Abstract
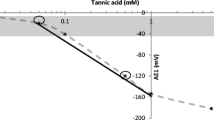
An electronic tongue (ET) based on potentiometric chemical sensors was assessed as a rapid tool for the quantification of bitterness in red wines. A set of 39 single cultivar Pinotage wines comprising 13 samples with medium to high bitterness was obtained from the producers in West Cape, South Africa. Samples were analysed with respect to a set of routine wine parameters and major phenolic compounds using Fourier transform infrared-multiple internal reflection spectroscopy (WineScan) and high-performance liquid chromatography, respectively. A trained sensory panel assessed the bitterness intensity of 15 wines, 13 of which had a bitter taste of medium to high intensity. Thirty-one wine samples including seven bitter-tasting ones were measured by the ET. Influence of the chemical composition of wine on the occurrence of the bitter taste was evaluated using one-way analysis of variance. It was found that bitter-tasting wines had higher concentrations of phenolic compounds (catechin, epicatechin, gallic and caffeic acids and quercetin) than non-bitter wines. Sensitivity of the sensors of the array to the phenolic compounds related to the bitterness was studied at different pH levels. Sensors displayed sensitivity to all studied compounds at pH 7, but only to quercetin at pH 3.5. Based on these findings, the pH of wine was adjusted to 7 prior to measurements. Calibration models for classification of wine samples according to the presence of the bitter taste and quantification of the bitterness intensity were calculated by partial least squares-discriminant analysis (PLS-DA) regression. Statistical significance of the classification results was confirmed by the permutation test. Both ET and chemical analysis data could discriminate between bitter and control wines with the correct classification rates of 94% and 91%, respectively. Prediction of the bitterness intensity with good accuracy (root mean square error of 2 and mean relative error of 6% in validation) was possible only using ET data.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Noble AC (1994) Physiol Behav 56:1251–1255
Peleg H, Gacon K, Schlich P, Noble AC (1999) J Sci Food Agric 79:1123–1128
Vidal S, Francis L, Noble A, Kwiatkowski M, Cheynier V, Waters E (2004) Anal Chim Acta 513:57–65
Hufnagel JC, Hofmann T (2008) J Agric Food Chem 56:1376–1386
Hufnagel JC, Hofmann T (2008) J Agric Food Chem 56:9190–9199
Burns DJW, Noble AC (1985) J Text Stud 16:365–380
Smith AK, June H, Noble AC (1996) Food Qual Pref 7:161–166
Fontoin H, Saucier C, Teissedre P-L, Glories Y (2008) Food Qual Pref 19:286–291
Lesschaeve I, Noble AC (2005) Am J Clin Nutr 81:330S–335S
Sponholz W-R (1993) In: Fleet GH (ed) Wine microbiology and biotechnology. Harwood Academic Publishers, Philadelphia
Lonvaud-Funel A (2002) Biotransformations: bioremediation technology for health and environmental protection. In: Singh VP, Stapleton RD (eds) Progress in industrial microbiology, vol 36. Elsevier Science, Amsterdam
Garai-Ibabe G, Ibarburu I, Berregi I, Claisse O, Lonvaud-Funel A, Irastorza A, Dueñas MT (2008) Int J Food Microb 121:253–261
Sauvageot N, Gouffi K, Laplace J-M, Auffray Y (2000) Int J Food Microb 55:167–170
Peri I, Mamrud-Brains H, Rodin S, Krizhanovsky V, Shai Y, Nir S, Naim M (2000) Am J Physiol Cell Physiol 278:C17–C25
Ciosek P, Wroblewski W (2007) Analyst 132:963–978
Legin A, Rudnitskaya A, Vlasov Yu (2003) In: Alegret S (ed) Integrated analytical systems, comprehensive analytical chemistry XXXIX. Elsevier, Amsterdam
