Abstract
Rationale
Affective biases seemingly play a crucial role for the onset and development of depression. Acute treatment with monoamine-based antidepressants positively influences emotional processing, and an early correction of biases likely results in repeated positive experiences that ultimately lead to improved mood.
Objectives
Using two conventional antidepressants, sertraline and duloxetine, we aimed to forward the characterization of a newly developed affective bias test (ABT) for rats. Further, we examined the effect of vortioxetine, a recently approved antidepressant, and the α2 adrenoceptor antagonist idazoxan on affective biases.
Methods
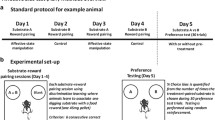
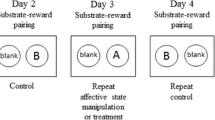
Sprague Dawley rats were tested in an affective bias test using a fully balanced within-subject study design. Rats learned to associate two different digging substrates with a reward during six reward-pairing days. The absolute value of the rewards was identical, but the affective state at the time of learning induces a positive or negative bias towards the treatment-paired digging substrate at recall. The choice bias between the two digging substrates at recall represents the affective bias. Sertraline (1, 3 and 10 mg/kg), duloxetine (1, 3 and 10 mg/kg), vortioxetine (1, 3 and 10 mg/kg) and idazoxan (3 and 10 mg/kg) were tested in the ABT.
Results and conclusions
All four drugs, regardless of their mechanism of action, induced a positive affective bias in the ABT, although the overall effect of treatment was not statistically significant for sertraline and duloxetine. The largest effects were induced by vortioxetine and idazoxan, both of which caused significant positive biases at all tested doses.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Akhondzadeh S, Mohammadi N, Noroozian M, Karamghadiri N, Ghoreishi A, Jamshidi AH, Forghani S (2009) Added ondansetron for stable schizophrenia: a double blind, placebo controlled trial. Schizophr Res 107:206–212
Alvarez E, Perez V, Dragheim M, Loft H, Artigas F (2012) A double-blind, randomized, placebo-controlled, active reference study of Lu AA21004 in patients with major depressive disorder. Int J Neuropsychopharmacol 15:589–600
Arnone D, Horder J, Cowen P, Harmer C (2009) Early effects of mirtazapine on emotional processing. Psychopharmacology 203:685–691
Beck AT (1967) Depression: clinical, experimental, and theoretical aspects. Harper & Row, New York
Bolden-Watson C, Richelson E (1993) Blockade by newly-developed antidepressants of biogenic amine uptake into rat brain synaptosomes. Life Sci 52:1023–1029
Boulenger JP, Loft H, Florea I (2012) A randomized clinical study of Lu AA21004 in the prevention of relapse in patients with major depressive disorder. J Psychopharmacol 26:1408–1416
Cassano GB, Puca F, Scapicchio PL, Trabucchi M (2002) Paroxetine and fluoxetine effects on mood and cognitive functions in depressed nondemented elderly patients. The Journal of Clinical Psychiatry 63:396
Chan SW, Goodwin GM, Harmer CJ (2007) Highly neurotic never-depressed students have negative biases in information processing. Psychol Med 37:1281–1291
