Abstract
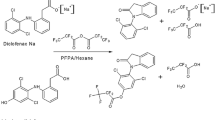
The use of a novel electrophoric derivatisation reagent, o-(pentafluorobenzyloxycarbonyl)-benzoyl chloride, for the quantitative determination of methylphenidate in plasma is described. The drug can be quantitatively measured down to 72 pg/mL plasma using only 250 μL of sample due to the extraordinary sensitivity of the derivatives under negative ion chemical ionisation mass spectrometry. Plasma samples were made alkaline with carbonate buffer and treated with extraction solvent n-hexane and reagent solution for 30 min, which, after concentration, was measured by GC-NICI-MS. The method is rapid as extraction and derivatisation occur in one single step. A stable isotope-labelled internal standard was used and its synthesis described. Full validation data are given to demonstrate the usefulness of the assay, including specificity, linearity, accuracy and precision, long-term stability, short-term stability, freeze–thaw stability, stock solution stability, autosampler stability, aliquot analysis, robustness, matrix effect, and prospective analytical batch size accuracy. The method has been successfully applied to pharmacokinetic profiling of the drug after oral application.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Cantwell DP (1996) Attention deficit disorder: a review of the past 10 years. J Am Acad Child Adolesc Psychiatry 35(8):978–987
Swanson JM, Sergeant JA, Taylor E, Sonuga-Barke EJS, Jensen PS, Cantwell DP (1998) Attention-deficit hyperactivity disorder and hyperkinetic disorder. Lancet 351(9100):429–433
Markowitz JS, Straughn AB, Patrick KS, DeVane CL, Pestreich L, Lee J, Wang Y, Muniz R (2003) Pharmacokinetics of methylphenidate after oral administration of two modified-release formulations in healthy adults. Clin Pharmacokinet 42(4):393–401
Wargin W, Patrick K, Kilts C, Gualtieri CT, Ellington K, Mueller RA, Kraemer G, Breese GR (1983) Pharmacokinetics of methylphenidate in man, rat and monkey. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 226(2):382–386
Sun Z, Murry DJ, Sanghani SP, Davis WI, Kedishvili NY, Zou Q, Hurley TD, Bosron WF (2004) Methylphenidate is stereoselectively hydrolyzed by human carboxylesterase CES1A1. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 310(2):469–476
Scharman EJ, Erdman AR, Cobaugh DJ, Olson KR, Woolf AD, Caravati EM, Chyka PA, Booze LL, Manoguerra AS, Nelson LS, Christianson G, Troutman WG, Association A, American Association of Poison Control C (2007) Methylphenidate poisoning: an evidence-based consensus guideline for out-of-hospital management. Clin Toxicol (Phila) 45(7):737–752
Delbeke FT (1996) Doping in cyclism: results of unannounced controls in Flanders (1987–1994). Int J Sports Med 17(6):434–438
Hickey G, Fricker P (1999) Attention deficit hyperactivity disorder, CNS stimulants and sport. Sports Med 27(1):11–21
Zhu H-J, Wang J-S, Patrick KS, Donovan JL, DeVane CL, Markowitz JS (2007) A novel HPLC fluorescence method for the quantification of methylphenidate in human plasma. J Chromatogr B Anal Technol Biomed Life Sci 858(1–2):91–95
Barbarin N, Mawhinney DB, Black R, Henion J (2003) High-throughput selected reaction monitoring liquid chromatography-mass spectrometry determination of methylphenidate and its major metabolite, ritalinic acid, in rat plasma employing monolithic columns. J Chromatogr B Anal Technol Biomed Life Sci 783(1):73–83
Doerge DR, Fogle CM, Paule MG, McCullagh M, Bajic S (2000) Analysis of methylphenidate and its metabolite ritalinic acid in monkey plasma by liquid chromatography/electrospray ionization mass spectrometry. Rapid Commun Mass Spectrom 14(8):619–623
