Abstract
Methyl-3-quinoxaline-2-carboxylic acid (MQCA) is a possible residue marker for three quinoxaline veterinary medicines (olaquindox, mequindox, and quinocetone). The wide application of mequindox/quinocetone or the illegal use of olaquindox leads to MQCA residue in animal’s original food, thereby threatening the safety of human food. The indirect competitive enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (IC-ELISA) with a specific coating antigen and monoclonal antibody (MAB) was established and optimized for detecting MQCA in swine liver. Samples were acidified with 2 mol l−1 hydrochloric acid, extracted with ethyl acetate–hexane–isopropanol (8 + 1 + 1, v/v/v) and then detected by IC-ELISA. The logarithm correlation of standards to OD values ranged from 0.2 to 200 μg l−1, with IC50 of 6.46 μg l−1. Negligible cross-reactivity happened to five quinoxaline antibiotics (olaquindox, mequindox, quinocetone, carbadox, and cyadox) and the metabolite of carbadox and cyadox (quinoxaline-2-carboxylic acid). When spiked with 1 to 100 μg kg−1 of MQCA, the recoveries ranged from 85.44 to 100.02 %, with the intra-assay coefficient of variation (CV) of 6.64–10.57 % and inter-assay CV of 7.29–10.88 %. The limit of detection for MQCA was 1.0 μg kg−1 in swine liver. Furthermore, incurred samples were detected by the IC-ELISA and then conformed by a reported LC/MS/MS method, it shown that there was good correlation between the two methods. All these results indicated that the IC-ELISA method is appropriate for surveillance MQCA residue in animal tissues.

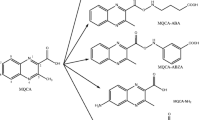
Synthesis route of 2-acrylic-1,4-binitrogen-quinoline combined to BSA(OVA) by active ester method




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Wu CM, Li Yan S, Jian Z, Cheng LL, Li YS, Yang CY, Feng PS, Zhang SX (2009) LC-MS-MS quantification of four quinoxaline-1,4-dioxides in swine feed. Chromatographia 70(11/12):1605–1611
Yue N, Ji BQ, Liu LQ, Tao GJ, Eremin SA, Wu LH (2009) Synthesis of olaquindox metabolite, methyl-3-quinoxaline-2-carboxylic acid for development of an immunoassay. Food Agric Immunol 20(2):173–183
Boison JO, Lee SC, Gedir RG (2009) A determinative and confirmatory method for residues of the metabolites of carbadox and olaquindox in porcine tissues. Anal Chim Acta 637(1/2):128–134
Joint FAO/WHO Expert Committee on Food Additives (1995) Evaluation of certain veterinary drug residues in food. Technical Series 851:19–21
Wu Y, Yu H, Wang Y, Huang L, Tao Y, Chen D, Peng D, Liu Z, Yuan Z (2007) Development of a high-performance liquid chromatography method for the simultaneous quantification of quinoxaline-2-carboxylic acid and methyl-3-quinoxaline-2-carboxylic acid in animal tissues. J Chromatogr 1146(1):1–7
Yang B, Huang L, Wang Y, Liu Y, Tao Y, Chen D, Liu Z, Fang K, Chen Y, Yuan Z (2010) Residue depletion and tissue-plasma correlation of methyl-3-quinoxaline-2-carboxylic acid after dietary administration of olaquindox in pigs. J Agric Food Chem 58(2):937–942
Dong YC, Zhang LF, Zhang KY, Yuan ZH (2010) An HPLC/MS-MS method for the determination of marker residues metabolites of quindoxins in edible tissues of swine and chicken. Chinese Journal of Veterinary Science 30(1):110–114
Zhang XJ, Zheng B, Zhang H, Chen XC, Mei GM (2011) Determination of marker residue of olaquindox in fish tissue by ultra performance liquid chromatography–tandem mass spectrometry. J Sep Sci 34(4):469–474
Huang LL, Xiao AG, Fan SX, Yin J, Chen P, Liu DC, Qiu YS, Wang YL, Yuan ZH (2005) Development of liquid chromatographic methods for determination of quinocetone and its main metabolites in edible tissues of swine and chicken. J AOAC Int 88(2):472–478
