Abstract
Introduction
Acute cocoa flavanols (CF) intake has been suggested to modulate cognitive function and neurovascular coupling (NVC). Whether increased NVC is solely driven by improved vascular responsiveness or also by neuronal activity remains unknown. This study investigated the effects of acute CF intake on cognitive performance, NVC, and neuronal activity in healthy subjects in normoxia and hypoxia (4000 m simulated altitude; 12.7% O2).
Methods
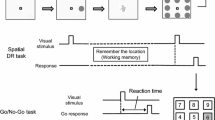
Twenty healthy subjects (age 23.2 ± 4.3 years) performed four trials. Participants performed a Stroop task and “cognition” battery 2 h after acute CF (530 mg CF, 100 mg epicatechin) or placebo intake, and 30 min after initial exposure to hypoxia or normoxia. Electroencephalogram and functional near-infrared spectroscopy were used to analyze hemodynamic changes and neuronal activity.
Results
CF enhanced NVC in the right prefrontal cortex during several tasks (risk decision making, visual tracking, complex scanning, spatial orientation), while neuronal activity was not affected. CF improved abstract thinking in normoxia, but not in hypoxia and did not improve other cognitive performances. Hypoxia decreased accuracy on the Stroop task, but performance on other cognitive tasks was preserved. NVC and neuronal activity during cognitive tasks were similar in hypoxia vs. normoxia, with the exception of increased β activity in the primary motor cortex during abstract thinking.
Conclusions
Acute CF intake improved NVC, but did not affect neuronal activity and cognitive performance in both normoxia and hypoxia. Most cognitive functions, as well as NVC and neuronal activity, did not decline by acute exposure to moderate hypoxia in healthy subjects.


Similar content being viewed by others
Reference list
Ando S, Hatamoto Y, Sudo M, Kiyonaga A, Tanaka H, Higaki Y (2013) The effects of exercise under hypoxia on cognitive function. PLoS One 8:e63630. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0063630
Andújar I, Recio MC, Giner RM, Ríos JL (2012) Cocoa polyphenols and their potential benefits for human health. Oxidative Med Cell Longev 2012:906252. https://doi.org/10.1155/2012/906252
Basner M, Savitt A, Moore TM, Port AM, McGuire S, Ecker AJ, Nasrini J, Mollicone DJ, Mott CM, McCann T, Dinges DF, Gur RC (2015) Development and validation of the cognition test battery for spaceflight. Aerosp Med Hum Perform 86:942–952. https://doi.org/10.3357/AMHP.4343.2015
Camfield DA, Scholey A, Pipingas A et al (2012) Steady state visually evoked potential (SSVEP) topography changes associated with cocoa flavanol consumption. Physiol Behav 105:948–957. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.physbeh.2011.11.013
Davranche K, Casini L, Arnal PJ, Rupp T, Perrey S, Verges S (2016) Cognitive functions and cerebral oxygenation changes during acute and prolonged hypoxic exposure. Physiol Behav 164:189–197. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.physbeh.2016.06.001
Decroix L, Tonoli C, Soares DD, Tagougui S, Heyman E, Meeusen R (2016) Acute cocoa flavanol improves cerebral oxygenation without enhancing executive function at rest or after exercise. Appl Physiol Nutr Metab 41:1225–1232. https://doi.org/10.1139/apnm-2016-0245
Del Rio D, Rodriguez-Mateos A, Spencer JPE et al (2013) Dietary (poly)phenolics in human health: structures, bioavailability, and evidence of protective effects against chronic diseases. Antioxid Redox Signal 18:1818–1892. https://doi.org/10.1089/ars.2012.4581
Duncan A, Meek JH, Clemence M, Elwell CE, Fallon P, Tyszczuk L, Cope M, Delpy DT (1996) Measurement of cranial optical path length as a function of age using phase resolved near infrared spectroscopy. Pediatr Res 39:889–894. https://doi.org/10.1203/00006450-199605000-00025
Field DT, Williams CM, Butler LT (2011) Consumption of cocoa flavanols results in an acute improvement in visual and cognitive functions. Physiol Behav 103:255–260. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.physbeh.2011.02.013
Fisher NDL, Sorond FA, Hollenberg NK (2006) Cocoa flavanols and brain perfusion. J Cardiovasc Pharmacol 47(Suppl 2):S210–S214. https://doi.org/10.1097/00005344-200606001-00017
Francis ST, Head K, Morris PG, Macdonald IA (2006) The effect of flavanol-rich cocoa on the fMRI response to a cognitive task in healthy young people. J Cardiovasc Pharmacol 47(Suppl 2):S215–S220. https://doi.org/10.1097/00005344-200606001-00018
Grassi D, Desideri G, Necozione S, di Giosia P, Barnabei R, Allegaert L, Bernaert H, Ferri C (2015) Cocoa consumption dose-dependently improves flow-mediated dilation and arterial stiffness decreasing blood pressure in healthy individuals. J Hypertens 33:294–303. https://doi.org/10.1097/HJH.0000000000000412
