Abstract
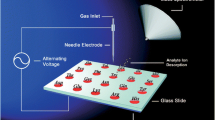
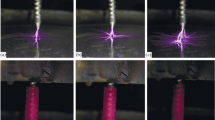
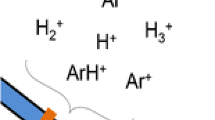
The similarity principles of electric plasmas, and the current-voltage characteristics of the most prominent kinds of discharges used for analytical applications, are discussed. Most of the discharges can be miniaturized, and some of the analytical applications of different discharges can be realized by use of dielectric barriers for analytical applications, for example element spectrometry, as an ionization source for ion-mobility spectrometry or organic mass spectrometry, and as an electrospray ionization source.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Manz A, Graber N, Widmer HM (1990) Sens Actuators B 1:244
Townsend JS (1915) Electricity in gases, 365
Paschen F (1889) Wied Ann 37:69
Holm R (1924) Phys Z 25:497
v Engel H, Steenbeck V (1934) Elektrische Gasentladungen, Vol. II. Springer, Berlin Heidelberg New York
Margenau H (1948) Phys Rev 73:197
Llewllyn Jones F, Morgan GD (1951) Proc Phys Soc Lond B 64:560
de la Rue W, Muller HW (1880) Phil Trans Roy Soc Lond 171:109
Carr WR (1903) Phil Trans Roy Soc Lond Ser A 201:403
Druyvesteyn MJ, Penning FM (1940) Rev Mod Phys 12:87
Francis G (1956) The glow discharge at low pressure. In: Flügge S (ed) Handbuch der Physik, Band XXII Gasentladungen II. Springer, Berlin Heidelberg New York
Hertz G, Rompe R (1965) Einführung in die Plasmaphysik und ihre technische Anwendung, Akademie Verlag Berlin
Loeb LB (1956) Electrical breakdown of gases with steady or direct current impulse potentials. In: Flügge S (ed) Handbuch der Physik, Band XXII Gasentladungen II. Springer, Berlin Heidelberg New York
Miclea M, Kunze K, Musa G, Franzke J, Niemax K (2001) Spectrochim Acta B 56:37
Kunze K, Miclea M, Musa G, Franzke J, Vadla C, Niemax K (2002) Spectrochim Acta B 57:137–146
Miclea M, Kunze K, Franzke J, Niemax K (2002) Spectrochim Acta B 57:1585–1592
Franzke J, Kunze K, Miclea M, Niemax K (2003) J Anal At Spectrom 18:802–807
Kunze K, Miclea M, Franzke J, Niemax K (2003) Spectrochim Acta B 58:1435–1443
Michels A, Tombrink S, Vautz W, Miclea M, Franzke J (2007) Spectrochim Acta B 62:1208–1215
Bos SJ, van Leeuwen SM, Karst U (2006) Anal Bioanal Chem 384:85–99
Raffaelli A, Saba A (2003) Mass Spectrom Rev 22:318–331
Borsdorf H, Schelhorn H, Flachowsky J, Doring HR, Stach J (2000) Anal Chim Acta 403:235–242
Eiceman GA, Karpas Z (1994) Ion mobility spectrometry, 1st edn. CRC Press, London, UK
Ewing RG, Eiceman GA, Stone JA (1999) Int J Mass Spectrom 193:57–58
Vautz W, Michels A, Franzke J (2008) Anal Bioanal Chem 391:2609–2615
Cole RB (1997) Electrospray ionization mass spectrometry, fundamentals, instrumentation and applications. Wiley, New York
Schilling M, Janasek D, Franzke J (2008) Anal Bioanal Chem 391:555–561
Acknowledgements
Financial support by the Bundesministerium für Bildung und Forschung and the Ministerium für Wissenschaft und Forschung des Landes Nordrhein-Westfalen is gratefully acknowledged. The authors gratefully acknowledge financial support by the Deutsche Forschungsgemeinschaft.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Franzke, J. The micro-discharge family (dark, corona, and glow-discharge) for analytical applications realized by dielectric barriers. Anal Bioanal Chem 395, 549–557 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00216-009-2799-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00216-009-2799-4