Abstract
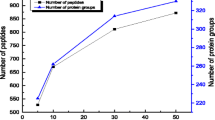
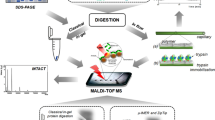
Initially, a poly (glycidyl methacrylate-co-acrylamide-co-methylenebisacrylamide) monolith was prepared in the 100 μm i.d. capillary, and then was grafted with polyethylenimine (Mw, ∼25,000) for adsorbing Cu2+, followed by chelating trypsin. As a result, efficient digestion for BSA (100 ng/μL) was completed within 50 s via such immobilized enzyme reactor (IMER); yielding 47% sequence coverage by matrix-assisted laser desorption/ionization-time of flight mass spectrometry (MALDI-TOF MS) analysis. Compared with the conventional method for preparing the metal-ion chelated IMER, the regeneration of such IMER can be achieved facilely by the respective 30 min desorption and re-adsorption of trypsin, and 51% sequence coverage was obtained for 50 s BSA digestion after regeneration. BSA down to femtomole was also efficiently digested by the prepared regenerable IMER. Meanwhile, after the consecutive digestion of myoglobin and BSA, there was not any mutual interference for both during MALDI-TOF MS identification, indicating the low nonspecific adsorption of such regenerable IMER. To test the applicability of regenerable IMER for complex sample profiling, proteins (150 ng) extracted from Escherichia coli were digested within 80 s by the regenerable IMER and further analyzed by nanoreversed phase liquid chromatography–electrospray ionization–mass spectrometry successfully, showing its practicability for the high throughput analysis of complex samples.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Domon B, Aebersold R (2006) Science 312:212–217
Cravatt BF, Simon GM, Yates JR (2007) Nature 450:991–1000
Motoyama A, Yates JR (2008) Anal Chem 80:7187–7193
Lopez-Ferrer D, Cañas B, Vázquez Lodeiro JC, Rial-Otero R, Moura I, Capelo JL (2006) Trends Anal Chem 25:996–1005
Monzo A, Sperling E, Guttman A (2009) Trends Anal Chem 28:854–864
Sproß J, Sinz A (2010) Anal Chem 82:1434–1443
Lin S, Yao GP, Qi DW, Li Y, Deng CH, Yang PY, Zhang XM (2008) Anal Chem 80:3655–3665
Ma JF, Zhang LH, Liang Z, Shan YC, Zhang YK (2011) Trends Anal Chem 30:691–697
Ma JF, Hou CY, Sun LL, Tao DY, Zhang YY, Shan YC, Liang Z, Zhang LH, Yang L, Zhang YK (2010) Anal Chem 82:9622–9625
Ma JF, Liu JX, Sun LL, Gao L, Liang Z, Zhang LH, Zhang YK (2009) Anal Chem 81:6534–6540
Krenkova J, Lacher NA, Svec F (2009) Anal Chem 81:2004–2012
Kato KS, Kato M, Toyo’oka T (2002) Anal Chem 74:2943–2949
Xu F, Wang WH, Tan YJ, Bruening ML (2010) Anal Chem 82:10045–10051
Gao J, Xu JD, Locascio LE, Lee CS (2001) Anal Chem 73:2648–2655
Li Y, Yan B, Xu XQ, Deng CH, Yang PY, Shen XZ, Zhang XM (2007) Rapid Commun Mass Spectrom 21:2263–2268
Guo Z, Xu SY, Lei ZD, Zou HF, Guo BC (2003) Electrophoresis 24:3633–3639
Ma JF, Hou CH, Liang Y, Wang TT, Liang Z, Zhang LH, Zhang YK (2011) Proteomics 11:991–995
Li Y, Xu XQ, Deng CH, Yang PY, Zhang XM (2007) J Proteome Res 6:3849–3855
Wei LM, Zhang W, Lu HJ, Yang PY (2010) Talanta 80:1298–1304
López-Ferrer D, Hixson KK, Smallwood H, Squier TC, Petritis K, Smith RD (2009) Anal Chem 81:6272–6277
Brady D, Jordaan J (2009) J Biotechnol Lett 31:1639–1650
Wu JM, Luan MM, Zhao JY (2006) Int J Biol Macromol 39:185–191
Arıca MY, Bayramǒglu G (2004) J Mol Catal B: Enzym 27:255–265
Bayramoğlu G, Yalcin E, Arıca MY (2005) Process Biochem 40:3505–3513
Shi QH, Tian Y, Dong XY, Bai S, Sun Y (2003) Eng J 16:317–322
Duan JC, Sun LL, Liang Z, Zhang J, Wang H, Zhang LH, Zhang WB, Zhang YK (2006) J Chromatogr A 1106:165–174
Duan JC, Liang Z, Yang C, Zhang J, Zhang LH, Zhang WB, Zhang YK (2006) Proteomics 6:412–419
Ma JF, Liang Z, Qiao XQ, Deng QL, Tao DY, Zhang LH, Zhang YK (2008) Anal Chem 80:2949–2956
Wu SB, Sun LL, Ma JF, Yang KG, Liang Z, Zhang LH, Zhang YK (2011) Talanta 83:1748–1753
Zhu GJ, Yang C, Zhang LH, Liang Z, Zhang WB, Zhang YK (2006) Talanta 70:2–6
Kruger NJ (2002) The protein protocols handbook part I. Humana, New Jersey, pp 15–21
Acknowledgments
The authors are grateful for the financial support from the National Nature Science Foundation (Grants 20935004 and 20775080), National Basic Research Program of China (Grant 2007CB914100) and the Analytical Method Innovation Program of MOST (2010IM030500).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
ESM 1
(PDF 189 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wu, S., Zhang, L., Yang, K. et al. Preparing a metal-ion chelated immobilized enzyme reactor based on the polyacrylamide monolith grafted with polyethylenimine for a facile regeneration and high throughput tryptic digestion in proteomics. Anal Bioanal Chem 402, 703–710 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00216-011-5501-6
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00216-011-5501-6