Abstract
Rationale
(R)-Ketamine produced beneficial effects in a variety of models of inflammatory diseases, including low dose of bacterial lipopolysaccharide (LPS) (0.5–1.0 mg/kg)-induced endotoxemia. LPS-treated mice have been used as animal model of delirium.
Objectives
We investigated the effects of (R)-ketamine in neuroinflammation and cognitive impairment in rodents after administration of high dose of LPS.
Methods
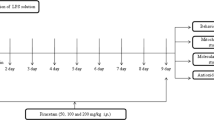
LPS (5 mg/kg) or saline was administered intraperitoneally (i.p.) to mice. (R)-Ketamine (10 mg/kg) was administrated i.p. 24 h before and/or 10 min after LPS injection.
Results
LPS (5.0 mg/kg) caused a remarkable splenomegaly and increased plasma levels of pro-inflammatory cytokines [i.e., interleukin (IL-6), IL-17A, and interferon (IFN)-γ]. There were positive correlations between spleen weight and plasma cytokines levels. Furthermore, LPS led to increased levels of pro-inflammatory cytokines in the prefrontal cortex (PFC) and hippocampus. Moreover, LPS impaired the natural and learned behaviors, as demonstrated by a decrease in the number of mice’s entries and duration in the novel arm in the Y maze test and an increase in the latency of mice to eat the food in the buried food test. Interestingly, the treatment with (R)-ketamine (twice 24 h before and 10 min after LPS injection) significantly attenuated LPS-induced splenomegaly, central and systemic inflammation, and cognitive impairment.
Conclusion
Our results highlighted the importance of combined prophylactic and therapeutic use of (R)-ketamine in the attenuation of LPS-induced systemic inflammation, neuroinflammation, and cognitive impairment in mice. It is likely that (R)-ketamine could be a prophylactic drug for delirium.



Similar content being viewed by others
Data Availability
The datasets analyzed during the current study are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
Abbreviations
- ELISA :
-
Enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay
- Iba-1 :
-
Ionized calcium-binding adapter molecule 1
- IFN :
-
Interferon
- IL :
-
Interleukin
- iNOS :
-
Inducible nitric oxide synthase
- LPS :
-
Lipopolysaccharide
- NMDAR :
-
N-Methyl-d-aspartate receptor
- PFC :
-
Prefrontal cortex
- TNF-α :
-
Tumor necrosis factor-α
References
Alqahtani F, Assiri MA, Mohany M, Imran I, Javaid S, Rasool MF, Shakeel W, Sivandzade F, Alanazi AZ, Al-Rejaie SS, Alshammari MA, Alasmari F, Alanazi MM, Alamri FF (2020) Coadministration of ketamine and perampanel improves behavioral function and reduces inflammation in acute traumatic brain injury mouse model. Biomed Res Int 2020:3193725. https://doi.org/10.1155/2020/3193725
Annane D, Sharshar T (2015) Cognitive decline after sepsis. Lancet Respir Med 3:61–69. https://doi.org/10.1016/S2213-2600(14)70246-2
Biesmans S, Meert TF, Bouwknecht JA, Acton PD, Davoodi N, De Haes P, Kuijlaars J, Langlois X, Matthews LJ, Ver DL, Hellings N, Nuydens R (2013) Systemic immune activation leads to neuroinflammation and sickness behavior in mice. Mediators Inflamm 2013:271359. https://doi.org/10.1155/2013/271359
Chang EI, Zarate MA, Arndt TJ, Richards EM, Rabaglino MB, Keller-Wood M, Wood CE (2018a) Ketamine reduces inflammation pathways in the hypothalamus and hippocampus following transient hypoxia in the late-gestation fetal sheep. Front Physiol 9:1858. https://doi.org/10.3389/fphys.2018.01858
Chang L, Toki H, Qu Y, Fujita Y, Mizuno-Yasuhira A, Yamaguchi JI, Chaki S, Hashimoto K (2018b) No sex-specific differences in the acute antidepressant actions of (R)-ketamine in an inflammation model. Int J Neuropsychopharmacol 21:932–937. https://doi.org/10.1093/ijnp/pyy053
Cunningham C, Maclullich AM (2013) At the extreme end of the psychoneuroimmunological spectrum: delirium as a maladaptive sickness behaviour response. Brain Behav Immun 28:1–13. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbi.2012.07.012
