Abstract
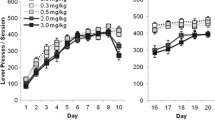
The purpose of this work was (1) to assess the ability of selected antipsychotic and comparison drugs to induce arrest of movement phenomena during operant responding and (2) to evaluate the capacity of muscarinic anitcholinergics to block such effects. The effects of haloperidol (0.02–0.12 mg/kg, IP, 45 min), raclopride (0.05–0.80 mg/kg, IP, 30 min) eticlopride (0.02–0.16 mg/kg, IP, 45 min), clozapine (1.0–8.0 mg/kg, IP, 60 min) and SCH 23390 (0.01–0.16 mg/kg, IP, 30 min) were administered to rats for 4 weeks in a between-groups dosing design. Operant responses in 15 min and the maximum duration of the rat’s muzzle entry into the reinforcement dipper well (the measure of arrest of movement that reflected microcatalepsy) were the quantitative measures of behavior. The D2 antagonists dose-relatedly decreased operant responding and increased maximum muzzle duration, effects that were significantly reversed by the anticholinergic scopolamine (0.1 mg/kg) or atropine (6.0 mg/kg). Although the atypical antipsychotic drug clozapine and the selective D1 antagonist SCH 23390 both significantly reduced operant responding, these drugs did not produce microcatalepsy. The results suggested that microcatalepsy expressed in the context of ongoing operant behavior may model low-dose extrapyramidal side effects.
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Received: 12 January 1998 / Final version: 27 March 1998
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Fowler, S., Liou, JR. Haloperidol, raclopride, and eticlopride induce microcatalepsy during operant performance in rats, but clozapine and SCH 23390 do not. Psychopharmacology 140, 81–90 (1998). https://doi.org/10.1007/s002130050742
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s002130050742