Winquist F, Krantz-Rülcker C, Lundström I (2003) In: Pearce TC, Gardner JW, Schiffman SS, Nagle HT (eds) Handbook of machine olfaction. Wiley-VCH Verlag GmbH, Weinheim
Tagaki S, Toko K, Wada K, Ohki T (2001) J Pharm Sci 90:2042–2048
Legin A, Rudnitskaya A, Clapham D, Seleznev B, Lord K, Vlasov Yu (2004) Anal Bioanal Chem 380:36–45
Zheng JY, Keeney MP (2006) J Pharm 310:118–124
Lorenz JK, Reo J, Hendl O, Worthington JH, Petrossian VD (2009) Int J Pharm 367:65–72
Fukunaga T, Toko K, Mori S, Nakabayashi Y, Kanda M (1996) Sens Mater 8:47–56
Kaneda H, Watari J, Takashio M, Okahat Y (2003) J Inst Brew 109:27–33
Kaneda H, Takashio M, Shinotsuka K, Okahata Y (2001) J Biosci Bioeng 92:221–226
Rudnitskaya A, Polshin E, Kirsanov D, Lammertyn J, Nicolai B, Saison D, Delvaux FR, Delvaux F, Legin A (2009) Anal Chim Acta 646:111–118
Apetrei C, Gutierez F, Rodriguez-Mendez ML, de Saja JA (2007) Sens Actuators B 121:567–575
Nieuwoudt HH, Prior BA, Pretorius IS, Manley M, Bauer FF (2004) J Agric Food Chem 52:3726–3735
Peng Z, Iland RG, Oberholster A, Sefton MA, Waters EJ (2002) Austr J Grape Wine Res 8:70–75
Revilla E, Ryan J (2000) J Chrom A 881:461–469
Lee CB, Lawless HT (1991) Chem Sens 16:225–238
Barker M, Rayens W (2003) J Chemometr 17:166–173
Westerhuis JA, Hoefsloot HCJ, Smit S, Vis DJ, Smilde AK, van Velzen EJJ, van Duijnhoven JPM, van Dorsten FA (2008) Metabolomics 4:81–89
Hernandez T, Estrella I, Perez-Gordo M, Alegria EG, Tenorio C, Ruiz-Larrrea F, Moreno-Arribas MV (2007) J Agric Food Chem 55:5260–5266
Cabrita MJ, Torres M, Palma V, Alves E, Patao R (2008) Costa Freitas AM. Talanta 74:1281–1286
Vivas N, Lonvaud-Funel A, Glories Y (1997) Food Microbiol 14:291–300
Campos FM, Figueiredo AR, Hogg TA, Couto JA (2009) Food Microbiol 26:409–414
Ito T, Radecka H, Umezawa K, Kimura T, Yashiro A, Ming Lin X, Kataoka M, Kimura E, Sessler JL, Odashima K, Umezawa Y (1998) Anal Sci 14:89–98
Rudnitskaya A, Delgadillo I, Rocha SM, Costa A-M, Legin A (2006) Anal Chim Acta 563:315–318
Fontoin H, Saucier C, Rudnitskaya A, Legin A, Teissedre P-L, Glories Y (2007) In the Proceedings of the XXXth World Congress on Vine and Wine, 10–16 June 2007, Budapest, Hungary, p 268
Herrero-Martinez JM, Sanmartin M, Roses M, Bosch E, Rаfols C (2005) Electrophoresis 26:1886–1895
Borges F, Lima JFLC, Pinto I, Reis S, Siquet C (2003) Helv Chim Acta 86:3081–3087
Erdemgil FZ, Sanli S, Sanli N, Ozkan G, Barbosa J, Guiteras J, Beltran JL (2007) Talanta 72:489–496
Reyes LF, Cisneros-Zevallos L (2007) Food Chem 100:885–894
Sangster J (1997) Octanol-water partition coefficients: fundamentals and physical chemistry 2 of Wiley series in solution chemistry. Wiley, Chichester
Tetko IV, Tanchuk VY (2002) J Chem Inf Comput Sci 42:1136–1145
Acknowledgments
Financial support of the work of A. Rudnitskaya by Pinotage Association, Stellenbosch, South Africa, is kindly acknowledged. Support of this work from F. Calitz (Biometry Unit, ARC Infruitec-Nietvoorbij, Stellenbosch), E. Moelich (Sensory Unit, Department of Food Science, Stellenbosch University) and individual cellars and winemakers is acknowledged. The provision of Pinotage wine through the Pinotage Association, Stellenbosch, South Africa, and L'Avenir Wine Estate, Stellenbosch, South Africa, is acknowledged.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Rudnitskaya, A., Nieuwoudt, H.H., Muller, N. et al. Instrumental measurement of bitter taste in red wine using an electronic tongue. Anal Bioanal Chem 397, 3051–3060 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00216-010-3885-3
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00216-010-3885-3