Grassi D, Ferri C, Desideri G (2016) Brain protection and cognitive function: cocoa flavonoids as nutraceuticals. Curr Pharm Des 22:145–151
Lamport DJ, Pal D, Moutsiana C, Field DT, Williams CM, Spencer JPE, Butler LT (2015) The effect of flavanol-rich cocoa on cerebral perfusion in healthy older adults during conscious resting state: a placebo controlled, crossover, acute trial. Psychopharmacology 232:3227–3234. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00213-015-3972-4
Lefferts WK, Hughes WE, White CN, Brutsaert TD, Heffernan KS (2016) Effect of acute nitrate supplementation on neurovascular coupling and cognitive performance in hypoxia. Appl Physiol Nutr Metab 41:133–141. https://doi.org/10.1139/apnm-2015-0400
MacLeod, MacDonald (2000) Interdimensional interference in the Stroop effect: uncovering the cognitive and neural anatomy of attention. Trends Cogn Sci 4:383–391
Macready AL, Kennedy OB, Ellis JA, Williams CM, Spencer JPE, Butler LT (2009) Flavonoids and cognitive function: a review of human randomized controlled trial studies and recommendations for future studies. Genes Nutr 4:227–242. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12263-009-0135-4
Manach C, Scalbert A, Morand C, et al (2004) Polyphenols: food sources and bioavailability 1,2
Massee L A., Ried K, Pase M, et al. (2015) The acute and sub-chronic effects of cocoa flavanols on mood, cognitive and cardiovascular health in young healthy adults: a randomized, controlled trial. Front Pharmacol 6. doi: https://doi.org/10.3389/fphar.2015.00093
Medvedev AV, Kainerstorfer JM, Borisov SV, VanMeter J (2011) Functional connectivity in the prefrontal cortex measured by near-infrared spectroscopy during ultrarapid object recognition. J Biomed Opt 16:016008. https://doi.org/10.1117/1.3533266
Mounier R, Brugniaux JV (2012) Counterpoint: hypobaric hypoxia does not induce different responses from normobaric hypoxia. J Appl Physiol 112:1784–1786. https://doi.org/10.1152/japplphysiol.00067.2012a
Murta T, Leite M, Carmichael DW, Figueiredo P, Lemieux L (2015) Electrophysiological correlates of the BOLD signal for EEG-informed fMRI. Hum Brain Mapp 36:391–414. https://doi.org/10.1002/hbm.22623
Nehlig A (2013) The neuroprotective effects of cocoa flavanol and its influence on cognitive performance. Br J Clin Pharmacol 75:716–727. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-2125.2012.04378.x
Neubauer JA, Sunderram J (2004) Oxygen-sensing neurons in the central nervous system. J Appl Physiol 96:367–374. https://doi.org/10.1152/japplphysiol.00831.2003
Ogoh S (2017) Relationship between cognitive function and regulation of cerebral blood flow. J Physiol Sci 67:345–351. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12576-017-0525-0
Okamoto M, Dan H, Sakamoto K, Takeo K, Shimizu K, Kohno S, Oda I, Isobe S, Suzuki T, Kohyama K, Dan I (2004) Three-dimensional probabilistic anatomical cranio-cerebral correlation via the international 10-20 system oriented for transcranial functional brain mapping. Neuroimage 21:99–111
Pascual-Marqui RD (2002) Standardized low-resolution brain electromagnetic tomography (sLORETA): technical details. Methods Find Exp Clin Pharmacol 24 Suppl D:5–12
Pase MP, Scholey AB, Pipingas A, Kras M, Nolidin K, Gibbs A, Wesnes K, Stough C (2013) Cocoa polyphenols enhance positive mood states but not cognitive performance: a randomized, placebo-controlled trial. J Psychopharmacol 27:451–458. https://doi.org/10.1177/0269881112473791
Perrey S (2008) Non-invasive NIR spectroscopy of human brain function during exercise. Methods 45:289–299. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ymeth.2008.04.005
Richard H, Benjamin S (1988) Cortical glucose metabolic rate correlates of abstract reasoning and attention studied with positron emission tomography. Intelligence 12:199–217
Rooks CR, Thom NJ, McCully KK, Dishman RK (2010) Effects of incremental exercise on cerebral oxygenation measured by near-infrared spectroscopy: a systematic review. Prog Neurobiol 92:134–150. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pneurobio.2010.06.002
Rupp T, Leti T, Jubeau M, Millet GY, Bricout VA, Levy P, Wuyam B, Perrey S, Verges S (2013) Tissue deoxygenation kinetics induced by prolonged hypoxic exposure in healthy humans at rest. J Biomed Opt 18:95002. https://doi.org/10.1117/1.JBO.18
Schneider S, Strüder HK (2009) Monitoring effects of acute hypoxia on brain cortical activity by using electromagnetic tomography. Behav Brain Res 197:476–480. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbr.2008.10.020
