Abstract
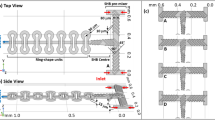
We have developed a three-dimensional passive micromixer based on new mixing principles, fluid twisting and flattening. This micromixer is constructed by repeating two microchannel segments, a “main channel” and a “flattened channel”, which are very different in size and are arranged perpendicularly. At the intersection of these segments the fluid inside the micromixer is twisted and then, in the flattened channel, the diffusion length is greatly reduced, achieving high mixing efficiency. Several types of micromixer were fabricated and the effect of microchannel geometry on mixing performance was evaluated. We also integrated this micromixer with a miniaturized DNA purification device, in which the concentration of the buffer solution could be rapidly changed, to perform DNA purification based on solid-phase extraction.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Burns MA, Johnson BN, Brahmasandra SN, Handique K, Webster JR, Krishnan M, Sammarco TS, Man PM, Jones D, Heldsinger D (1998) Science 282:484–487
Kricka LJ, Wilding P (2003) Anal Bioanal Chem 377:820–825
Bilitewski U, Genrich M, Kadow S, Mersal G (2003) Anal Bioanal Chem 377:556–569
Zhu X, Kim ES (1998) Sens Actuators A 66:355–360
Yang Z, Goto H, Matsumoto M, Maeda R (2000) Electrophoresis 21:116–119
Lu LH, Ryu KS, Liu C (2002) J Microelectromech Syst 11:462–469
Oddy MH, Santiago JG, Mikkelsen JC (2001) Anal Chem 73:5822–5832
Wu HY, Liu CH (2005) Sens Actuators A 118:107–115
Liu RH, Stremler MA, Sharp KV, Olsen MG, Santiago JG, Adrian RJ, Aref H, Beebe DJ (2000) J Microelectromech Syst 9:190–197
Stroock AD, Dertinger SKW, Ajdari A, Mezić I, Stone HA, Whitesides GM (2002) Science 295:647–651
Park SJ, Kim JK, Park J, Chung S, Chung C, Chang JK (2004) J Micromech Microeng 14:6–14
Schwesinger N, Frank T, Wurmus H (1996) J Micromech Microeng 6:99–102
Bessoth FG, deMello AJ, Manz A (1999) Anal Commun 36:213–215
Mae K, Maki T, Hasegawa I, Eto U, Mizutani Y, Honda N (2004) Chem Eng J 101:31–38
Ehrfeld W, Golbig K, Hessel V, Löwe H, Richter T (1999) Ind Eng Chem Res 38:1075–1082
Johnson TJ, Ross D, Locascio LE (2002) Anal Chem 74:45–51
Chung YC, Hsu YL, Jen CP, Lu MC, Lin YC (2004) Lab Chip 4:70–77
Jeon MK, Kim JH, Noh J, Kim SH, Park HG, Woo SI (2005) J Micromech Microeng 15:346–350
Kirner T, Albert J, Günther M, Mayer G, Reinhäckel K, Köhler JM (2004) Chem Eng J 101:65–74
Kim DJ, Oh HJ, Park TH, Choo JB, Lee SH (2005) Analyst 130:293–298
Nguyen NT, Wu Z (2005) J Micromech Microeng 15:R1–R16
Tian H, Huhmer AFR, Landers JP (2000) Anal Biochem 283:175–191
Lee NY, Yamada M, Seki M (2004) Anal Sci 20:483–487
Yamada M, Seki M (2004) Anal Chem 76:895–899
Gill P, Jeffreys AJ, Werrett DJ (1985) Nature 318:577–579
Budowle B, Chakraborty R, Giusti AM, Eisenberg AJ, Allen RC (1991) Am J Hum Genet 48:137–144
Roy R (1997) Forensic Sci Int 87:63–71
Hayes JM, Budowle B, Freund M (1995) J Forensic Sci 40:888–892
Weigl BH, Yager P (1999) Science 283:346–347
Acknowledgements
This research was supported in part by Grant-in-Aids for JSPS Fellows, Scientific Research (B) (No. 16310101), and Priority Areas (A) (No. 13025216) from the Ministry of Education, Science, Sports and Culture of Japan, and by the Research Association of Micro Chemical Process Technology, Japan.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lee, N.Y., Yamada, M. & Seki, M. Development of a passive micromixer based on repeated fluid twisting and flattening, and its application to DNA purification. Anal Bioanal Chem 383, 776–782 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00216-005-0073-y
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00216-005-0073-y