Abstract
Rationale
Although striatal dopamine (DA) is important in alcohol abuse, the nature of DA release during actual alcohol drinking is unclear, since drinking includes self-administration of both conditioned flavor stimuli (CS) of the alcoholic beverage and subsequent intoxication, the unconditioned stimulus (US).
Objectives
Here, we used a novel self-administration analog to distinguish nucleus accumbens (NAcc) DA responses specific to the CS and US.
Methods
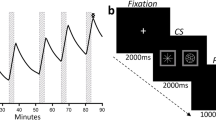
Right-handed male heavy drinkers (n = 26) received three positron emission tomography (PET) scans with the D2/D3 radioligand [11C]raclopride (RAC) and performed a pseudo self-administration task that separately administered a flavor CS of either a habitually consumed beer or the appetitive control Gatorade®, concomitant with the US of ethanol intoxication (0.06 g/dL intravenous (IV) administration) or IV saline. Scan conditions were Gatorade flavor + saline (Gat&Sal), Gatorade flavor + ethanol (Gat&Eth), and beer flavor + ethanol (Beer&Eth).
Results
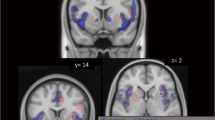
Ethanol (US) reduced RAC binding (inferring DA release) in the left (L) NAcc [Gat&Sal > Gat&Eth]. Beer flavor (CS) increased DA in the right (R) NAcc [Gat&Eth > Beer&Eth]. The combination of beer flavor and ethanol (CS + US), [Gat&Sal > Beer&Eth], induced DA release in bilateral NAcc. Self-reported intoxication during scanning correlated with L NAcc DA release. Relative to saline, infusion of ethanol increased alcoholic drink wanting.
Conclusions
Our findings suggest lateralized DA function in the NAcc, with L NAcc DA release most reflecting intoxication, R NAcc DA release most reflecting the flavor CS, and the conjoint CS + US producing a bilateral NAcc response.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Alleweireldt AT, Weber SM, Kirschner KF, Bullock BL, Neisewander JL (2002) Blockade or stimulation of D1 dopamine receptors attenuates cue reinstatement of extinguished cocaine-seeking behavior in rats. Psychopharmacology (Berl) 159(3):284–293
Besson C, Louilot A (1995) Asymmetrical involvement of mesolimbic dopaminergic neurons in affective perception. Neuroscience 68(4):963–968
Bjork JM, Hommer DW (2007) Anticipating instrumentally obtained and passively-received rewards: a factorial fMRI investigation. Behav Brain Res 177(1):165–170
Boileau I, Assaad JM, Pihl RO, Benkelfat C, Leyton M, Diksic M et al (2003) Alcohol promotes dopamine release in the human nucleus accumbens. Synapse 49(4):226–231
Bossert JM, Poles GC, Wihbey KA, Koya E, Shaham Y (2007) Differential effects of blockade of dopamine D1-family receptors in nucleus accumbens core or shell on reinstatement of heroin seeking induced by contextual and discrete cues. J Neurosci 27(46):12655–12663
Brodie MS, Shefner SA, Dunwiddie TV (1990) Ethanol increases the firing rate of dopamine neurons of the rat ventral tegmental area in vitro. Brain Res 508(1):65–69
Bucholz KK, Cadoret R, Cloninger CR, Dinwiddie SH, Hesselbrock VM, Nurnberger JI Jr et al (1994) A new, semi-structured psychiatric interview for use in genetic linkage studies: a report on the reliability of the SSAGA. J Stud Alcohol 55(2):149–158
Crombag HS, Bossert JM, Koya E, Shaham Y (2008) Review. Context-induced relapse to drug seeking: a review. Philos Trans R Soc Lond B Biol Sci 363(1507):3233–3243
Czachowski CL, Chappell AM, Samson HH (2001) Effects of raclopride in the nucleus accumbens on ethanol seeking and consumption. Alcohol Clin Exp Res 25(10):1431–1440
de Wit H, Stewart J (1981) Reinstatement of cocaine-reinforced responding in the rat. Psychopharmacology (Berl) 75(2):134–143
de Wit H, Stewart J (1983) Drug reinstatement of heroin-reinforced responding in the rat. Psychopharmacology (Berl) 79(1):29–31
Di Chiara G, Imperato A (1988) Drugs abused by humans preferentially increase synaptic dopamine concentrations in the mesolimbic system of freely moving rats. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 85(14):5274–5278
Doyon WM, Anders SK, Ramachandra VS, Czachowski CL, Gonzales RA (2005) Effect of operant self-administration of 10 % ethanol plus 10 % sucrose on dopamine and ethanol concentrations in the nucleus accumbens. J Neurochem 93(6):1469–1481
Epstein DH, Preston KL, Stewart J, Shaham Y (2006) Toward a model of drug relapse: an assessment of the validity of the reinstatement procedure. Psychopharmacology (Berl) 189(1):1–16
Fei X, Mock BH, DeGrado TR, Wang JQ, Glick-Wilson BE, Sullivan ML et al (2004) An improved synthesis of PET dopamine D2 receptors radioligand [11C]raclopride. Synth Commun 34(10)
