Abstract
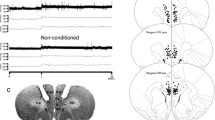
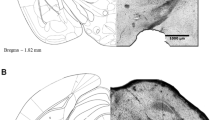
The prelimbic (PL) medial prefrontal cortex is a brain region highly involved in the control of emotional responses, being modulated by several neurotransmitter systems, including the cholinergic and endocannabinoid. Activation of muscarinic type 1 (M1) receptors in the brain induces retrograde suppression of inhibition through the induction of endocannabinoid release, which, in turn, activates cannabinoid type 1 (CB1) receptors. No study so far, however, has been conducted to investigate if the cholinergic and endocannabinoid systems interact in the PL to modulate anxiety-related behaviors. Thus, the present work aimed at verifying if intra-PL administration of neostigmine, an acetylcholinesterase inhibitor, would produce changes in anxiety-like behavior and if these effects are mediated by M1 and CB1 receptor activation. Independent groups of animals received bilateral injections of vehicle, the M1 receptor antagonist pirenzepine (0.06, 0.6, and 6 nmol), the CB1 receptor antagonist AM251 (0.1 nmol), or the fatty acid amide hydrolase (FAAH) enzyme inhibitor URB597 (1, 3, and 10 pmol), followed by vehicle or neostigmine (0.01, 0.1, and 1 nmol), and were submitted to the elevated plus-maze (EPM) test. Neostigmine (1 nmol) decreased open arm exploration of the maze. This anxiogenic-like effect was reproduced in another anxiety-related animal model, the light–dark box. Previous injection of pirenzepine or AM251 abolished this response in the EPM, whereas URB597 had no effect. These results suggest that CB1 and M1 receptors interact in the PL to control anxiety-like behaviors.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Arnal F, Coté LJ, Ginsburg S, Lawrence GD, Naini A, Sano M (1990) Studies on new, centrally active and reversible acetylcholinesterase inhibitors. Neurochem Res 15(6):587–591
Bonner TI, Buckley NJ, Young AC, Brann MR (1987) Identification of a family of muscarinic acetylcholine receptor genes. Science 237(4814):527–532
Degroot A, Treit D (2002) Dorsal and ventral hippocampal cholinergic systems modulate anxiety in the plus-maze and shock-probe tests. Brain Res 949(1–2):60–70
Di Marzo V, De Petrocellis L (2010) Endocannabinoids as regulators of transient receptor potential (TRP) channels: a further opportunity to develop new endocannabinoid-based therapeutic drugs. Curr Med Chem 17(14):1430–1449
Duman RS (2014) Pathophysiology of depression and innovative treatments: remodeling glutamatergic synaptic connections. Dialogues Clin Neurosci 16(1):11–27
Fedoce AG, Ferreira-Junior NC, Reis DG, Corrêa FM, Resstel LB (2016) M3 muscarinic receptor in the ventral medial prefrontal cortex modulating the expression of contextual fear conditioning in rats. Psychopharmacology (Berl) 233(2):267–80
Fogaça MV, Aguiar DC, Moreira FA, Guimarães FS (2012a) The endocannabinoid and endovanilloid systems interact in the rat prelimbic medial prefrontal cortex to control anxiety-like behavior. Neuropharmacology 63(2):202–210
Fogaça MV, Lisboa SF, Aguiar DC, Moreira FA, Gomes FV, Casarotto PC, Guimarães FS (2012b) Fine-tuning of defensive behaviors in the dorsal periaqueductal gray by atypical neurotransmitters. Braz J Med Biol Res 45(4):357–365
Fogaça MV, Reis FM, Campos AC, Guimarães FS (2014) Effects of intra-prelimbic prefrontal cortex injection of cannabidiol on anxiety-like behavior: involvement of 5HT1A receptors and previous stressful experience. Eur Neuropsychopharmacol 24:410–419
Fukudome Y, Ohno-Shosaku T, Matsui M, Omori Y, Fukaya M, Tsubokawa H, Taketo MM, Watanabe M, Manabe T, Kano M (2004) Two distinct classes of muscarinic action on hippocampal inhibitory synapses: M2-mediated direct suppression and M1/M3-mediated indirect suppression through endocannabinoid signalling. Eur J Neurosci 19(10):2682–2692
