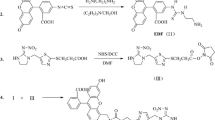
Abstract
A fluorescence polarization (FP) immunoassay, based on a monoclonal antibody and an ochratoxin A (OTA)-fluorescein tracer, has been developed for rapid screening of OTA in red wine. Wine samples were diluted with methanol and passed through aminopropyl solid-phase extraction columns prior to the FP assay. Average recoveries from samples spiked with OTA at levels of 2.0 and 5.0 ng/mL were 79% with RDS of 11% (n = 6). The limit of detection of the FP immunoassay was 0.7 ng/mL OTA, and the whole analysis was performed in less than 10 min. The assay was tested on 154 red wine samples (naturally contaminated or spiked at level ranging from 0.1 to 5.0 ng/mL) and compared with an high-performance liquid chromatography/immunoaffinity column clean-up method, showing a good correlation (r = 0.9222). Their compliance with the European regulation (2.0 ng/mL OTA maximum permitted level) was correctly assessed for 70% of the analyzed samples of red wine, whereas confirmatory analyses were required for the remaining ones with OTA levels close to the regulatory limit. No false-negative or positive results were observed using the FP immunoassay. The proposed FP assay is a useful screening method for OTA in red wines, when high throughput is required, that could also be used for white and rosé wines, which are known to contain less interfering compounds such as polyphenols.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Benford D, Boyle C, Dekant W, Fuchs R, Gaylor DW, Hard G, McGregor DB, Pitt JI, Plestina R, Shephard G, Solfrizzo M, Verger PJP, Walker R (2001) In: Safety evaluation of certain mycotoxins in food. FAO Food and Nutrition Paper 74, WHO Food Additives Series 47, WHO, Geneva, pp 281–415
Kuiper-Goodman T (1996) Food Addit Contam 13:53–57
IARC (1993) Monographs on the evaluation of carcinogenic risk to humans, vol 56. IARC, Lyon
SCOOP (2002) Report of experts participating in Task 3.2.7, Brussels, Belgium. http://europa.eu.int/comm/food/fs/scoop/3.2.7_en.pdf. Accessed 04 June 2009
Visconti A, Perrone G, Cozzi G, Solfrizzo M (2008) Food Addit Contam 25:193–202
European Commission (2006) Off J Eur Union L364:5–24
Visconti A, Pascale M, Centonze G (2001) J AOAC Int 84:1818–1827
Ongunjimi AA, Choudary PV (1999) FEMS Immununol Med Microbiol 23:213–220
Ngundi MM, Shriver-Lake LC, Moore MH, Lassman ME, Ligler FS, Taitt CR (2005) Anal Chem 77:148–154
Mateo R, Medina A, Mateo EM, Mateo F, Jiménez M (2007) Int J Food Microbiol 119:79–83
Prieto-Simón B, Campàs M, Marty JL, Noguer T (2008) Biosens Bioelectron 23:995–1002
Smith DS, Eremin SA (2008) Anal Bioanal Chem 391:1499–1507
Nasir MS, Jolley ME (2002) J Agric Food Chem 50:3116–3121
Maragos CM, Jolley ME, Plattner RD, Nasir MS (2001) J Agric Food Chem 49:596–602
Maragos CM, Kim E (2004) J Food Prot 67:1039–1043
Lippolis V, Pascale M, Visconti A (2006) J Food Prot 69:2712–2719
Chun HS, Choi EH, Chang H-J, Choi S-W, Eremin SA (2009) Anal Chim Acta 639:83–89
Shim WB, Kolosova AY, Kim YJ, Yang ZY, Park SJ, Eremin SA, Lee IS, Chung DH (2004) Int J Food Sci Technol 39:829–837
Nistor C, Oubina A, Marco M-P, Barcelo D, Emneus J (2001) Anal Chim Acta 426:185–195
Kolosova AY, Park JH, Eremin SA, Kang SJ, Chung DH (2003) J Agric Food Chem 51:1107–1114
Visconti A, Pascale M, Centonze G (1999) J Chromatogr A 864:89–101
OIV (2006) Recueil des methodes internationales d’analyse des vins et des mouts, Caractéristiques chromatiques, Vol. 1. OIV, Paris
Miller JC, Miller JN (1984) Statistics for analytical chemistry. Ellis Horwood, Chichester
Pezet R, Pont V, Cuenat P (1994) J Chromatogr A 663:191–197
Drabent R, Pliszka B, Olszewska T (1999) J Photochem Photobiol B: Biol 50:53–58
Varelis P, Leong SL, Hocking A, Giannikopoulos G (2006) Food Addit Contam 23:1308–1315
Acknowledgments
Financial support from the Italian Ministry of Education, University and Research, MIUR Project no. 12818 “SIVINA” (D.M. 593/200) is gratefully acknowledged. S.A. Eremin would like to thank the Italian National Research Council (CNR) for receiving a grant within the Short-term Mobility Program 2007 of the CNR.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zezza, F., Longobardi, F., Pascale, M. et al. Fluorescence polarization immunoassay for rapid screening of ochratoxin A in red wine. Anal Bioanal Chem 395, 1317–1323 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00216-009-2994-3
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00216-009-2994-3