Scholey A (2017) Nutrients for neurocognition in health and disease: measures, methodologies and mechanisms. Proc Nutr Soc 77:1–11. https://doi.org/10.1017/S0029665117004025
Scholey A, Owen L (2013) Effects of chocolate on cognitive function and mood: a systematic review. Nutr Rev 71:665–681. https://doi.org/10.1111/nure.12065
Scholey AB, French SJ, Morris PJ, Kennedy DO, Milne AL, Haskell CF (2010) Consumption of cocoa flavanols results in acute improvements in mood and cognitive performance during sustained mental effort. J Psychopharmacol 24:1505–1514. https://doi.org/10.1177/0269881109106923
Schramm DD, Karim M, Schrader HR, Holt RR, Kirkpatrick NJ, Polagruto JA, Ensunsa JL, Schmitz HH, Keen CL (2003) Food effects on the absorption and pharmacokinetics of cocoa flavanols. Life Sci 73:857–869. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0024-3205(03)00373-4
Schroeter H, Heiss C, Balzer J, Kleinbongard P, Keen CL, Hollenberg NK, Sies H, Kwik-Uribe C, Schmitz HH, Kelm M (2006) (−)-Epicatechin mediates beneficial effects of flavanol-rich cocoa on vascular function in humans. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 103:1024–1029. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.0510168103
Shannon OM, Duckworth L, Barlow MJ, Deighton K, Matu J, Williams EL, Woods D, Xie L, Stephan BCM, Siervo M, O'Hara JP (2017) Effects of dietary nitrate supplementation on physiological responses, cognitive function, and exercise performance at moderate and very-high simulated altitude. Front Physiol 8:1–15. https://doi.org/10.3389/fphys.2017.00401
Sinn N, Howe PRC (2008) Mental health benefits of omega-3 fatty acids may be mediated by improvements in cerebral vascular function *. doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bihy.2008.02.003
Socci V, Tempesta D, Desideri G, de Gennaro L Ph. D., Ferrara M (2017) Enhancing human cognition with cocoa flavonoids. Front Nutr 4, 19. https://doi.org/10.3389/fnut.2017.00019
Spencer JPE (2008) Food for thought: the role of dietary flavonoids in enhancing human memory, learning and neuro-cognitive performance. Proc Nutr Soc 67:238–252. https://doi.org/10.1017/S0029665108007088
Spencer JPE (2009) Flavonoids and brain health: multiple effects underpinned by common mechanisms. Genes Nutr 4:243–250. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12263-009-0136-3
Steinbrink J, Villringer A, Kempf F, Haux D, Boden S, Obrig H (2006) Illuminating the BOLD signal: combined fMRI-fNIRS studies. Magn Reson Imaging 24:495–505. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mri.2005.12.034
Taylor L, Watkins SL, Marshall H, Dascombe BJ, Foster J (2016) The impact of different environmental conditions on cognitive function: a focused review. Front Physiol 6:1–12. https://doi.org/10.3389/fphys.2015.00372
Thompson T, Steffert T, Ros T, Leach J, Gruzelier J (2008) EEG applications for sport and performance. Methods 45:279–288. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ymeth.2008.07.006
Trans Cranial T (2012) Cortical functions. Trans Crainial Technol 1:66. https://doi.org/10.4324/9780203135549
Turner CE, Barker-Collo SL, Connell CJW, Gant N (2015) Acute hypoxic gas breathing severely impairs cognition and task learning in humans. Physiol Behav 142:104–110. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.physbeh.2015.02.006
Wilson MH, Newman S, Imray CH (2009) The cerebral effects of ascent to high altitudes. Lancet Neurol 8:175–191. https://doi.org/10.1016/S1474-4422(09)70014-6
Wong RHX, Raederstorff D, Howe PRC (2016) Acute resveratrol consumption improves neurovascular coupling capacity in adults with type 2 diabetes mellitus. Nutrients. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu8070425
Acknowledgements
We kindly thank Pascale Fanca Berthon from Naturex® to manufacture, produce, and provide us with the supplements.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
The study protocol was approved by the Ethical Committee of the Brussels University hospital and was carried out in accordance with the Declaration of Helsinki.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest. LD has a grant “Lotto Sport Science Chair.”
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Decroix, L., De Pauw, K., Van Cutsem, J. et al. Acute cocoa flavanols intake improves cerebral hemodynamics while maintaining brain activity and cognitive performance in moderate hypoxia. Psychopharmacology 235, 2597–2608 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00213-018-4952-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00213-018-4952-2