Furey ML, Drevets WC (2006) Antidepressant efficacy of the antimuscarinic drug scopolamine: a randomized, placebo-controlled clinical trial. Arch Gen Psychiatry 63(10):1121–9
Griebel G, Holmes A (2013) 50 years of hurdles and hope in anxiolytic drug discovery. Nat Rev 12:667–687
Heidbreder CA, Groenewegen HJ (2003) The medial prefrontal cortex in the rat: evidence for a dorso-ventral distinction based upon functional and anatomical characteristics. Neurosci Biobehav Rev 27:555–579
Janowsky DS, el-Yousef MK, Davis JM, Sekerke HJ (1972) A cholinergic-adrenergic hypothesis of mania and depression. Lancet 2(7778):632–635
Jiang L, López-Hernández GY, Lederman J, Talmage DA, Role LW (2014a) Optogenetic studies of nicotinic contributions to cholinergic signaling in the central nervous system. Rev Neurosci 25(6):755–771
Jiang S, Li Y, Zhang C, Zhao Y, Bu G, Xu H, Zhang YW (2014b) M1 muscarinic acetylcholine receptor in Alzheimer’s disease. Neurosci Bull 30(2):295–307
Kennedy B, Janowsky DS, Risch SC, Ziegler MG (1984) Central cholinergic stimulation causes adrenal epinephrine release. J Clin Invest 74(3):972–975
Kim J, Isokawa M, Ledent C, Alger BE (2002) Activation of muscarinic acetylcholine receptors enhances the release of endogenous cannabinoids in the hippocampus. J Neurosci 22(23):10182–10191
Lau BK, Vaughan CW (2008) Muscarinic modulation of synaptic transmission via endocannabinoid signalling in the rat midbrain periaqueductal gray. Mol Pharmacol 74(5):1392–1398
Lee SW, Woo CW, Kim JG (1994) Selectivity of oxomemazine for the M1 muscarinic receptors. Arch Pharm Res 17(6):443–451
Lisboa SF, Stecchini MF, Corrêa FM, Guimarães FS, Resstel LB (2010) Different role of the ventral medial prefrontal cortex on modulation of innate and associative learned fear. Neuroscience 171(3):760–768
Mailleux P, Vanderhaeghen JJ (1992) Distribution of neuronal cannabinoid receptor in the adult rat brain: a comparative receptor binding radioautography and in situ hybridization histochemistry. Neuroscience 48(3):655–668
Marsicano G, Lutz B (1999) Expression of the cannabinoid receptor CB1 in distinct neuronal subpopulations in the adult mouse forebrain. Eur J Neurosci 11(12):4213–4225
McLaughlin RJ, Hill MN, Gorzalka BB (2014) A critical role for prefrontocortical endocannabinoid signaling in the regulation of stress and emotional behavior. Neurosci Biobehav Rev 42:116–131
Millan MJ (2003) The neurobiology and control of anxious states. Prog Neurobiol 70:83–244
Mineur YS, Obayemi A, Wigestrand MB, Fote GM, Calarco CA, Li AM, Picciotto MR (2013) Cholinergic signaling in the hippocampus regulates social stress resilience and anxiety- and depression-like behavior. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 110(9):3573–3578
Musella A, De Chiara V, Rossi S, Prosperetti C, Bernardi G, Maccarrone M, Centonze D (2009) TRPV1 channels facilitate glutamate transmission in the striatum. Mol Cell Neurosci 40:89–97
Musella A, De Chiara V, Rossi S, Cavasinni F, Castelli M, Cantarella C, Mataluni G, Bernardi G, Centonze D (2010) Transient receptor potential vanilloid 1 channels control acetylcholine/2-arachidonoylglicerol coupling in the striatum. Neuroscience 167(3):864–871
Narushima M, Uchigashima M, Fukaya M, Matsui M, Manabe T, Hashimoto K, Watanabe M, Kano M (2007) Tonic enhancement of endocannabinoid-mediated retrograde suppression of inhibition by cholinergic interneuron activity in the striatum. J Neurosci 27(3):496–506
Ong WY, Mackie K (1999) A light and electron microscopic study of the CB1 cannabinoid receptor in primate brain. Neuroscience 92(4):1177–1191
Paxinos G, Watson C (2005) The rat brain in stereotaxic coordinates. Academic, New York
Pellow S, Chopin P, File SE, Briley M (1985) Validation of open:closed arm entries in an elevated plus-maze as a measure of anxiety in the rat. J Neurosci Methods 14(3):149–167
