Abstract
Glycosylation is an important posttranslational modification of proteins and plays a crucial role in both cellular functions and secretory pathways. Sialic acids (SAs), a family of nine-carbon-containing acidic monosaccharides, often terminate the glycan structures of cell surface molecules and secreted glycoproteins and perform an important role in many biological processes. Hence, a more profound profiling of the sialylated glycoproteomics may improve our knowledge of this modification and its effects on protein functions. Here, we systematically investigated different strategies to enrich the SA proteins in human plasma using a newly developed technology that utilizes titanium dioxide for sialylated N-glycoproteomics profiling by mass spectrometry. Our results showed that using a combination of a filter-aided sample preparation method, TiO2 chromatography, multiple enzyme digestion, and two-dimensional reversed-phase peptide fractionation led to a more profound profiling of the SA proteome. In total, 982 glycosylation sites in 413 proteins were identified, among which 37.8 % were newly identified, to establish the largest database of sialic acid containing proteins from human plasma.

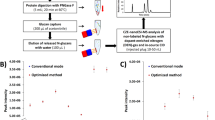
Numbers of identified SA glycosites with different strategies






Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- SA:
-
Sialic acid
- FASP:
-
Filter-aided sample preparation
- TiO2 :
-
Titanium dioxide
- EGFR:
-
Epidermal growth factor receptor
- RP:
-
Reversed-phase
- LC-MS:
-
Liquid chromatography–mass spectrometry
Reference
Hagglund P, Bunkenborg J, Elortza F, Jensen ON, Roepstorff P (2004) A new strategy for identification of N-glycosylated proteins and unambiguous assignment of their glycosylation sites using HILIC enrichment and partial deglycosylation. J Proteome Res 3(3):556–566
Ohtsubo K, Marth JD (2006) Glycosylation in cellular mechanisms of health and disease. Cell 126(5):855–867
Paradis V (2005) Glycomics: a new taste of cirrhosis marker. J Hepatol 43(5):913–914
Ponnio M, Alho H, Nikkari ST, Olsson U, Rydberg U, Sillanaukee P (1999) Serum sialic acid in a random sample of the general population. Clin Chem 45(10):1842–1849
Martinez-Duncker I, Salinas-Marin R, Martinez-Duncker C (2011) Towards in vivo imaging of cancer sialylation. Int J Mol Imaging 2011:283497
Kondo A, Miyamoto T, Yonekawa O, Giessing AM, Osterlund EC, Jensen ON (2009) Glycopeptide profiling of beta-2-glycoprotein I by mass spectrometry reveals attenuated sialylation in patients with antiphospholipid syndrome. J Proteomics 73(1):123–133
Pang PC, Chiu PC, Lee CL, Chang LY, Panico M, Morris HR, Haslam SM, Khoo KH, Clark GF, Yeung WS, Dell A (2011) Human sperm binding is mediated by the sialyl-Lewis(x) oligosaccharide on the zona pellucida. Science (New York, NY) 333(6050):1761–1764
Liu YC, Yen HY, Chen CY, Chen CH, Cheng PF, Juan YH, Chen CH, Khoo KH, Yu CJ, Yang PC, Hsu TL, Wong CH (2011) Sialylation and fucosylation of epidermal growth factor receptor suppress its dimerization and activation in lung cancer cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 108(28):11332–11337
Trebbien R, Larsen LE, Viuff BM (2011) Distribution of sialic acid receptors and influenza A virus of avian and swine origin in experimentally infected pigs. Virol J 8:434
Cohen M, Varki A (2010) The sialome—far more than the sum of its parts. OMICS 14(4):455–464
Sun B, Ranish JA, Utleg AG, White JT, Yan X, Lin B, Hood L (2007) Shotgun glycopeptide capture approach coupled with mass spectrometry for comprehensive glycoproteomics. Mol Cell Proteomics 6(1):141–149
Lohrig K, Sickmann A, Lewandrowski U (2011) Strong cation exchange chromatography for analysis of sialylated glycopeptides. Methods Mol Biol 753:299–308