Cipriani A, Koesters M, Furukawa TA, Nosé M, Purgato M, Omori IM, Trespidi C, Barbui C (2012) Duloxetine versus other anti-depressive agents for depression. Cochrane Database Syst Rev 10:CD006533
Cottingham C, Wang Q (2012) Alpha2 adrenergic receptor dysregulation in depressive disorders: implications for the neurobiology of depression and antidepressant therapy. Neurosci Biobehav Rev 36:2214–2225
Culang-Reinlieb ME, Sneed JR, Keilp JG, Roose SP (2012) Change in cognitive functioning in depressed older adults following treatment with sertraline or nortriptyline. Int J Geriatr Psychiatry 27:777–784
Disner SG, Beevers CG, Haigh EA, Beck AT (2011) Neural mechanisms of the cognitive model of depression. Nat Rev Neurosci 12:467–477
Engleman EA, Perry KW, Mayle DA, Wong DT (1995) Simultaneous increases of extracellular monoamines in microdialysates from hypothalamus of conscious rats by duloxetine, a dual serotonin and norepinephrine uptake inhibitor. Neuropsychopharmacology 12:287–295
Ferguson JM, Wesnes KA, Schwartz GE (2003) Reboxetine versus paroxetine versus placebo: effects on cognitive functioning in depressed patients. Int Clin Psychopharmacol 18
Fontana DJ, Daniels SE, Henderson C, Eglen RM, Wong EH (1995) Ondansetron improves cognitive performance in the Morris water maze spatial navigation task. Psychopharmacology 120:409–417
Gallassi R, Di Sarro R, Morreale A, Amore M (2006) Memory impairment in patients with late-onset major depression: the effect of antidepressant therapy. J Affect Disord 91:243–250
Gobert A, Rivet JM, Cistarelli L, Melon C, Millan MJ (1997) Alpha2-adrenergic receptor blockade markedly potentiates duloxetine- and fluoxetine-induced increases in noradrenaline, dopamine, and serotonin levels in the frontal cortex of freely moving rats. J Neurochem 69:2616–2619
Gotlib IH, Krasnoperova E, Yue DN, Joormann J (2004) Attentional biases for negative interpersonal stimuli in clinical depression. J Abnorm Psychol 113:121–135
Greer TL, Sunderajan P, Grannemann BD, Kurian BT, Trivedi MH (2014) Does duloxetine improve cognitive function independently of its antidepressant effect in patients with major depressive disorder and subjective reports of cognitive dysfunction? Depress Res Treat 2014:627863
Grossman E, Rea RF, Hoffman A, Goldstein DS (1991) Yohimbine increases sympathetic nerve activity and norepinephrine spillover in normal volunteers. Am J Phys 260:R142–R147
Grossman F, Potter WZ, Brown EA, Maislin G (1999) A double-blind study comparing idazoxan and bupropion in bipolar depressed patients. J Affect Disord 56:237–243
Guilloux JP, Mendez-David I, Pehrson A, Guiard BP, Repérant C, Orvoën S, Gardier AM, Hen R, Ebert B, Miller S, Sanchez C, David DJ (2013) Antidepressant and anxiolytic potential of the multimodal antidepressant vortioxetine (Lu AA21004) assessed by behavioural and neurogenesis outcomes in mice. Neuropharmacology 73:147–159
Gur RC, Erwin RJ, Gur RE, Zwil AS, Heimberg C, Kraemer HC (1992) Facial emotion discrimination: II. Behavioral findings in depression. Psychiatry Res 42:241–251
Halbreich, Montgomery (2005) Pharmacotherapy for mood, anxiety, and cognitive disorders. American Psychiatric Press, Inc.