Pertwee RG (2012) Targeting the endocannabinoid system with cannabinoid receptor agonists: pharmacological strategies and therapeutic possibilities. Philos Trans R Soc Lond B Biol Sci 367(1607):3353–3363
Rey AA, Purrio M, Viveros MP, Lutz B (2012) Biphasic effects of cannabinoids in anxiety responses: CB1 and GABA(B) receptors in the balance of GABAergic and glutamatergic neurotransmission. Neuropsychopharmacology 37(12):2624–2634
Risch SC, Cohen RM, Janowsky DS, Kalin NH, Sitaram N, Gillin JC, Murphy DL (1981) Physostigmine induction of depressive symptomatology in normal human subjects. Psychiatry Res 4(1):89–94
Saricicek A, Esterlis I, Maloney KH, Mineur YS, Ruf BM, Muralidharan A, Chen JI, Cosgrove KP, Kerestes R, Ghose S, Tamminga CA, Pittman B, Bois F, Tamagnan G, Seibyl J, Picciotto MR, Staley JK, Bhagwagar Z (2012) Persistent β2*-nicotinic acetylcholinergic receptor dysfunction in major depressive disorder. Am J Psychiatry 169(8):851–859
Sienkiewicz-Jarosz H, Maciejak P, Bidziński A, Szyndler J, Siemiatkowski M, Członkowska A, Lehner M, Płaźnik A (2003) Exploratory activity and a conditioned fear response: correlation with cortical and subcortical binding of the alpha4beta2 nicotinic receptor agonist [3H]-epibatidine. Pol J Pharmacol 55(1):17–23
Sotres-Bayon F, Quirk GJ (2010) Prefrontal control of fear: more than just extinction. Curr Opin Neurobiol 20:231–235
Szabo B, Schlicker E (2005) Effects of cannabinoids on neurotransmission. Handb Exp Pharmacol 168:327–365
Uchigashima M, Narushima M, Fukaya M, Katona I, Kano M, Watanabe M (2007) Subcellular arrangement of molecules for 2-arachidonoyl-glycerol-mediated retrograde signaling and its physiological contribution to synaptic modulation in the striatum. J Neurosci 27(14):3663–3676
Vertes RP (2004) Differential projections of the infralimbic and prelimbic cortex in the rat. Synapse 51:32–58
Vertes RP (2006) Interactions among the medial prefrontal cortex, hippocampus and midline thalamus in emotional and cognitive processing in the rat. Neuroscience 142(1):1–20
Zarrindast MR, Nasehi M, Piri M, Heidari N (2011) Effects of cholinergic system of dorsal hippocampus of rats on MK-801 induced anxiolytic-like behavior. Neurosci Lett 505(2):65–70
Zilles K, Schröder H, Schröder U, Horvath E, Werner L, Luiten PG, Maelicke A, Strosberg AD (1989) Distribution of cholinergic receptors in the rat and human neocortex. EXS 57:212–228
Acknowledgments
We thank J. C. Aguiar and L. Argentin for their technical support.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Procedures were conducted in conformity with the Brazilian Society of Neuroscience and Behavior guidelines for the care and use of laboratory animals, which are in compliance with international laws and politics. The local ethics committee approved the experimental procedures.
Conflict of interest
Authors do not declare any conflict of interest.
Funding source
This study was supported by grants from CAPES, CNPq (470311/2012-6) and FAPESP (2012/17626-7 and 2012/09300-4). CAPES, CNPq, or FAPESP had no further role in study design; in the collection, analysis, and interpretation of data; in the writing of the report; and in the decision to submit the paper for publication.
Additional information
M. V. Fogaça, A. G. Fedoce and N. C. Ferreira-Junior contributed equally to this work.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Fogaça, M.V., Fedoce, A.G., Ferreira-Junior, N.C. et al. Involvement of M1 and CB1 receptors in the anxiogenic-like effects induced by neostigmine injected into the rat prelimbic medial prefrontal cortex. Psychopharmacology 233, 1377–1385 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00213-016-4228-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00213-016-4228-7