Cunningham C, Sanderson DJ (2008) Malaise in the water maze: untangling the effects of LPS and IL-1beta on learning and memory. Brain Behav Immun 22:1117–1127. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbi.2008.05.007
Curtin NM, Boyle NT, Mills KH, Connor TJ (2009) Psychological stress suppresses innate IFN-gamma production via glucocorticoid receptor activation: reversal by the anxiolytic chlordiazepoxide. Brain Behav Immun 23:535–547. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbi.2009.02.003
Deiner S, Silverstein JH (2009) Postoperative delirium and cognitive dysfunction. Bri J Anesth 103:i41-146. https://doi.org/10.1093/bja/aep291
De Kock M, Loix S, Lavand’Homme P (2013) Ketamine and peripheral inflammation. CNS Neurosci Ther 19:403–410. https://doi.org/10.1111/cns.12104
D’Esposito M, Postle BR (2015) The cognitive neuroscience of working memory. Annu Rev Psychol 66:115–142. https://doi.org/10.1146/annurev-psych-010814-015031
Draper A, Koch RM, van der Meer JW, Aj AM, Pickkers P, Husain M, van der Schaaf ME (2018) Effort but not reward sensitivity is altered by acute sickness induced by experimental endotoxemia in humans. Neuropsychopharmacology 43:1107–1118. https://doi.org/10.1038/npp.2017.231
Duning T, Ilting-Reuke K, Beckhuis M, Oswald D (2021) Postoperative delirium – treatment and prevention. Curr Opin Anaesthesiol 34:27–32. https://doi.org/10.1097/ACO.0000000000000939
Fu L, Zhu P, Qi S, Li C, Zhao K (2018) MicroRNA-92a antagonism attenuates lipopolysaccharide (LPS)-induced pulmonary inflammation and injury in mice through suppressing the PTEN/AKT/NF-kappaB signaling pathway. Biomed Pharmacother 107:703–711. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biopha.2018.08.040
Fujita Y, Hashimoto K (2020) Decreased bone mineral density in ovariectomized mice is ameliorated after subsequent repeated intermittent administration of (R)-ketamine, but not (S)-ketamine. Neuropsychopharmacol Rep 40:401–406. https://doi.org/10.1002/npr2.12132
Fujita A, Fujita Y, Pu Y, Chang L, Hashimoto K (2020) MPTP-induced dopaminergic neurotoxicity in mouse brain is attenuated after subsequent intranasal administration of (R)-ketamine: a role of TrkB signaling. Psychopharmacology 237:83–92. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00213-019-05346-5
Fujita Y, Hashimoto Y, Hashimoto H, Chang L, Hashimoto K (2021) Dextran sulfate sodium-induced inflammation and colitis in mice are ameliorated by (R)-ketamine, but not (S)-ketamine: a role of TrkB signaling. Eur J Pharmacol 897:173954. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ejphar.2021.173954
Griffin EW, Skelly DT, Murray CL, Cunningham C (2013) Cyclooxygenase-1-dependent prostaglandins mediate susceptibility to systemic inflammation-induced acute cognitive dysfunction. J Neurosci 33:15248–15258. https://doi.org/10.1523/JNEUROSCI.6361-11.2013
Hashimoto K (2015) Inflammatory biomarkers as differential predictors of antidepressant response. Int J Mol Sci 16:7796–7801. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms16047796
Hashimoto K (2019) Rapid-acting antidepressant ketamine, its metabolites and other candidates: a historical overview and future perspective. Psychiatry Clin Neurosci 73:613–627. https://doi.org/10.1111/pcn.12902
Hashimoto K (2020) Molecular mechanisms of the rapid-acting and long-lasting antidepressant actions of (R)-ketamine. Biochem Pharmacol 177:113935. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bcp.2020.113935
Hennessy E, Gormley S, Lopez-Rodriguez AB, Murray C, Murray C, Cunningham C (2017) Systemic TNF-alpha produces acute cognitive dysfunction and exaggerated sickness behavior when superimposed upon progressive neurodegeneration. Brain Behav Immun 59:233–244. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbi.2016.09.011