Nilsson J, Ruetschi U, Halim A, Hesse C, Carlsohn E, Brinkmalm G, Larson G (2009) Enrichment of glycopeptides for glycan structure and attachment site identification. Nat Methods 6(11):809–811
Larsen MR, Jensen SS, Jakobsen LA, Heegaard NH (2007) Exploring the sialiome using titanium dioxide chromatography and mass spectrometry. Mol Cell Proteomics 6(10):1778–1787
Wang WLHLZ (2011) Tandem mass spectrometric characterization of fetuin sialylated glycopeptides enriched by TiO2 microcolumn. Chin J Chem 29(11):2229–2235
Anderson NL, Anderson NG (2002) The human plasma proteome: history, character, and diagnostic prospects. Mol Cell Proteomics 1(11):845–867
Li D, Fu Y, Sun R, Ling CX, Wei Y, Zhou H, Zeng R, Yang Q, He S, Gao W (2005) pFind: a novel database-searching software system for automated peptide and protein identification via tandem mass spectrometry. Bioinformatics (Oxford, England) 21(13):3049–3050
Deshpande N, Jensen PH, Packer NH, Kolarich D (2010) GlycoSpectrumScan: fishing glycopeptides from MS spectra of protease digests of human colostrum sIgA. J Proteome Res 9(2):1063–1075
Couto N, Barber J, Gaskell SJ (2011) Matrix-assisted laser desorption/ionisation mass spectrometric response factors of peptides generated using different proteolytic enzymes. J Mass Spectrom: JMS 46(12):1233–1240
Lam MP, Lau E, Siu SO, Ng DC, Kong RP, Chiu PC, Yeung WS, Lo C, Chu IK (2011) Online combination of reversed-phase/reversed-phase and porous graphitic carbon liquid chromatography for multicomponent separation of proteomics and glycoproteomics samples. Electrophoresis 32(21):2930–2940
Gong Y, Li X, Yang B, Ying W, Li D, Zhang Y, Dai S, Cai Y, Wang J, He F, Qian X (2006) Different immunoaffinity fractionation strategies to characterize the human plasma proteome. J Proteome Res 5(6):1379–1387
Wagner M, Adamczak R, Porollo A, Meller J (2005) Linear regression models for solvent accessibility prediction in proteins. J Comput Biol 12(3):355–369
Zielinska DF, Gnad F, Schropp K, Wisniewski JR, Mann M (2012) Mapping N-glycosylation sites across seven evolutionarily distant species reveals a divergent substrate proteome despite a common core machinery. Mol Cell 46(4):542–548
Thaysen-Andersen M, Packer NH (2012) Site-specific glycoproteomics confirms that protein structure dictates formation of N-glycan type, core fucosylation and branching. Glycobiology 22(11):1440–1452
Dennis G Jr, Sherman BT, Hosack DA, Yang J, Gao W, Lane HC, Lempicki RA (2003) DAVID: Database for Annotation, Visualization, and Integrated Discovery. Genome Biol 4(5):P3
Farrah T, Deutsch EW, Omenn GS, Campbell DS, Sun Z, Bletz JA, Mallick P, Katz JE, Malmstrom J, Ossola R, Watts JD, Lin B, Zhang H, Moritz RL, Aebersold R (2011) A high-confidence human plasma proteome reference set with estimated concentrations in PeptideAtlas. Mol Cell Proteomics: MCP 10(9):1–14
Acknowledgment
We are grateful for financial support from the National Key Program for Basic Research of China (2011CB910603, 2013CB911204); National High Technology Research and Development Program of China (2012AA020203, 2012AA020202); International Scientific Cooperation Project of China (2011DFB30370); and the National Natural Science Foundation of China (21275005,31100591,21235001), Beijing Nova Program (Z121107002512014).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
ESM 1
(PDF 489 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhao, X., Ma, C., Han, H. et al. Comparison and optimization of strategies for a more profound profiling of the sialylated N-glycoproteomics in human plasma using metal oxide enrichment. Anal Bioanal Chem 405, 5519–5529 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00216-013-6971-5
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00216-013-6971-5