Abstract
A freeze-dried mussel tissue certified reference material (CRM-FDMT1) containing multiple groups of shellfish toxins has been prepared. Toxin groups present in the material include okadaic acid and the dinophysistoxins, azaspiracids, yessotoxins, pectenotoxins, spirolides and domoic acid. In this work, analytical methods have been examined for the characterisation of the candidate CRM. A comprehensive extraction procedure was developed, which gave good recovery (>98%) for all lipophilic toxins studied. A fast liquid chromatography–mass spectrometry (LC-MS) method was developed that separates the major toxins according to the MS ionisation mode of optimum sensitivity. Matrix effects associated with analysis of these extracts using the developed LC-MS method were assessed. Standard addition and matrix-matched calibration procedures were evaluated to compensate for matrix effects. The methods and approaches will be used for the precise characterisation of the homogeneity and stability of the various toxins in CRM-FDMT1 and for the accurate assignment of certified values. The developed methods also have excellent potential for application in routine regulatory monitoring of shellfish toxins.

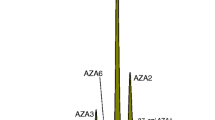
LC-MS/MS chromatogram of CRM-FDMT1: a mussel tissue CRM containing multiple groups of phycotoxins







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Anonymous (2004) Regulation (EC) No 853/2004 of the European parliament and of the council of 29 April 2004 laying down specific hygiene rules for food of animal origin. Official Journal of the European Union L 139 of 30 April 2004
McCarron P, Emteborg H, Nulty C, Rundberget T, Loader JI, Miles CO, Teipel K, Quilliam MA, Hess P (2011) A mussel tissue certified reference material for multiple toxins. Part 1: design and preparation. Anal Bioanal Chem. doi:10.1007/s00216-011-4786-9
Quilliam MA, Hess P, Dell'Aversano C (2001) Recent developments in the analysis of phycotoxins by liquid chromatography-mass spectrometry. De Koe WJ, Samson RA, van Egmond HP, Gilbert J, Sabino M (Eds) Proceedings of the Xth International IUPAC Symposium on Mycotoxins and Phycotoxins, 21–25 May 2000, Guaruja (Brazil), pp 383–391
McNabb P, Selwood AI, Holland PT, Aasen J, Aune T, Eaglesham G, Hess P, Igarishi M, Quilliam M, Slattery D, van de Riet J, van Egmond HP, Van den Top H, Yasumoto T (2005) Multiresidue method for determination of algal toxins in shellfish: single-laboratory validation and interlaboratory study. J AOAC Int 88:761–772
Fux E, McMillan D, Bire R, Hess P (2007) Development of an ultra-performance liquid chromatography-mass spectrometry method for the detection of lipophilic marine toxins. J Chromatogr A 1157:273–280
Stobo LA, Lacaze JP, Scott AC, Gallacher S, Smith EA, Quilliam MA (2005) Liquid chromatography with mass spectrometry—detection of lipophilic shellfish toxins. J AOAC Int 88:1371–1382
Gerssen A, Mulder PPJ, McElhinney MA, de Boer J (2009) Liquid chromatography–tandem mass spectrometry method for the detection of marine lipophilic toxins under alkaline conditions. J Chromatogr A 1216:1421–1430
Hess P, Nguyen L, Aasen J, Keogh M, Kilcoyne J, McCarron P, Aune T (2005) Tissue distribution, effects of cooking and parameters affecting the extraction of azaspiracids from mussels, prior to analysis by liquid chromatography coupled to mass spectrometry. Toxicon 46:62–71
Quilliam MA (1995) Analysis of diarrhetic shellfish poisoning toxins in shellfish tissue by liquid chromatography with fluorometric and mass spectrometric detection. J AOAC Int 78:555–570
Rodrigues SM, Vale P, Botelho MJ, Gomes SS (2009) Extraction recoveries and stability of diarrhetic shellfish poisoning (DSP) toxins in naturally contaminated samples. Food Addit Contam A 26:229–235
McCarron P, Emteborg H, Hess P (2007) Freeze-drying for the stabilisation of shellfish toxins in mussel tissue (Mytilus edulis) reference materials. Anal Bioanal Chem 387:2475–2486
