharide-modified gold nanorods for in vivo targeted delivery and noninvasive imaging by nir irradiation. Bioconjug Chem 23:2173–2182
Vigderman L, Khanal BP, Zubarev ER (2012) Functional gold nanorods: synthesis, self-assembly, and sensing applications. Adv Mater 24:4811–4841
Alkilany AM, Nagaria PK, Hexel CR, Shaw TJ, Murphy CJ, Wyatt MD (2009) Cellular uptake and cytotoxicity of gold nanorods: molecular origin of cytotoxicity and surface effects. Small 5:701–708
Leonov AP, Zheng JW, Clogston JD, Stern ST, Patri AK, Wei A (2008) Detoxification of gold nanorods by treatment with polystyrenesulfonate. Acs Nano 2:2481–2488
Si S, Leduc C, Delville MH, Lounis B (2012) Short gold nanorod growth revisited: the critical role of the bromide counterion. Chemphyschem 13:193–202
Gigault J, Cho TJ, MacCuspie RI, Hackley VA (2013) Gold nanorod separation and characterization by asymmetric-flow field flow fractionation with uv-vis detection. Anal Bioanal Chem 405:1191–1202
Runyon JR, Goering A, Yong KT, Williams SKR (2013) Preparation of narrow dispersity gold nanorods by asymmetrical flow field-flow fractionation and investigation of surface plasmon resonance. Anal Chem 85:940–948
Boca SC, Astilean S (2010) Detoxification of gold nanorods by conjugation with thiolated poly(ethylene glycol) and their assessment as sers-active carriers of raman tags. Nanotechnology 21:1–8
Grabinski C, Schaeublin N, Wijaya A, D'Couto H, Baxamusa SH, Hamad-Schifferli K, Hussain SM (2011) Effect of gold nanorod surface chemistry on cellular response. Acs Nano 5:2870–2879
Palegrosdemange C, Simon ES, Prime KL, Whitesides GM (1991) Formation of self-assembled monolayers by chemisorption of derivatives of oligo(ethylene glycol) of structure hs(ch2)11(och2ch2)meta-oh on gold. J Am Chem Soc 113:12–20
Latham AH, Williams ME (2006) Versatile routes toward functional, water-soluble nanoparticles via trifluoroethylester-peg-thiol ligands. Langmuir 22:4319–4326
Xia XH, Yang MX, Wang YC, Zheng YQ, Li QG, Chen JY, Xia YN (2012) Quantifying the coverage density of poly(ethylene glycol) chains on the surface of gold nanostructures. Acs Nano 6:512–522
Yang ZH, Galloway JA, Yu HU (1999) Protein interactions with poly(ethylene glycol) self-assembled monolayers on glass substrates: diffusion and adsorption. Langmuir 15:8405–8411
Du H, Chandaroy P, Hui SW (1997) Grafted poly-(ethylene glycol) on lipid surfaces inhibits protein adsorption and cell adhesion. Biochim Biophys Acta Biomembr 1326:236–248
Sacchetti C, Motamedchaboki K, Magrini A, Palmieri G, Mattei M, Bernardini S, Rosato N, Bottini N, Bottini M (2013) Surface polyethylene glycol conformation influences the protein corona of polyethylene glycol-modified single-walled carbon nanotubes: potential implications on biological performance. Acs Nano 7:1974–1989
Moghimi SM, Szebeni J (2003) Stealth liposomes and long circulating nanoparticles: critical issues in pharmacokinetics, opsonization and protein-binding properties. Prog Lipid Res 42:463–478
Kaufmann S, Papastavrou G, Kumar K, Textor M, Reimhult E (2009) A detailed investigation of the formation kinetics and layer structure of poly(ethylene glycol) tether supported lipid bilayers. Soft Matter 5:2804–2814
Jokerst JV, Lobovkina T, Zare RN, Gambhir SS (2011) Nanoparticle pegylation for imaging and therapy. Nanomedicine 6:715–728
Levin CS, Bishnoi SW, Grady NK, Halas NJ (2006) Determining the conformation of thiolated poly(ethylene glycol) on au nanoshells by surface-enhanced raman scattering spectroscopic assay. Anal Chem 78:3277–3281
Murphy CJ, Thompson LB, Alkilany AM, Sisco PN, Boulos SP, Sivapalan ST, Yang JA, Chernak DJ, Huang JY (2010) The many faces of gold nanorods. J Phys Chem Lett 1:2867–2875
Murphy CJ, Thompson LB, Chernak DJ, Yang JA, Sivapalan ST, Boulos SP, Huang JY, Alkilany AM, Sisco PN (2011) Gold nanorod crystal growth: from seed-mediated synthesis to nanoscale sculpting. Curr Opin Colloid Interface 16:128–134
Kinnear C, Dietsch H, Clift MJD, Endes C, Rothen-Rutishauser B, Petri-Fink A (2013) Gold nanorods: controlling their surface chemistry and complete detoxification by a two-step place exchange. Angew Chem Int Edit 52:1934–1938
Akbulut O, Mace CR, Martinez RV, Kumar AA, Nie ZH, Patton MR, Whitesides GM (2012) Separation of nanoparticles in aqueous multiphase systems through centrifugation. Nano Lett 12:4060–4064
Li SA, Chang Z, Liu JF, Bai L, Luo L, Sun XM (2011) Separation of gold nanorods using density gradient ultracentrifugation. Nano Res 4:723–728
Gordel M, Olesiak-Banska J, Matczyszyn K, Nogues C, Pawlik K, Buckle M, Samoc M (2012) Shape and size separation of gold nanoparticles using glucose gradient density. In Nanophotonics iv, Andrews DL, Nunzi JM, Ostendorf A (Eds). Proceedings of the SPIE: Brussels, Belgium
Thunemann AF, Kegel J, Polte J, Emmerling F (2008) Superparamagnetic maghemite nanorods: analysis by coupling field-flow fractionation and small-angle x-ray scattering. Anal Chem 80:5905–5911
Schimpf M, Caldwell K, Giddings JC (2000) Field flow fractionation handbook. Wiley, New York
Zhong LB, Zhou X, Bao SX, Shi YF, Wang Y, Hong SM, Huang YC, Wang X, Xie ZX, Zhang QQ (2011) Rational design and sers properties of side-by-side, end-to-end and end-to-side assemblies of au nanorods. J Mater Chem 21:14448–14455
Kampf N, Ben-Yaakov D, Andelman D, Safran SA, Klein J (2009) Direct measurement of sub-debye-length attraction between oppositely charged surfaces. Prog Lipid Res 103:1183041–1183044
Mori Y, Kimura K, Tanigaki M (1990) Influence of particle wall and particle particle interactions on retention behavior in sedimentation field-flow fractionation. Anal Chem 62:2668–2672
Israelachvili JN (2011) Chapter 14—electrostatic forces between surfaces in liquids. In intermolecular and surface forces, 3rd edn. Academic, San Diego
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Published in the topical collection Field-Flow Fractionation with guest editors S. Kim R. Williams and Karin D. Caldwell.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
ESM 1
(PDF 4.82 mb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Nguyen, T.M., Gigault, J. & Hackley, V.A. PEGylated gold nanorod separation based on aspect ratio: characterization by asymmetric-flow field flow fractionation with UV-Vis detection. Anal Bioanal Chem 406, 1651–1659 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00216-013-7318-y
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00216-013-7318-y