Abstract
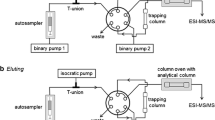
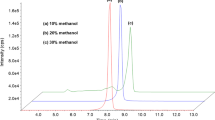
We present data for a comparison of a liquid-chromatographic method coupled with tandem mass spectrometry (LC-MS/MS) and a high-performance liquid-chromatographic method with column switching and UV spectrophotometric detection. The two methods were developed for determination of naltrexone and 6β-naltrexol in blood serum or plasma aiming to be used for therapeutic drug monitoring to guide the treatment of patients with naltrexone. For the high-performance liquid chromatography (HPLC)/UV detection, online sample cleanup was conducted on Perfect Bond C18 material with 2% (vol/vol) acetonitrile in deionized water. Drugs were separated on a C18 column using 11.5% (vol/vol) acetonitrile and 0.4% (vol/vol) N,N,N,N-tetramethylethylenediamine within 20 min. LC-MS/MS used naltrexone-d 3 and 6β-naltrexol-d 4 as internal standards. After protein precipitation, the chromatographic separation was performed on a C18 column by applying a methanol gradient (5–100%, vol/vol) with 0.1% formic acid over 9.5 min. The HPLC/UV method was found to be linear for concentrations ranging from 2 to 100 ng/ml, with a regression correlation coefficient of r 2 > 0.998 for naltrexone and 6β-naltrexol. The limit of quantification was 2 ng/ml for naltrexone and 6β-naltrexol. For the LC-MS/MS method the calibration curves were linear (r² > 0.999) from 0.5 to 200 ng/ml for both substances, and the limit of quantification was 0.5 ng/ml. The concentrations measured by the two methods correlated significantly for both substances (r² > 0.967; p < 0.001). Both methods could be used for therapeutic drug monitoring. The HPLC/UV method was advantageous regarding automatization and costs, whereas LC-MS/MS was superior with regard to sensitivity.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ohara H, Miyabe Y, Deyashiki Y, Matsuura K, Hara A (1995) Biochem Pharmacol 50:221–227
Malspeis L, Bathala MS, Ludden TM, Bhat HB, Frank SG, Sokoloski TD, Morrison BE, Reuning RH (1975) Chem Pathol Pharmacol 12:43–65
Cone EJ, Gorodetzky CW, Yeh SY (1974) Drug Metab Dispos 2:506–512
Blumberg H, Ikeda C (1976) Fed Proc 35:469
Dunbar JL, Turncliff RZ, Dong Q, Silverman BL, Ehrich EW, Lasseter KC (2006) Alcohol Clin Exp Res 30:480–490
Wall ME, Brine DR, Perez-Reyes M (1981) Drug Metab Dispos 9:369–375
Meyer MC, Straughn AB, Lo MW, Schary WL, Whitney CC (1984) J Clin Psychiatry 45:15–19
Derendorf H, El-Din A, El-Koussi A, Garrett ER (1984) J Pharm Sci 73:621–624
O‘Connor EF, Cheng SWT, North WG (1989) J Chromatogr Biomed Appl 491:240–247
Zuccaro P, Altieri I, Betto P, Pacifici R, Ricciarello G, Pini LA, Sternieri E, Pichini S (1991) J Chromatogr 567:485–490
Davidson AF, Emm TA, Pieniaszek HJ Jr (1996) J Pharm Biomed Anal 14:1717–1725
Vereby K, Kogan MJ, DePace A, Mulle SJ (1976) J Chromatogr 118:331
Reunig RH, Ashcraft SB, Morrison BE (1981) NIDA Res Monogr 28:25
Monti KM, Foltz RL, Chinn DM (1991) J Anal Toxicol 15:136–140
Valiveti S, Nalluri BN, Hammell DC, Paudel KS, Stinchcomb AL (2004) J Chromatogr B 810:259–267
Iyer SS, Kellogg GE, Karnes HAT (2007) J Chromatogr Sci 45:694–700
Clavijo C, Bendrick-Peart J, Zhang YL, Johnson G, Gasparic A, Christians U (2008) J Chromatogr B Anal Technol Biomed Life 874:33–41
Slawson MH, Chen M, Moody D, Comer SD, Nuwayser ES, Fang WB, Foltz RL (2007) J Anal Toxicol 31:453–461
Baumann P, Hiemke C, Ulrich S, Eckermann G, Gaertner I, Gerlach M, Kuss HJ, Laux G, Müller-Oerlinghausen B, Rao ML, Riederer P, Zernig G (2004) Pharmacopsychiatry 37:243–265
Navaratnam V, Jamaludin A, Raman N, Mohamed M, Mansor SM (1994) Drug Alcohol Depend 34:231–236
Schuh KJ, Walsh SL, Stitzer ML (1999) Psychopharmacology 145:162–174
Dunbar JL, Turncliff RZ, Dong Q, Silverman BL, Ehrich EW, Lasseter KC (2006) Alcohol Clin Exp Res 30:480–490
Ferrari A, Bertolotti M, Dell’Utri A, Sterinieri E (1998) Drug Alcohol Depend 52:211–220
European Medicines Agency ICH Topic E 6 (R1): guideline for good clinical practice; step 5 [Online]. 07.2002 [Last access 17-11-09]. URL: http://www.emea.europa.eu/pdfs/human/ich/013595en.pdf
World Medical Association Declaration of Helsinki (1997) JAMA 277:925–926
Kirchherr H, Kühn-Velten WN (2006) J Chromatogr B Anal Technol Biomed Life Sci 843:100–113
Kassenärztliche Bundesvereinigung (2009) Einheitlicher Bewertungsmaßstab. http://www.kbv.de/ebm2009/ebmgesamt.htm
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Brünen, S., Krüger, R., Finger, S. et al. Determination of naltrexone and 6β-naltrexol in human blood: comparison of high-performance liquid chromatography with spectrophotometric and tandem-mass-spectrometric detection. Anal Bioanal Chem 396, 1249–1257 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00216-009-3301-z
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00216-009-3301-z