Hoogland I, Westhoff D, Engelen-Lee JY, Melief J, Valls SM, Houben-Weerts J, Huitinga I, van Westerloo DJ, van der Poll T, van Gool WA, van de Beek D (2018) Microglial activation after systemic stimulation with lipopolysaccharide and Escherichia coli. Front Cell Neurosci 12:110. https://doi.org/10.3389/fncel.2018.00110
Huang N, Hua D, Zhan G, Li S, Zhu B, Jiang R, Yang L, Bi J, Xu H, Hashimoto K, Luo A, Yang C (2019a) Role of Actinobacteria and Coriobacteriia in the antidepressant effects of ketamine in an inflammation model of depression. Pharmacol Biochem Behav 176:93–100. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pbb.2018.12.001
Huang N, Wang Y, Zhan G, Yu F, Li S, Hua D, Jiang R, Li S, Wu Y, Yang L, Zhu B, Hua F, Luo A, Yang C (2019b) Contribution of skeletal muscular glycine to rapid antidepressant effects of ketamine in an inflammation-induced mouse model of depression. Psychopharmacology 236:3513–3523. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00213-019-05319-8
Inouye SK, Westendorp RG, Saczynski JS (2014) Delirium in elderly people. Lancet 383:911–922. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0140-6736(13)60688-1
Jackson JC, Hopkins RO, Miller RR, Gordon SM, Wheeler AP, Ely EW (2009) Acute respiratory distress syndrome, sepsis, and cognitive decline: a review and case study. South Med J 102:1150–1157
Jaehne EJ, Corrigan F, Toben C, Jawahar MC, Baune BT (2015) The effect of the antipsychotic drug quetiapine and its metabolite norquetiapine on acute inflammation, memory and anhedonia. Pharmacol Biochem Behav 135:136–144. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pbb.2015.05.021
Karlsgodt KH, Sanz J, van Erp TG, Bearden CE, Nuechterlein KH, Cannon TD (2009) Re-evaluating dorsolateral prefrontal cortex activation during working memory in schizophrenia. Schizophr Res 108:143–150. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.schres.2008.12.025
Kealy J, Murray C, Griffin EW, Lopez-Rodriguez AB, Healy D, Tortorelli LS, Lowry JP, Watne LO, Cunningham C (2020) Acute inflammation alters brain energy metabolism in mice and humans: role in suppressed spontaneous activity, impaired cognition, and delirium. J Neurosci 40:5681–5696. https://doi.org/10.1523/JNEUROSCI.2876-19.2020
Leslie DL, Marcantonio ER, Zhang Y, Leo-Summers L, Inouye SK (2008) One-year health care costs associated with delirium in the elderly population. Arch Intern Med 168:27–32. https://doi.org/10.1001/archinternmed.2007.4
Lestage J, Verrier D, Palin K, Dantzer R (2002) The enzyme indoleamine 2,3-dioxygenase is induced in the mouse brain in response to peripheral administration of lipopolysaccharide and superantigen. Brain Behav Immun 16:596–601. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0889-1591(02)00014-4
Lisman J, Buzsaki G, Eichenbaum H, Nadel L, Ranganath C, Redish AD (2017) Viewpoints: how the hippocampus contributes to memory, navigation and cognition. Nat Neurosci 20:1434–1447. https://doi.org/10.1038/nn.4661
Lu Y, Ding X, Wu X, Huang S (2020) Ketamine inhibits LPS-mediated BV2 microglial inflammation via NMDA receptor blockage. Fundam Clin Pharmacol 34:229–237. https://doi.org/10.1111/fcp.12508
Makinson R, Lloyd K, Grissom N, Reyes TM (2019) Exposure to in utero inflammation increases locomotor activity, alters cognitive performance and drives vulnerability to cognitive performance deficits after acute immune activation. Brain Behav Immun 80:56–65. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbi.2019.02.022
Mastrodonato A, Cohensedgh O, LaGamma CT, McGowan JC, Hunsberger HC, Denny CA (2020) Prophylactic (R, S)-ketamine selectively protects against inflammatory stressors. Behav Brain Res 378:112238. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbr.2019.112238
McCusker J, Cole MG, Dendukuri N, Belzile E (2003) Does delirium increase hospital stay? J Am Geriatr Soc 51:1539–1546. https://doi.org/10.1046/j.1532-5415.2003.51509.x