Gerber GJ, Stretch R (1975) Drug-induced reinstatement of extinguished self-administration behavior in monkeys. Pharmacol Biochem Behav 3(6):1055–1061
Grant S, London ED, Newlin DB, Villemagne VL, Liu X, Contoreggi C et al (1996) Activation of memory circuits during cue-elicited cocaine craving. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 93(21):12040–12045
Green BG, Dalton P, Cowart B, Shaffer G, Rankin K, Higgins J (1996) Evaluating the ‘Labeled Magnitude Scale’ for measuring sensations of taste and smell. Chem Senses 21(3):323–334
Hamlin AS, Newby J, McNally GP (2007) The neural correlates and role of D1 dopamine receptors in renewal of extinguished alcohol-seeking. Neuroscience 146(2):525–536
Ichise M, Liow JS, Lu JQ, Takano A, Model K, Toyama H et al (2003) Linearized reference tissue parametric imaging methods: application to [11C]DASB positron emission tomography studies of the serotonin transporter in human brain. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab 23(9):1096–1112
Imperato A, Di Chiara G (1986) Preferential stimulation of dopamine release in the nucleus accumbens of freely moving rats by ethanol. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 239(1):219–228
Innis RB, Cunningham VJ, Delforge J, Fujita M, Gjedde A, Gunn RN et al (2007) Consensus nomenclature for in vivo imaging of reversibly binding radioligands. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab 27(9):1533–1539
Joutsa J, Johansson J, Niemela S, Ollikainen A, Hirvonen MM, Piepponen P et al (2012) Mesolimbic dopamine release is linked to symptom severity in pathological gambling. Neuroimage 60(4):1992–1999
Kareken DA, Bragulat V, Dzemidzic M, Cox C, Talavage T, Davidson D et al (2010) Family history of alcoholism mediates the frontal response to alcoholic drink odors and alcohol in at-risk drinkers. Neuroimage 50(1):267–276
Marciani L, Pfeiffer JC, Hort J, Head K, Bush D, Taylor AJ et al (2006) Improved methods for fMRI studies of combined taste and aroma stimuli. J Neurosci Methods 158(2):186–194
Martin-Soelch C, Szczepanik J, Nugent A, Barhaghi K, Rallis D, Herscovitch P et al (2011) Lateralization and gender differences in the dopaminergic response to unpredictable reward in the human ventral striatum. Eur J Neurosci 33(9):1706–1715
Neto LL, Oliveira E, Correia F, Ferreira AG (2008) The human nucleus accumbens: where is it? A stereotactic, anatomical and magnetic resonance imaging study. Neuromodulation J Int Neuromodulation Soc 11(1):13–22
Oberlin BG, Dzemidzic M, Tran SM, Soeurt CM, Albrecht DS, Yoder KK et al (2013) Beer flavor provokes striatal dopamine release in male drinkers: mediation by family history of alcoholism. Neuropsychopharmacology 38(9):1617–1624
O’Connor S, Morzorati S, Christian J, Li TK (1998) Clamping breath alcohol concentration reduces experimental variance: application to the study of acute tolerance to alcohol and alcohol elimination rate. Alcohol Clin Exp Res 22(1):202–210
Phillips PE, Stuber GD, Heien ML, Wightman RM, Carelli RM (2003) Subsecond dopamine release promotes cocaine seeking. Nature 422(6932):614–618
Ramchandani VA, Bolane J, Li TK, O’Connor S (1999) A physiologically-based pharmacokinetic (PBPK) model for alcohol facilitates rapid BrAC clamping. Alcohol Clin Exp Res 23(4):617–623
Ramchandani VA, Umhau J, Pavon FJ, Ruiz-Velasco V, Margas W, Sun H et al (2011) A genetic determinant of the striatal dopamine response to alcohol in men. Mol Psychiatry 16(8):809–817
Robinson TE, Berridge KC (1993) The neural basis of drug craving: an incentive-sensitization theory of addiction. Brain Res Brain Res Rev 18(3):247–291
Robinson TE, Berridge KC (2008) Review. The incentive sensitization theory of addiction: some current issues. Philos Trans R Soc Lond B Biol Sci 363(1507):3137–3146
Sanchis-Segura C, Spanagel R (2006) Behavioural assessment of drug reinforcement and addictive features in rodents: an overview. Addict Biol 11(1):2–38
Saunders JB, Aasland OG, Babor TF, de la Fuente JR, Grant M (1993) Development of the Alcohol Use Disorders Identification Test (AUDIT): WHO Collaborative Project on Early Detection of Persons with Harmful Alcohol Consumption–II. Addiction 88(6):791–804
Schultz W, Dayan P, Montague PR (1997) A neural substrate of prediction and reward. Science 275(5306):1593–1599
Setiawan E, Pihl RO, Dagher A, Schlagintweit H, Casey KF, Benkelfat C et al (2014) Differential striatal dopamine responses following oral alcohol in individuals at varying risk for dependence. Alcohol Clin Exp Res 38(1):126–134
