Abstract.
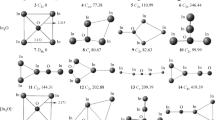
Ab initio molecular orbital theory and density functional theory have been used to study nine isomers of N7 ionic clusters with low spin at the HF/6-31G*, MP2/6-31G*, B3LYP/6-31G*, and B3LYP/6-311(+)G* levels of theory. All stationary points are examined with harmonic vibrational frequency analyses. Four N7 + isomers and five N7 − isomers are determined to be local minima or very close to the minima on their potential-energy hypersurfaces, respectively. For N7 + and N7 −, the energetically low lying isomers are open-chain structures (C 2 v and C 2 v or C2). The results are very similar to those of other known odd-number nitrogen ions, such as N5 +, N9 +, and N9 −, for which the open-chain structures are also the global minima. This research suggests that the N7 ionic clusters are likely to be stable and to be potential high-energy-density materials if they could be synthesized.
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Received: 16 July 2001 / Accepted: 8 October 2001 / Published online: 21 January 2002
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Liu, Y., Zhao, J. & Li, Q. Structures and stability of N7+ and N7− clusters. Theor Chem Acc 107, 140–146 (2002). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00214-001-0311-0
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00214-001-0311-0