Abstract.
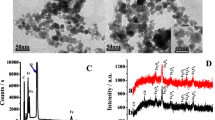
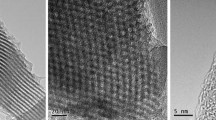
Nanostructured sodium montmorillonite was prepared via a colloidal chemical approach and deposited onto glassy carbon electrodes (GCE). Subsequently, hemoglobin was spontaneously adsorbed onto the clay membrane-modified electrode. The colloidal clay nanoparticles and the adsorbed protein were characterized by scanning electron microscopy (SEM) and atomic force microscopy (AFM). The electrochemical impedance behavior of the system was studied using a microlithographically fabricated interdigitated microsensor electrode (IME). The interaction of the clay nanoparticles with hemoglobin was investigated by UV-VIS spectroscopy and electrochemical methods. The heme protein adsorbed in this way displayed a well-defined electrode process and the electron transfer was confirmed to originate from its heme site. Furthermore, nitric oxide affects the hemoglobin electrochemistry.
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Electronic Publication
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lei, C., Wollenberger, U., Bistolas, N. et al. Electron transfer of hemoglobin at electrodes modified with colloidal clay nanoparticles. Anal Bioanal Chem 372, 235–239 (2002). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00216-001-1200-z
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00216-001-1200-z