Ito S, Tsukada K (2002) Matrix effect and correction by standard addition in quantitative liquid chromatographic-mass spectrometric analysis of diarrhetic shellfish poisoning toxins. J Chromatogr A 943:39–46
Fux E, Rode D, Bire R, Hess P (2008) Approaches to the evaluation of matrix effects in the liquid chromatography-mass spectrometry (LC-MS) analysis of three regulated lipophilic toxin groups in mussel matrix (Mytilus edulis). Food Addit Contam A 25:1024–1032
King R, Bonfiglio R, Fernandez-Metzler C, Miller-Stein C, Olah T (2000) Mechanistic investigation of ionization suppression in electrospray ionization. J Am Soc Mass Spectrom 11:942–950
These A, Scholz J, Preiss-Weigert A (2009) Sensitive method for the determination of lipophilic marine biotoxins in extracts of mussels and processed shellfish by high-performance liquid chromatography–tandem mass spectrometry based on enrichment by solid-phase extraction. J Chromatogr A 1216:4529–4538
McElhinney MA (2007) Matrix effects. development of clean-up and LC-techniques contributing towards a reference LCMS method for the analysis of lipophilic marine toxins. MPhil Thesis, Dublin Institute of Technology
Gerssen A, Olst EHW, Mulder PPJ, Boer J (2010) In-house validation of a liquid chromatography tandem mass spectrometry method for the analysis of lipophilic marine toxins in shellfish using matrix-matched calibration. Anal Bioanal Chem 397:3079–3088
NRC-CNRC (2002) Certified calibration solution for the spiromine toxins, 13-desmethyl spirolide C. Certificate of analysis, Institute for Marine Biosciences, Halifax, NS, Canada
Yasumoto T, Takizawa A (1997) Fluorometric measurement of yessotoxins in shellfish by high-pressure liquid chromatography. Biosci Biotechnol Biochem 61:1775–1777
Kilcoyne J, Fux E (2010) Strategies for the elimination of matrix effects in the liquid chromatography tandem mass spectrometry analysis of the lipophilic toxins okadaic acid and azaspiracid-1 in molluscan shellfish. J Chromatogr A 1217:7123–7130
Gerssen A, McElhinney MA, Mulder PPJ, Bire R, Hess P, Boer J (2009) Solid phase extraction for removal of matrix effects in lipophilic marine toxin analysis by liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry. Anal Bioanal Chem 394:1213–1226
McCarron P, Kilcoyne J, Miles CO, Hess P (2009) Formation of azaspiracids-3, -4, -6, and -9 via decarboxylation of carboxyazaspiracid metabolites from shellfish. J Agric Food Chem 57:160–169
Yasumoto T, Murata M, Oshima Y, Sano M, Matsumoto GK, Clardy J (1985) Diarrhetic shellfish toxins. Tetrahedron 41:1019–1025
Mountfort DO, Suzuki T, Truman P (2001) Protein phosphatase inhibition adapted for determination of total DSP in contaminated mussel. Toxicon 39:383–390
Doucet E, Ross N, Quilliam MA (2007) Enzymatic hydrolysis of esterified diarrhetic shellfish poisoning toxins and pectenotoxins. Anal Bioanal Chem 389:335–342
Torgersen T, Wilkins AL, Rundberget T, Miles CO (2008) Characterization of fatty acid esters of okadaic acid and related toxins in blue mussels (Mytilus edulis) from Norway. Rapid Commun Mass Spectrom 22:1127–1136
Acknowledgements
Technical assistance from Elliott Wright is gratefully acknowledged. Dr. Jeremy Melanson is thanked for reviewing this manuscript. This is NRCC manuscript number 51796.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
ESM 1
Electronic supplementary material (PDF 70.4 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
McCarron, P., Giddings, S.D. & Quilliam, M.A. A mussel tissue certified reference material for multiple phycotoxins. Part 2: liquid chromatography–mass spectrometry, sample extraction and quantitation procedures. Anal Bioanal Chem 400, 835–846 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00216-011-4803-z
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00216-011-4803-z