Abstract
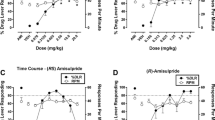
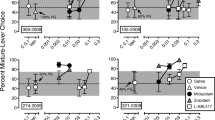
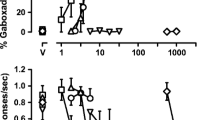
Rationale: Long-term use of benzodiazepine agonists can have adverse effects (e.g., development of dependence), thereby limiting their clinical usefulness. Objectives: The goal of the current study was to examine the discriminative stimulus effects of flumazenil in untreated and diazepam-treated monkeys to determine whether this type of procedure could be used to examine benzodiazepine dependence. Methods: Flumazenil (0.32 mg/kg s.c.) was established as a discriminative stimulus in eight monkeys receiving 5.6 mg/kg/day of diazepam (p.o.); four responded under a fixed ratio (FR)5 schedule of stimulus-shock termination (SST) and four responded under a FR5 schedule of food presentation. For comparison, 1.0 mg/kg flumazenil (s.c.) was established as a discriminative stimulus in four untreated monkeys responding under a FR5 schedule of SST. Results: Flumazenil dose-dependently increased responding on the flumazenil-appropriate lever in all monkeys. In diazepam-treated monkeys, Ro 15-4513, ethyl beta-carboline-3-carboxylate and bretazenil substituted for flumazenil with pentylenetetrazole substituting in some monkeys; other drugs failed to substitute for flumazenil. Acute administration of 10.0 mg/kg diazepam (s.c.) shifted the flumazenil dose–effect curve threefold to the right of the control dose–effect curve. Temporary suspension of diazepam treatment produced a time-related increase in flumazenil-lever responding that was reversed by diazepam. In untreated monkeys, midazolam substituted for flumazenil, with other drugs, including those with primary mechanisms of action at non-γ-aminobutyric acidA receptors, substituting in some monkeys. Ro 15-4513 did not substitute in any untreated monkey. Conclusions: The flumazenil discriminative stimulus appears to be pharmacologically selective in treated monkeys with only negative and low efficacy positive modulators substituting for flumazenil; in contrast, a variety of drugs substitute for flumazenil in untreated monkeys. This apparent difference in selectivity suggests that diazepam treatment modifies the flumazenil discriminative stimulus perhaps due to the development of dependence.
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Received: 30 November 1998 / Final version: 25 May 1999
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Gerak, L., France, C. Discriminative stimulus effects of flumazenil in untreated and in diazepam-treated rhesus monkeys. Psychopharmacology 146, 252–261 (1999). https://doi.org/10.1007/s002130051114
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s002130051114