Singleton EG, Tiffany ST, Henningfield JE (2000) Alcohol Craving Questionnaire (ACQ-NOW): background, scoring, and administration. Intramural Research Program, National Institute on Drug Abuse, Baltimore
Sobell MB, Sobell LC, Klajner F, Pavan D, Basian E (1986) The reliability of a timeline method for assessing normal drinker college students’ recent drinking history: utility for alcohol research. Addict Behav 11(2):149–161
Sullivan JM, Risacher SL, Normandin MD, Yoder KK, Froehlich JC, Morris ED (2011) Imaging of alcohol-induced dopamine release in rats:preliminary findings with [(11) C]raclopride PET. Synapse 65(9):929–937
Tiffany ST (1999) Cognitive concepts of craving. Alcohol Res Health 23(3):215–224
Tomer R, Aharon-Peretz J (2004) Novelty seeking and harm avoidance in Parkinson’s disease: effects of asymmetric dopamine deficiency. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry 75(7):972–975
Tomer R, Goldstein RZ, Wang GJ, Wong C, Volkow ND (2008) Incentive motivation is associated with striatal dopamine asymmetry. Biol Psychol 77(1):98–101
Tzourio-Mazoyer N, Landeau B, Papathanassiou D, Crivello F, Etard O, Delcroix N et al (2002) Automated anatomical labeling of activations in SPM using a macroscopic anatomical parcellation of the MNI MRI single-subject brain. Neuroimage 15(1):273–289
Urban NB, Kegeles LS, Slifstein M, Xu X, Martinez D, Sakr E et al (2010) Sex differences in striatal dopamine release in young adults after oral alcohol challenge: a positron emission tomography imaging study with [(1)(1)C]raclopride. Biol Psychiatry 68(8):689–696
Weiss F, Lorang MT, Bloom FE, Koob GF (1993) Oral alcohol self-administration stimulates dopamine release in the rat nucleus accumbens: genetic and motivational determinants. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 267(1):250–258
Wong DF, Kuwabara H, Schretlen DJ, Bonson KR, Zhou Y, Nandi A et al (2006) Increased occupancy of dopamine receptors in human striatum during cue-elicited cocaine craving. Neuropsychopharmacology 31(12):2716–2727
Xi ZX, Newman AH, Gilbert JG, Pak AC, Peng XQ, Ashby CR Jr et al (2006) The novel dopamine D3 receptor antagonist NGB 2904 inhibits cocaine’s rewarding effects and cocaine-induced reinstatement of drug-seeking behavior in rats. Neuropsychopharmacology 31(7):1393–1405
Yoder KK, Kareken DA, Seyoum RA, O’Connor SJ, Wang C, Zheng QH et al (2005) Dopamine D(2) receptor availability is associated with subjective responses to alcohol. Alcohol Clin Exp Res 29(6):965–970
Yoder KK, Constantinescu CC, Kareken DA, Normandin MD, Cheng TE, O’Connor SJ et al (2007) Heterogeneous effects of alcohol on dopamine release in the striatum: a PET study. Alcohol Clin Exp Res 31(6):965–973
Yoder KK, Morris ED, Constantinescu CC, Cheng TE, Normandin MD, O’Connor SJ et al (2009) When what you see isn’t what you get: alcohol cues, alcohol administration, prediction error, and human striatal dopamine. Alcohol Clin Exp Res 33(1):139–149
Yoder KK, Kareken DA, Morris ED (2011) Assessing dopaminergic neurotransmission with PET: basic theory and applications in alcohol research. Curr Med Imaging Rev 7:118–124
Yoder KK, Albrecht DS, Kareken DA, Federici LM, Perry KM, Patton EA et al (2012) Reliability of striatal [11C]raclopride binding in smokers wearing transdermal nicotine patches. Eur J Nucl Med Mol Imaging 39(2):220–225
Acknowledgments
We gratefully acknowledge Kevin Perry, Wendy Territo, Michele Beal, Courtney Robbins (Dept. of Radiology and Imaging Sciences), Dr. William Eiler, and Traci Mitchell (Dept. of Neurology) for technical assistance, and Dwight Hector for design and construction of the gustometer. This study was supported by R01 AA017661 (DAK), the Indiana Alcohol Research Center P60 AA007611 for additional support to DAK, and TR000006 (Indiana Clinical and Translational Sciences Institute, Clinical Research Center at Indiana University School of Medicine), T32 AA007462 (BGO), and R01 AA018354 (KKY).
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest and maintain full control of all primary data and agree to allow the journal to review the data upon request.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Oberlin, B.G., Dzemidzic, M., Tran, S.M. et al. Beer self-administration provokes lateralized nucleus accumbens dopamine release in male heavy drinkers. Psychopharmacology 232, 861–870 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00213-014-3720-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00213-014-3720-1