Abstract
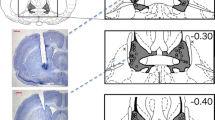
Unilateral infusion of the selective 5-HT1B agonist, CP-93,129 (3-(1,2,5,6-tetrahydropyrid-4-yl) pyrrolo[3,2-b]pyrid-5-one) into the parabrachial nucleus (PBN) of the pons reduced food consumption by rats. The hypophagia was dose-related (ED50 ≈ 1 nmol) and associated with fewer observations of feeding and more periods of inactivity. Water intake, grooming and exploratory activity were unaffected. CP-93,129 also decreased food intake when injected into the hypothalamic paraventricular nucleus, but this action was 50-fold less potent than administration into the PBN. Autoradiography demonstrated 5-HT1B sites in the PBN; this binding was displaced by CP-93,129. The results implicate parabrachial 5-HT1B receptors in mediating serotonergic enhancement of satiation.
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Received: 11 November 1997/Final version: 20 November 1997
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lee, M., Aloyo, V., Fluharty, S. et al. Infusion of the serotonin1B (5-HT1B) agonist CP-93,129 into the parabrachial nucleus potently and selectively reduces food intake in rats. Psychopharmacology 136, 304–307 (1998). https://doi.org/10.1007/s002130050570
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s002130050570