Liu Y, Si H, He L, Ding H, Huang X, Chen J, Chen Z, Zeng Z (2010) Identification of mequindox and its metabolites by high performance liquid chromatography combined with ion trap-time of flight-mass spectrometry. Chinese Journal of Analytical Chemistry Chinese Version 38(1):82–86
Shen J, Yang C, Wu C, Feng P, Wang Z, Li Y, Li Y, Zhang S (2010) Identification of the major metabolites of quinocetone in swine urine using ultra-performance liquid chromatography/electrospray ionization quadrupole time-of-flight tandem mass spectrometry. Rapid Communications in Mass Spectrometry 24(3):375–383
Wu H, Yang C, Wang Z, Shen J, Zhang S, Feng P, Li L, Cheng L (2012) Metabolism profile of quinocetone in swine by ultra-performance liquid chromatography quadrupole time-of-flight mass spectrometry. European Journal of Drug Metabolism and Pharmacokinetics 37(2):141–154
Cheng L, Wang Z, Shen J, Li L, Wu H, Zhang S (2012) A specific UPLC/ESI-MS/MS method for analysis of cyadox and its three main metabolites in fish samples. Analytical Methods 4(1):217–221
Liu K, Cao X, Wang Z, Li L, Shen J, Cheng L, Zhang S (2012) Analysis of mequindox and its two metabolites in swine liver by UPLC-MS/MS. Analytical Methods 4(3):859–863
Hutchinson MJ, Young PB, Kennedy DG (2005) Confirmation of carbadox and olaquindox metabolites in porcine liver using liquid chromatography–electrospray, tandem mass spectrometry. J Chromatogr B 816:15–20
Wang XY, Zhang LF, Xue FQ, Zhang KY, Qiu MQ (2007) Detection of methyl-3-quinoxaline-2-carboxylic acid in fishes by high performance liquid chromatography–tandem mass spectrometry. Veterinary Science in China 37(8):718–720
Chen W, Jiang Y, Ji B, Zhu C, Liu L, Peng C, Kim JM, Qiao R, Jin Z, Wang L, Zhu S, Xu C (2009) Automated and ultrasensitive detection of methyl-3-quinoxaline-2-carboxylic acid by using gold nanoparticles probes SIA-rt-PCR. Biosens Bioelectron 24(9):2858–2863
Le T, Xu J, Jb Y-Y, He HQ, Niu XD, Chen Y (2012) Development and validation of an immunochromatographic assay for the rapid detection of quinoxaline-2-carboxylic acid, the major metabolite of carbadox in the edible tissues of pigs. Food Additives and Contaminants 29(6):925–934
Duan Z-J, Fan L-P, Fang G-Z, Yi J-H, Wang S (2011) Novel surface molecularly imprinted sol–gel polymer applied to the online solid phase extraction of methyl-3-quinoxaline-2-carboxylic acid and quinoxaline-2-carboxylic acid from pork muscle. Anal Bioanal Chem 401(7):2291–2299
Zhou XW, Hu XQ (2003) Instrumental analysis and experimental technology of biochemistry. Chemistry Industry Press, Beijing, pp 271–272
Peng D, Zhang Z, Chen D, Wang Y, Tao Y, Yuan Z (2011) Development and validation of an indirect competitive enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay for monitoring quinoxaline-2-carboxylic acid in the edible tissues of animals. Food Additives and Contaminants 28(11):1524–1533
Kohler G, Milstein C (1975) Continuous cultures of fused cells secreting antibody of predefined specificity. Nature 256(5517):495–497
Acknowledgment
This research was supported by the National Basic Research Program of China (No. 2009CB118801).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Cheng, L., Shen, J., Wang, Z. et al. A sensitive and specific ELISA for determining a residue marker of three quinoxaline antibiotics in swine liver. Anal Bioanal Chem 405, 2653–2659 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00216-012-6696-x
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00216-012-6696-x