Murray C, Sanderson DJ, Barkus C, Deacon RM, Rawlins JN, Bannerman DM, Cunningham C (2012) Systemic inflammation induces acute working memory deficits in the primed brain: relevance for delirium. Neurobiol Aging 33:603-616.e3. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neurobiolaging.2010.04.002
Oliveira-Lima OC, Carvalho-Tavares J, Rodrigues MF, Gomez MV, Oliveira A, Resende RR, Gomez RS, Vaz BG, Pinto M (2019) Lipid dynamics in LPS-induced neuroinflammation by DESI-MS imaging. Brain Behav Immun 79:186–194. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbi.2019.01.029
Pandharipande PP, Girard TD, Jackson JC, Morandi A, Thompson JL, Pun BT, Brummel NE, Hughes CG, Vasilevskis EE, Shintani AK, Moons KG, Geevarghese SK, Canonico A, Hopkins RO, Bernard GR, Dittus RS, Ely EW (2013) Long-term cognitive impairment after critical illness. N Engl J Med 369:1306–1316. https://doi.org/10.1056/NEJMoa1301372
Peng M, Zhang C, Dong Y, Zhang Y, Nakazawa H, Kaneki M, Zheng H, Shen Y, Marcantonio ER, Xie Z (2016) Battery of behavioral tests in mice to study postoperative delirium. Sci Rep 6:29874. https://doi.org/10.1038/srep29874
Peng Z, Gong X, Yang Y, Huang L, Zhang Q, Zhang P, Wan R, Zhang B (2017) Hepatoprotective effect of quercetin against LPS/d-GalN induced acute liver injury in mice by inhibiting the IKK/NF-kappaB and MAPK signal pathways. Int Immunopharmacol 52:281–289. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.intimp.2017.09.022
Pu Y, Yang J, Chang L, Qu Y, Wang S, Zhang K, Xiong Z, Zhang J, Tan Y, Wang X, Fujita Y, Ishima T, Wang D, Hwang SH, Hammock BD, Hashimoto K (2020) Maternal glyphosate exposure causes autism-like behaviors in offspring through increased expression of soluble epoxide hydrolase. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 117:11753–11759. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.1922287117
Savage JC, St-Pierre MK, Hui CW, Tremblay ME (2019) Microglial ultrastructure in the hippocampus of a lipopolysaccharide-induced sickness mouse model. Front Neurosci 13:1340. https://doi.org/10.3389/fnins.2019.01340
Schedlowski M, Engler H, Grigoleit JS (2014) Endotoxin-induced experimental systemic inflammation in humans: a model to disentangle immune-to-brain communication. Brain Behav Immun 35:1–8. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbi.2013.09.015
Schmidt R, Schmidt H, Curb JD, Masaki K, White LR, Launer LJ (2002) Early inflammation and dementia: a 25-year follow-up of the Honolulu-Asia Aging Study. Ann Neurol 52:168–174. https://doi.org/10.1002/ana.10265
Seemann S, Lupp A (2016) Administration of AMD3100 in endotoxemia is associated with pro-inflammatory, pro-oxidative, and pro-apoptotic effects in vivo. J Biomed Sci 23:68. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12929-016-0286-8
Skelly DT, Griffin EW, Murray CL, Harney S, O’Boyle C, Hennessy E, Dansereau MA, Nazmi A, Tortorelli L, Rawlins JN, Bannerman DM, Cunningham C (2019) Acute transient cognitive dysfunction and acute brain injury induced by systemic inflammation occur by dissociable IL-1-dependent mechanisms. Mol Psychiatry 24:1533–1548. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41380-018-0075-8
Sultan ZW, Jaeckel ER, Krause BM, Grady SM, Murphy CA, Sanders RD, Banks MI (2021) Electrophysiological signatures of acute systemic lipopolysaccharide-induced inflammation: potential implications for delirium science. Br J Anaesth 126:996–1008. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bja.2020.12.040
Sun J, Zhang S, Zhang X, Zhang X, Dong H, Qian Y (2015) IL-17A is implicated in lipopolysaccharide-induced neuroinflammation and cognitive impairment in aged rats via microglial activation. J Neuroinflammation 12:165. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12974-015-0394-5
