Abstract
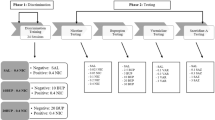
Rationale: Discrimination of a drug’s interoceptive stimulus effects often depends substantially on training and testing conditions. Objectives: We examined changes in nicotine discrimination behavior in humans as a function of lowering the training dose and of varying the discrimination testing procedure. Methods: Smokers and never-smokers (n=10 each) were initially trained to discriminate 20 µg/kg nicotine by nasal spray from placebo (0) and tested on generalization of discrimination responding across a range of doses from 0 to 20 µg/kg. Each subsequently learned to reliably discriminate progressively smaller doses of nicotine from placebo until his or her threshold dose for discrimination was identified (mean=2.7 µg/kg). A repeat testing of generalization responding across 0–20 µg/kg was then conducted, using placebo and the subject’s threshold dose as training doses. Generalization testing involved both two-choice and three-choice (novel response option) quantitative procedures. Results: A significant shift to the left was seen in nicotine-appropriate responding in the two-choice procedure when the nicotine training dose was lowered (i.e. from the first to the second test of generalization). In the three-choice procedure, however, there was no such leftward shift. Instead, in never-smokers, a flattening of nicotine-appropriate responding occurred with a lowering of the training dose, while novel-appropriate responding significantly increased. The subjective effects of ”head rush” and, in never-smokers only, ”jittery” also showed a shift to the left in their relationship with nicotine generalization dose when the training dose was lowered. Conclusions: These results confirm the importance of training and testing conditions on discrimination behavior and subjective drug responses within subjects and demonstrate the utility of the novel-response, three-choice procedure for assessing qualitatively different stimulus effects of novel drug doses.
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Received: 21 December 1998 / Final version: 11 March 1999
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Perkins, K., Fonte, C., Sanders, M. et al. Effects of training dose and two- versus three-choice testing procedure on nicotine discrimination responding in humans. Psychopharmacology 145, 418–425 (1999). https://doi.org/10.1007/s002130051076
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s002130051076