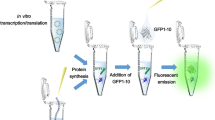
Abstract
Heteroisotope and heteroatom tagging with [34S]-enriched methionine (Met), selenomethionine (SeMet), and telluromethionine (TeMet) was applied to in vitro translation. Green fluorescent protein (GFP) and JNK stimulatory phosphatase-1 (JSP-1) genes were translated with wheat germ extract (WGE) in the presence of Met derivatives. GFPs containing Met derivatives were subjected to HPLC coupled with treble detection, i.e., a photodiode array detector, a fluorescence detector, and an inductively coupled plasma mass spectrometer (ICP-MS). The activities of JSP-1-containing Met derivatives were also measured. GFP and JSP-1 containing [34S]-Met and SeMet showed comparable fluorescence intensities and enzyme activities to those containing naturally occurring Met. TeMet was unstable and decomposed in WGE, whereas SeMet was stable throughout the experimental period. Thus, although Te was the most sensitive to ICP-MS detection among S, Se, and Te, TeMet was less incorporated into the proteins than Met and SeMet. Finally, the potential of heteroisotope and heteroatom tagging of desired proteins in in vitro translation followed by ICP-MS detection was discussed.

TeMet was less incorporated into GFP than Met and SeMet due to its instability in WGE





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Sanz-Medel A (2005) Anal Bioanal Chem 381:1–2
Sanz-Medel A, Montes-Bayón M, Fernández Sánchez ML (2003) Anal Bioanal Chem 377:236–247
Łobiński R, Schaumlöffel D, Szpunar J (2006) Mass Spectrom Rev 25:255–289
Szpunar J (2005) Analyst 130:442–465
Pereira Navaza A, Ruiz Encinar J, Sanz-Medel A (2007) Angew Chem Int Ed Engl 46:569–571
Michalke B, Schramel P (1999) Electrophoresis 20:2547–2553
Baranov VI, Quinn Z, Bandura DR, Tanner SD (2002) Anal Chem 74:1629–1636
Nojima T, Kondoh Y, Takenaka S, Ichihara T, Takagi M, Tashiro H, Matsumoto K (2001) Nucleic Acids Res Suppl 1:105–106
Matsumoto K, Yuan J, Wang G, Kimura H (1999) Anal Biochem 276:81–87
Suzuki KT (2005) J Health Sci 51:107–114
B’Hymer C, Caruso JA (2006) J Chromatogr A 1114:1–20
Meija J, Montes-Bayón M, Caruso JA, Sanz-Medel A (2006) Trends Anal Chem 25:44–51
Birringer M, Pilawa S, Flohé L (2002) Nat Prod Rep 19:693–718
O’Gara M, Adams GM, Gong W, Kobayashi R, Blumenthal RM, Cheng X (1997) Eur J Biochem 247:1009–1018
Pavlov MY, Ehrenberg M (1996) Arch Biochem Biophys 328:9–16
Madin K, Sawasaki T, Ogasawara T, Endo Y (2000) Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 97:559–564
Schindler PT, Macherhammer F, Arnold S, Reuss M, Siemann M (1999) Electrophoresis 20:806–812
Yokota T, Nara Y, Kashima A, Matsubara K, Misawa S, Kato R, Sugio S (2007) Proteins 66:272–278
Schindler PT, Baumann S, Reuss M, Siemann M (2000) Electrophoresis 21:2606–2609
Prasher DC, Eckenrode VK, Ward WW, Prendergast FG, Cormier MJ (1992) Gene 111:229–233
Knapp FF Jr (1979) J Org Chem 44:1007–1009
Ogra Y, Ishiwata K, Suzuki KT (2005) Anal Chim Acta 554:123–129
Divjak B, Goessler W (1999) J Chromatogr A 844:161–169
Koplík R, Pavelková H, Cincibuchová J, Mestek O, Kvasnika F, Suchánek M (2002) J Chromatogr B Anal Technol Biomed Life Sci 770:261–273
Suzuki KT, Yoneda S, Itoh M, Ohmichi M (1995) J Chromatogr B Biomed Sci Appl 670:63–71
Boles JO, Lebioda L, Dunlap RB, Odom JD (1995) SAAS Bull Biochem Biotechnol 8:29–34
Budisa N, Karnbrock W, Steinbacher S, Humm A, Prade L, Neuefeind T, Moroder L, Huber R (1997) J Mol Biol 25:616–623
Kigawa T, Yamaguchi-Nunokawa E, Kodama K, Matsuda T, Yabuki T, Matsuda N, Ishitani R, Nureki O, Yokoyama S (2002) J Struct Funct Genomics 2:29–35
Acknowledgements
We would like to acknowledge Grants-in-Aid from the Ministry of Education, Culture, Sports, Science and Technology of Japan (Nos. 16689005, 16209004, and 19390033), and the financial support from Agilent Technologies Foundation, USA. We also wish to thank ZOEGENE Co. for the in vitro translation kit and control mRNA, and Showa Denko for the HPLC system.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ogra, Y., Kitaguchi, T., Suzuki, N. et al. In vitro translation with [34S]-labeled methionine, selenomethionine, and telluromethionine. Anal Bioanal Chem 390, 45–51 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00216-007-1546-y
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00216-007-1546-y