Walker AK, Wing EE, Banks WA, Dantzer R (2019) Leucine competes with kynurenine for blood-to-brain transport and prevents lipopolysaccharide-induced depression-like behavior in mice. Mol Psychiatry 24:1523–1532. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41380-018-0076-7
Ward JL, Harting MT, Cox CJ, Mercer DW (2011) Effects of ketamine on endotoxin and traumatic brain injury induced cytokine production in the rat. J Trauma 70:1471–1479. https://doi.org/10.1097/TA.0b013e31821c38bd
Wei Y, Chang L, Hashimoto K (2020) A historical review of antidepressant effects of ketamine and its enantiomers. Pharmacol Biochem Behav 190:172870. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pbb.2020.172870
Wei Y, Chang L, Hashimoto K (2021) Molecular mechanisms underlying the antidepressant actions of arketamine: beyond the NMDA receptor. Mol Psychiatry in Press. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41380-021-01121-1
Whitlock EL, Vannucci A, Avidan MS (2011) Postoperative delirium. Mineva Anesthesiol 77:448–456
Xiong Z, Chang L, Qu Y, Pu Y, Wang S, Fujita Y, Ishima T, Chen J, Hashimoto K (2020) Neuronal brain injury after cerebral ischemic stroke is ameliorated after subsequent administration of (R)-ketamine, but not (S)-ketamine. Pharmacol Biochem Behav 191:172904. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pbb.2020.172904
Yamaguchi JI, Toki H, Qu Y, Yang C, Koike H, Hashimoto K, Mizuno-Yasuhira A, Chaki S (2018) (2R,6R)-Hydroxynorketamine is not essential for the antidepressant actions of (R)-ketamine in mice. Neuropsychopharmacology 43:1900–1907. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41386-018-0084-y
Yamanashi T, Malicoat JR, Steffen KT, Zarei K, Li R, Purnell BS, Najafi A, Saito K, Singh U, Toth BA, Lee S, Dailey ME, Cui H, Kaneko K, Cho HR, Iwata M, Buchanan GF, Shinozaki G (2021) Bispectral EEG (BSEEG) quantifying neuro-inflammation in mice induced by systemic inflammation: a potential mouse model of delirium. J Psychiatr Res 133:205–211. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jpsychires.2020.12.036
Yang JJ, Wang N, Yang C, Shi JY, Yu HY, Hashimoto K (2015) Serum interleukin-6 is a predictive biomarker for ketamine’s antidepressant effect in treatment-resistant patients with major depression. Biol Psychiatry 77:e19–e20. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biopsych.2014.06.021
Yang C, Qu Y, Abe M, Nozawa D, Chaki S, Hashimoto K (2017) (R)-Ketamine shows greater potency and longer lasting antidepressant effects than its metabolite (2R,6R)-hydroxynorketamine. Biol Psychiatry 82:e43–e44. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biopsych.2016.12.020
Yang C, Yang JJ, Luo A, Hashimoto K (2019) Molecular and cellular mechanisms underlying the antidepressant effects of ketamine enantiomers and its metabolites. Transl Psychiatry 9:280. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41398-019-0624-1
Yang L, Zhou R, Tong Y, Chen P, Shen Y, Miao S, Liu X (2020) Neuroprotection by dihydrotestosterone in LPS-induced neuroinflammation. Neurobiol Dis 140:104814. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.nbd.2020.104814
Zhang K, Hashimoto K (2019) Lack of opioid system in the antidepressant actions of ketamine. Biol Psychiatry 85:e25–e27. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biopsych.2018.11.006
Zhang JC, Li SX, Hashimoto K (2014a) R (−)-ketamine shows greater potency and longer lasting antidepressant effects than S (+)-ketamine. Pharmacol Biochem Behav 116:137–141. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pbb.2013.11.033
Zhang JC, Wu J, Fujita Y, Yao W, Ren Q, Yang C, Li SX, Shirayama Y, Hashimoto K (2014b) Antidepressant effects of TrkB ligands on depression-like behavior and dendritic changes in mice after inflammation. Int J Neuropsychopharmacol 18: pyu077. https://doi.org/10.1093/ijnp/pyu077.
