Abstract.
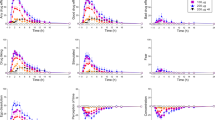
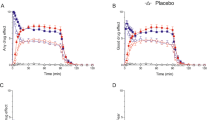
Rationale: Intravenous administration of the selective serotonin re-uptake inhibitor, citalopram (20 mg), is known to increase plasma prolactin (PRL) and cortisol in human subjects. This suggests that citalopram may be a useful tool to probe brain serotonin function. Objective: To find out whether lower doses of intravenous citalopram would be sufficient to increase plasma prolactin and cortisol. Methods: Eleven subjects were tested on three occasions in a double-blind, cross-over design receiving: (a) placebo, (b) citalopram 5 mg and (c) citalopram 10 mg infused intravenously over a 30-min period. A further six subjects received intravenous citalopram (10 mg) on two occasions receiving in addition the 5-HT2A/2C receptor antagonist, cyproheptadine (4 mg orally) or placebo, 6 h before each infusion in a double-blind, randomised, cross-over design. Plasma PRL and cortisol levels were measured before and for 150 min after the infusion. Results: Citalopram increased plasma PRL and cortisol in a dose-related manner. Cyproheptadine lowered baseline PRL and cortisol but did not attenuate the endocrine responses to citalopram. Citalopram infusions were well-tolerated. Conclusions: Low-dose citalopram has potential utility as a neuroendocrine challenge test. The endocrine responses to citalopram are probably not mediated predominantly by 5-HT2A/2C receptors.
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Electronic Publication
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Attenburrow, .MJ., Mitter, .P., Whale, .R. et al. Low-dose citalopram as a 5-HT neuroendocrine probe. Psychopharmacology 155, 323–326 (2001). https://doi.org/10.1007/s002130100729
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s002130100729