Abstract
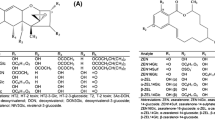
Cereals and cereal-based food have often been found to be contaminated with the mycotoxins deoxynivalenol (DON) and zearalenone (ZON), after infection of the grain with the pathogenic fungus Fusarium. Both the pathogen and the infected plants can chemically modify DON and ZON, including acetylation, glucosidation, and sulfation. Analytical strategies for detection and quantification of DON and ZON are well known and established but often fail to recognize the respective metabolites, which are, therefore, also referred to as “masked” mycotoxins. However, several masked forms are also known to be harmful to mammals. Failure to detect these could lead to significant underestimation of the toxic potential of a particular sample. To monitor the levels of DON and ZON metabolites in cereals and cereal-based food, we have developed a LC–MS–MS method capable of simultaneous determination of DON, ZON, and eight of their masked metabolites, namely deoxynivalenol-3-glucoside (D3G), 3-acetyl-deoxynivalenol (3ADON), zearalenone-4-glucoside (Z4G), α-zearalenol (α-ZOL), β-zearalenol (β-ZOL), α-zearalenol-4-glucoside (α-ZG), β-zearalenol-4-glucoside (β-ZG), and zearalenone-4-sulfate (Z4S). The suitability of several cleanup strategies including C18-SPE, primary and secondary amines (PSA), MycoSep push-through columns, and immunoaffinity columns was evaluated. The final method used no sample cleanup and was successfully validated for four cereal-based food matrices, namely cornflour, porridge, beer, and pasta, showing good recoveries and precision for all analytes.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Leonard K, Bushnell W (2004) (eds) Fusarium head blight of wheat and barley. APS Press St, Paul, MN, USA
van Egmond HP, Schothorst RC, Jonker MA (2007) Anal Bioanal Chem 389:147–157
European Commission Regulation No 1126 (2007) Off J Eur Union L255:14–17
Engelhardt G, Ruhland M, Wallnöfer PR (1999) Adv Food Sci 21:71–78
Karlovsky P (1999) Nat Toxins 7:1–23
Berthiller F, Dall’Asta C, Schuhmacher R, Lemmens M, Adam G, Krska R (2005) J Agric Food Chem 53:3421–3425
Engelhardt G, Zill G, Wohner B, Wallnöfer PR (1988) Naturwissenschaften 75:309–310
Böswald C, Engelhardt G, Vogel H, Wallnöfer PR (1995) Nat Toxins 3:138–144
Joint FAO/WHO Expert Committee on Food Additives (JECFA) (2000) WHO Food Additives Series 44, http://www.inchem.org/documents/jecfa/jecmono/v44jec14.htm
Berthiller F, Werner U, Sulyok M, Krska R, Hauser MT, Schuhmacher R (2006) Food Addit Contam 23:1194–1200
El-Sharkawy S, Selim MI, Afifi MS, Halaweish FT (1991) Appl Environ Microbiol 57:549–552
Plasencia J, Mirocha CJ (1991) Appl Environ Microbiol 57:146–150
Gareis M, Bauer J, Thiem J, Plank G, Grabley S, Gedek B (1990) J Vet Med 37:236–240
Krska and Josephs (2001) Fresenius J Anal Chem 369:469–476
Fitzpatrick DW, Picken CA, Murphy LC, Buhr MM (1989) Comp Biochem Physiol C 94(2):691–694
Schneweis I, Meyer K, Engelhardt G, Bauer J (2002) J Agric Food Chem 50:1736–1738
Young CJ, Fulcher GR, Hayhoe JH, Scott PM, Dexter JE (1984) J Agric Food Chem 32:659–664
Berthiller F, Corradini R, Dall’Asta C, Marchelli R, Sulyok M, Krska R, Adam G, Schuhmacher R (2009) Food Addit Contam [epub ahead of print]
Lancova K, Hajslova J, Poustka J, Krplova A, Zachariasova M, Dostalek P, Sachambula L (2008) Food Addit Contam 25:732–744
Berthiller F, Hametner C, Krenn P, Schweiger W, Ludwig R, Adam G, Krska R, Schuhmacher R (2009) Food Addit Contam A 26:207–213
Sulyok M, Berthiller F, Krska R, Schuhmacher R (2006) Rap Commun Mass Spectrom 20:2649–2659
Wegscheider W, Rohrer C, Neuböck R (1999) Validata (Excel-Makro zur Methodenvalidierung), Version 3.02.48
Berthiller F, Schuhmacher R, Buttinger G, Krska R (2005) J Chromatogr A 1062:209–216
Häubl G, Berthiller F, Rechthaler J, Jaunecker G, Binder EM, Krska R, Schuhmacher R (2006) Food Addit Contam 23:1187–1193
Cramer B, Bretz M, Humpf H-U (2007) J Agric Food Chem 55:8353–8358
Acknowledgements
The authors thank the Christian Doppler Forschungsgesellschaft and the UK Food Standard Agency (FSA) for financial support.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Vendl, O., Berthiller, F., Crews, C. et al. Simultaneous determination of deoxynivalenol, zearalenone, and their major masked metabolites in cereal-based food by LC–MS–MS. Anal Bioanal Chem 395, 1347–1354 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00216-009-2873-y
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00216-009-2873-y