Hales CA, Stuart SA, Anderson MH, Robinson ESJ (2014) Modelling cognitive affective biases in major depressive disorder using rodents. Br J Pharmacol 171:4524–4538
Harmer CJ (2013) Emotional processing and antidepressant action. Curr Top Behav Neurosci 14:209–222
Harmer CJ, Bhagwagar Z, Perrett DI, Vollm BA, Cowen PJ, Goodwin GM (2003a) Acute SSRI administration affects the processing of social cues in healthy volunteers. Neuropsychopharmacology 28:148–152
Harmer CJ, Hill SA, Taylor MJ, Cowen PJ, Goodwin GM (2003b) Toward a neuropsychological theory of antidepressant drug action: increase in positive emotional bias after potentiation of norepinephrine activity. Am J Psychiatry 160:990–992
Harmer CJ, Shelley NC, Cowen PJ, Goodwin GM (2004) Increased positive versus negative affective perception and memory in healthy volunteers following selective serotonin and norepinephrine reuptake inhibition. AJP 161:1256–1263
Harmer CJ, Heinzen J, O'Sullivan U, Ayres RA, Cowen PJ (2008) Dissociable effects of acute antidepressant drug administration on subjective and emotional processing measures in healthy volunteers. Psychopharmacology 199:495–502
Harmer CJ, Goodwin GM, Cowen PJ (2009a) Why do antidepressants take so long to work? A cognitive neuropsychological model of antidepressant drug action. Br J Psychiatry 195:102–108
Harmer CJ, O'Sullivan U, Favaron E, Massey-Chase R, Ayres R, Reinecke A, Goodwin GM, Cowen PJ (2009b) Effect of acute antidepressant administration on negative affective bias in depressed patients. AJP 166:1178–1184
Herrera-Guzmán I, Gudayol-Ferré E, Herrera-Guzmán D, Guárdia-Olmos J, Hinojosa-Calvo E, Herrera-Abarca JE (2009) Effects of selective serotonin reuptake and dual serotonergic-noradrenergic reuptake treatments on memory and mental processing speed in patients with major depressive disorder. J Psychiatr Res 43:855
Horiguchi M, Huang M, Meltzer HY (2011) The role of 5-hydroxytryptamine 7 receptors in the phencyclidine-induced novel object recognition deficit in rats. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 338:605–614
Horisawa T, Ishibashi T, Nishikawa H, Enomoto T, Toma S, Ishiyama T, Taiji M (2011) The effects of selective antagonists of serotonin 5-HT7 and 5-HT1A receptors on MK-801-induced impairment of learning and memory in the passive avoidance and Morris water maze tests in rats: mechanistic implications for the beneficial effects of the novel atypical antipsychotic lurasidone. Behav Brain Res 220:83–90
Katona C, Hansen T, Olsen CK (2012) A randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled, duloxetine-referenced, fixed-dose study comparing the efficacy and safety of Lu AA21004 in elderly patients with major depressive disorder. Int Clin Psychopharmacol 27:215–223
Lewis CJ, Havler ME, Humphrey MJ, Lloyd-Jones JG, Mccleavy MA, Muir NC, Waltham K (1988) The pharmacokinetics and metabolism of idazoxan in the rat. Xenobiotica 18:519
Llorca PM, Lanon C, Brignone M, Rive B, Salah S, Ereshefsky L, Francois C (2014) Relative efficacy and tolerability of vortioxetine versus selected antidepressants by indirect comparisons of similar clinical studies. Current Medical Research & Opinion 30(12):2589–2606
Mahableshwarkar AR, Zajecka J, Jacobson W, Chen Y, Keefe RS (2015) A randomized, placebo-controlled, active-reference, double-blind, flexible-dose study of the efficacy of vortioxetine on cognitive function in major depressive disorder. Neuropsychopharmacology 40:2025–2037
Meneses A (2004) Effects of the 5-HT7 receptor antagonists SB-269970 and DR 4004 in autoshaping Pavlovian/instrumental learning task. Behav Brain Res 155:275–282
Millan MJ, Lejeune F, Gobert A (2000) Reciprocal autoreceptor and heteroreceptor control of serotonergic, dopaminergic and noradrenergic transmission in the frontal cortex: relevance to the actions of antidepressant agents. J Psychopharmacol 14:114–138
