Abstract.
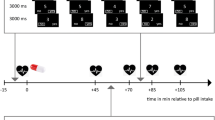
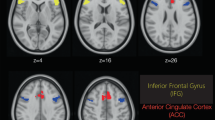
The amnesic properties of benzodiazepines result from an impairment in explicit (conscious) acquisition of new material. Rationale: Explicit encoding of new material has consistently resulted in an increase in regional cerebral blood flow (rCBF) in the left prefrontal cortex, as measured by positron emission tomography (PET). Objective: PET was used to determine whether an amnesic dose of midazolam (0.075 mg/kg) attenuated activation in this area during explicit memory encoding. Methods: A second condition (condition A) used a task to control for the automatic processing that occurs during explicit learning (condition E). Results: The subjects who received midazolam (n=7) recognised significantly fewer words than those who received placebo (n=8), but were not impaired with regard to automatic processing. rCBF was significantly increased in the left prefrontal cortex during explicit encoding of word lists in all subjects and in the temporal lobe and parieto-occipital regions during automatic processing. rCBF was significantly decreased in the prefrontal, superior temporal and parieto-occipital regions following midazolam. The midazolam-induced deactivation in the prefrontal cortex did not affect rCBF activations induced by the explicit memory condition (E–A). Conclusions: These results suggest that a specific interaction with prefrontal cortex activation does not underlie the amnesic effect of midazolam. However, it remains possible that a threshold level of prefrontal rCBF is necessary for encoding and that, after midazolam, this was not reached.
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Electronic Publication
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Bagary, M., Fluck, E., File, S. et al. Is benzodiazepine-induced amnesia due to deactivation of the left prefrontal cortex?. Psychopharmacology 150, 292–299 (2000). https://doi.org/10.1007/s002130000419
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s002130000419