Zhang JC, Yao W, Hashimoto K (2016) Brain-derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF)-TrkB signaling in inflammation-related depression and potential therapeutic targets. Curr Neuropharmacol 14:721–731. https://doi.org/10.2174/1570159x14666160119094646
Zhang JC, Yao W, Dong C, Yang C, Ren Q, Ma M, Hashimoto K (2017) Blockade of interleukin-6 receptor in the periphery promotes rapid and sustained antidepressant actions: a possible role of gut-microbiota-brain axis. Transl Psychiatry 7:e1138. https://doi.org/10.1038/tp.2017.112
Zhang K, Dong C, Fujita Y, Fujita A, Hashimoto K (2018) 5-Hydroxytryptamine-independent antidepressant actions of (R)-ketamine in a chronic social defeat stress model. Int J Neuropsychopharmacol 21:157–163. https://doi.org/10.1093/ijnp/pyx100
Zhang J, Qu Y, Chang L, Pu Y, Hashimoto K (2019) (R)-Ketamine rapidly ameliorates the decreased spine density in the medial prefrontal cortex and hippocampus of susceptible mice after chronic social defeat stress. Int J Neuropsychopharmacol 22:675–679. https://doi.org/10.1093/ijnp/pyz048
Zhang J, Ma L, Chang L, Pu Y, Qu Y, Hashimoto K (2020) A key role of the subdiaphragmatic vagus nerve in the depression-like phenotype and abnormal composition of gut microbiota in mice after lipopolysaccharide administration. Transl Psychiatry 10:186. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41398-020-00878-3
Funding
This study was supported by grant from Japan Agency for Medical Research and Development (AMED) (to K.H., JP20dm0107119).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
KH worked on experimental design. JCZ, LM, XYW, JJS, and YGQ performed the experiments. JCZ analyzed the data. KH and JCZ contributed to the writing of the manuscript. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval and consent to participate
All animal experiments were carried out in strict accordance with the recommendations in the Guide for the Care and Use of Laboratory Animals of the National Institutes of Health, USA, and approved by the Chiba University Institutional Animal Care and Use Committee (permission number: 2–308).
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Competing interests
Dr. Hashimoto is the inventor of filed patent applications on “The use of R-ketamine in the treatment of psychiatric diseases,” “(S)-norketamine and salt thereof as pharmaceutical,” “R-ketamine and derivative thereof as prophylactic or therapeutic agent for neurodegeneration disease or recognition function disorder,” “Preventive or therapeutic agent and pharmaceutical composition for inflammatory diseases or bone diseases,” and “R-ketamine and its derivatives as a preventive or therapeutic agent for a neurodevelopmental disorder” by the Chiba University. Dr. Hashimoto also declares that he has received research support and consultant from Dainippon Sumitomo, Otsuka, and Taisho. The other authors have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher's note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Jiancheng Zhang and Li Ma contributed equally to this work.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhang, J., Ma, L., Wan, X. et al. (R)-Ketamine attenuates LPS-induced endotoxin-derived delirium through inhibition of neuroinflammation. Psychopharmacology 238, 2743–2753 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00213-021-05889-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00213-021-05889-6