Abstract
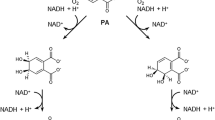
n-Butyl benzyl phthalate (BBP) is an endocrine-disrupting chemical. A bacterium species capable of using BBP as the sole source of carbon and energy was isolated from mangrove sediment. Effects of BBP concentration, pH, temperature, and salinity on BBP biodegradation were studied. The optimum pH, temperature, and salinity for the BBP biodegradation were 7.0, 37°C, and 15 g L−1, respectively. BBP was completely degraded within 6 days under optimum conditions, and the biodegradation of BBP could be fitted to a first-order kinetic model. The major metabolites of BBP biodegradation were identified as mono-butyl phthalate, mono-benzyl phthalate, phthalic acid, and benzoic acid by using high-performance liquid chromatography and gas chromatography–mass spectrometry. A preliminary metabolic pathway was proposed for the biodegradation of BBP.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Harris CA, Henttu P, Parker MG, Sumpter JP (1997) Environ Health Persp 105:802–810
Colon I, Caro D, Bourdony CJ, Rosario O (2000) Environ Health Persp 108:895–900
Petroviæ M, Eljarrat E, López MJ, Barceló D (2001) Trends Anal Chem 20:637–648
Nyholm N, Ingerslev F, Berg UT, Pedersen JP, Larsen HF (1996) Chemosphere 33:851–864
Piersma AH, Verhoef A, Biesebeek JT, Pieters MN, Slob W (2000) Reprod Toxicol 14:417–425
Cartwright CD, Owen SA, Thompson IP, Burns RG (2000) FEMS Microbiol Lett 186:27–34
Vega D, Bastide J (2003) Chemosphere 51:663–668
Wang Y, Fan Y, Gu JD (2004) Intern Biodeter Biodegr 53:93–101
Kim YH, Lee J, Ahn JY, Gu MB, Moon SH (2002) Appl Environ Microbiol 68:4684–4688
Chatterjee S, Dutta TK (2003) Biochem Biophys Res Comm 309:36–43
Prevot AB, Basso A, Baiocchi C, Pazzi M, Marci G, Augugliaro V, Palmisano, Pramauro E (2004) Anal Bioanal Chem 378:214–220
Zwiener C, Seeger S, Glauner T, Frimmel FH (2002) Anal Bioanal Chem 372:569–575
Xu XR, Gu JD (2004) Microchem J 77:71–77
Lanyi K, Dinya Z (2003) Microchem J 75:1–14
Mascolo G, Lopez A, Detomaso A, Lovecchio G (2005) J Chromatogr A 1067:191–196
Farran A, Ruiz S (2004) J Chromatogr A 1024:267–274
Pace G, Berton A, Calligaro L, Mantovani A, Uguagllati P (1995) J Chromatogr A 706:345–351
Lu HT, Li HB, Chen F, Wong MH, Jiang Y (2004) Chromatographia 60:113–116
Gómez-Hens A, Aguilar-Caballos MP (2003) Trends Anal Chem 22:847–857
Nativelle C, Picard K, Valentin I, Lhuguenot JC, Chagnon MC (1999) Food Chem Toxicol 37:905–917
Staple AC, Peterson DR, Parkerton TH, Adams WJ (1997) Chemosphere 35:667–749
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Xu, XR., Li, HB. & Gu, JD. Elucidation of n-butyl benzyl phthalate biodegradation using high-performance liquid chromatography and gas chromatography–mass spectrometry. Anal Bioanal Chem 386, 370–375 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00216-006-0627-7
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00216-006-0627-7