Marchei E, Farre M, Pellegrini M, Rossi S, Garcia Algar O, Vall O, Pichini S (2009) Liquid chromatography–electrospray ionization mass spectrometry determination of methylphenidate and ritalinic acid in conventional and non-conventional biological matrices. J Pharm Biomed Anal 49(2):434–439
Marchei E, Munoz JA, Garcia-Algar O, Pellegrini M, Vall O, Zuccaro P, Pichini S (2008) Development and validation of a liquid chromatography–mass spectrometry assay for hair analysis of methylphenidate. Forensic Sci Int 176(1):42–46
Yang Y, Kameoka J, Wachs T, Henion JD, Craighead HG (2004) Quantitative mass spectrometric determination of methylphenidate concentration in urine using an electrospray ionization source integrated with a polymer microchip. Anal Chem 76(9):2568–2574
Ramos L, Bakhtiar R, Tse FL (2000) Liquid–liquid extraction using 96-well plate format in conjunction with liquid chromatography/tandem mass spectrometry for quantitative determination of methylphenidate (Ritalin) in human plasma. Rapid Commun Mass Spectrom 14(9):740–745
LeVasseur NL, Zhu H-J, Markowitz JS, DeVane CL, Patrick KS (2008) Enantiospecific gas chromatographic–mass spectrometric analysis of urinary methylphenidate: implications for phenotyping. J Chromatogr B Anal Technol Biomed Life Sci 862(1–2):140–149
Aoyama T, Kotaki H, Honda Y, Nakagawa F (1990) Kinetic analysis of enantiomers of threo-methylphenidate and its metabolite in two healthy subjects after oral administration as determined by a gas chromatographic–mass spectrometric method. J Pharm Sci 79(6):465–469
Lin SN, Andrenyak DM, Moody DE, Foltz RL (1999) Enantioselective gas chromatography–negative ion chemical ionization mass spectrometry for methylphenidate in human plasma. J Anal Toxicol 23(6):524–530
Patrick KS, Ellington KR, Breese GR, Kilts CD (1985) Gas chromatographic–mass spectrometric analysis of methylphenidate and p-hydroxymethylphenidate using deuterated internal standards. J Chromatogr A 343(2):329–338
Patrick KS, Jarvi EJ (1990) Capillary gas chromatographic–mass spectrometric analysis of plasma methylphenidate. J Chromatogr A 528(1):214–221
Nakajima K, Kotaki H, Saitoh Y, Nakagawa F (1986) Determination of methylphenidate and its main metabolite in plasma by gas chromatography–chemical ionization mass spectrometry. Chem Pharm Bull 34(4):1701–1708
Bach GA, Henion J (1998) Quantitative capillary electrophoresis–ion-trap mass spectrometry determination of methylphenidate in human urine. J Chromatogr B Biomed Sci Appl 707(1–2):275–285
Leis HJ, Fauler G, Raspotnig G, Windischhofer W (2000) Negative ion chemical ionization for the determination of methylphenidate in human plasma by stable isotope dilution gas chromatography/mass spectrometry. J Mass Spectrom 35(9):1100–1104
Leis HJ, Windischhofer W (2010) o-(Pentafluorobenzyloxycarbonyl)benzoyl chloride: a novel electrophoric derivatisation reagent for amino compounds designed for negative ion chemical ionisation mass spectrometry. Rapid Commun Mass Spectrom 24(22):3320–3324. doi:10.1002/rcm.4775
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Published in the special issue on Analytical Sciences in Austria with Guest Editors G. Allmaier, W. Buchberger and K. Francesconi.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Leis, H.J., Schütz, H. & Windischhofer, W. Quantitative determination of methylphenidate in plasma by gas chromatography negative ion chemical ionisation mass spectrometry using o-(pentafluorobenzyloxycarbonyl)-benzoyl derivatives. Anal Bioanal Chem 400, 2663–2670 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00216-011-5048-6
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00216-011-5048-6