Abstract.
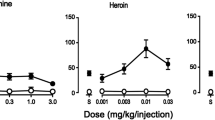
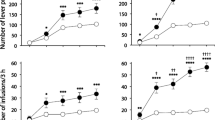
Rationale: Although common in humans, little is known about the reinforcing efficacy of smoked heroin in laboratory animals. Objectives: To evaluate the reinforcing efficacy of smoked heroin in non-opioid dependent, non-human primates. Methods: Self-administration and location-preference measures were obtained by having monkeys live in two chambers with heroin self-administration (0, 0.3, 0.6 mg/kg; eight dosings available per day) specific to one chamber and no commodity available in the other chamber. Operant responding reinforced by smoked heroin provided a self-administration measure of reinforcement, and the length of time monkeys spent in the heroin-associated chamber provided a location preference estimate of reinforcing efficacy. Results: Four of six monkeys acquired heroin self-administration: these monkeys completed six to eight smoking trials each day when either of the active heroin doses was available. Urine toxicology confirmed that monkeys were absorbing the smoked heroin. The number of completed smoking trials rapidly decreased under extinction conditions, indicating that smoked heroin was an efficacious reinforcer using the self-administration measure. Monkeys developed a location preference for the chamber where heroin was self-administered, indicating that smoked heroin was an efficacious reinforcer using the location-preference measure. Conclusions: Smoked heroin is an efficacious reinforcer in non-opioid dependent rhesus monkeys as measured using a self-administration procedure and estimated using a location-preference procedure.
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Electronic Publication
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Foltin, R.W., Evans, S.M. Location preference related to smoked heroin self-administration by rhesus monkeys. Psychopharmacology 155, 419–425 (2001). https://doi.org/10.1007/s002130100721
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s002130100721