Mørk A, Pehrson A, Brennum LT, Nielsen SM, Zhong H, Lassen AB, Miller S, Westrich L, Boyle NJ, Sanchez C, Fischer CW, Liebenberg N, Wegener G, Bundgaard C, Hogg S, Bang-Andersen B, Stensbøl TB (2012) Pharmacological effects of Lu AA21004: a novel multimodal compound for the treatment of major depressive disorder. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 340:666–675
Mørk A, Montezinho LP, Miller S, Trippodi-Murphy C, Plath N, Li Y, Gulinello M, Sanchez C (2013) Vortioxetine (Lu AA21004), a novel multimodal antidepressant, enhances memory in rats. Pharmacol Biochem Behav 105:41–50
Murai N, Fushiki H, Honda S, Murakami Y, Iwashita A, Irie M, Tamura S, Nagakura Y, Aoki T (2015) Relationship between serotonin transporter occupancies and analgesic effects of AS1069562, the (+)-isomer of indeloxazine, and duloxetine in reserpine-induced myalgia rats. Neuroscience 289:262–269
Murphy SE, Norbury R, O'Sullivan U, Cowen PJ, Harmer CJ (2009) Effect of a single dose of citalopram on amygdala response to emotional faces. Br J Psychiatry 194:535–540
Nebes RD, Pollock BG, Houck PR, Butters MA, Mulsant BH, Zmuda MD, Reynolds CF III (2003) Persistence of cognitive impairment in geriatric patients following antidepressant treatment: a randomized, double-blind clinical trial with nortriptyline and paroxetine. J Psychiatr Res 37:99–108
Osman OT, Rudorfer MV, Potter WZ (1989) Idazoxan: a selective alpha-2-antagonist and effective sustained antidepressant in two bipolar depressed patients. Arch Gen Psychiatry 46:958–959
Raskin J, Wiltse CG, Siegal A, Sheikh J, Xu J, Dinkel JJ, Rotz BT, Mohs RC (2007) Efficacy of duloxetine on cognition, depression, and pain in elderly patients with major depressive disorder: an 8-week, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial. Am J Psychiatry 164:900–909
Shestyuk AY, Deldin PJ, Brand JE, Deveney CM (2005) Reduced sustained brain activity during processing of positive emotional stimuli in major depression. Biol Psychiatry 57:1089–1096
Sloan DM, Bradley MM, Dimoulas E, Lang PJ (2002) Looking at facial expressions: dysphoria and facial EMG. Biol Psychol 60:79–90
Stuart SA, Butler P, Munafo MR, Nutt DJ, Robinson ES (2013) A translational rodent assay of affective biases in depression and antidepressant therapy. Neuropsychopharmacology 38:1625–1635
Stuart SA, Butler P, Munafo MR, Nutt DJ, Robinson ES (2015) Distinct neuropsychological mechanisms may explain delayed- versus rapid-onset antidepressant efficacy. Neuropsychopharmacology 40:2165–2174
Tremaine LM, Welch WM, Ronfeld RA (1989) Metabolism and disposition of the 5-hydroxytryptamine uptake blocker sertraline in the rat and dog. Drug Metab Dispos 17:542–550
van Veldhuizen MJA, Feenstra MGP, Heinsbroek RPW, Boer GJ (1993) In vivo microdialysis of noradrenaline overflow: effects of alpha-adrenoceptor agonists and antagonists measured by cumulative concentration-response curves. Br J Pharmacol 109:655–660
Walter DS, Flockhart IR, Haynes MJ, Howlett DR, Lane AC, Burton R, Johnson J, Dettmar PW (1984) Effects of idazoxan on catecholamine systems in rat brain. Biochem Pharmacol 33:2553–2557
Weikop P, Kehr J, Scheel-Kruger J (2004) The role of alpha1- and alpha2-adrenoreceptors on venlafaxine-induced elevation of extracellular serotonin, noradrenaline and dopamine levels in the rat prefrontal cortex and hippocampus. J Psychopharmacol 18:395–403
Acknowledgments
The study was funded by GluTarget and Department of Drug Design and Pharmacology, University of Copenhagen. Vortioxetine was kindly donated by H. Lundbeck A/S.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
Emma SJ. Robinson has received research funding from MRC, BBSRC and Wellcome Trust and industrial collaboration grant funding from Eli Lilly, Pfizer and MSD. The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Refsgaard, L.K., Haubro, K., Pickering, D.S. et al. Effects of sertraline, duloxetine, vortioxetine, and idazoxan in the rat affective bias test. Psychopharmacology 233, 3763–3770 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00213-016-4407-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00213-016-4407-6