Abstract
Rationale
Yohimbine demonstrated both anxiogenic and anxiolytic properties under different conditions in rodents. Few studies were conducted on zebrafish, a newly emerged vertebrate model organism. Zebrafish larvae are particularly suitable for high-throughput screening of drug effects.
Objectives
The aim of this study was to elucidate the effect of yohimbine on the anxiety-related behaviors of zebrafish larvae.
Methods
AB strain zebrafish larvae at both 5 and 7 days postfertilization (dpf) were treated with different concentrations of yohimbine. General locomotor activities and thigmotaxis behavior were analyzed under continuous illumination, which represented normal condition, or under alternating light-dark challenges, which represented stressful environment.
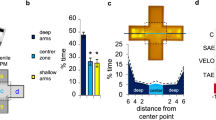
Results
Under continuous illumination, the 5-dpf larvae demonstrated increased swimming distances at low yohimbine concentrations, whereas the 7-dpf larvae demonstrated progressively decreased swimming distances with increases in yohimbine concentration. Low concentrations of yohimbine reduced thigmotaxis of the larvae, while high concentrations of yohimbine increased it. During the dark period of the light-dark challenge phase, low concentrations of yohimbine increased swimming distances of the larvae at both 5 and 7 dpf, while high concentrations of yohimbine decreased it. Yohimbine induced increased thigmotaxis in both 5- and 7-dpf larvae during the dark period.
Conclusions
Under normal condition (lights on), low doses of yohimbine were anxiolytic in both the 5- and 7-dpf larvae, whereas high doses of yohimbine were anxiogenic only in the 7-dpf larvae. Under mildly stressful condition (lights off), yohimbine treatment demonstrated dose-dependent effects to potentiate anxiety-related behaviors in both the 5- and 7-dpf larvae, although the significant dose varied with age.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ackermann GE, Paw BH (2003) Zebrafish: a genetic model for vertebrate organogenesis and human disorders. Front Biosci 8:d1227–d1253
Ahmad F, Richardson MK (2013) Exploratory behaviour in the open field test adapted for larval zebrafish: impact of environmental complexity. Behav Processes 92:88–98
Bhattacharya SK, Satyan KS, Chakrabarti A (1997) Anxiogenic action of caffeine: an experimental study in rats. J Psychopharmacol 11:219–224
Braun AA, Skelton MR, Vorhees CV, Williams MT (2011) Comparison of the elevated plus and elevated zero mazes in treated and untreated male Sprague-Dawley rats: effects of anxiolytic and anxiogenic agents. Pharmacol Biochem Behav 97:406–415
Buske C, Gerlai R (2012) Maturation of shoaling behavior is accompanied by changes in the dopaminergic and serotoninergic systems in zebrafish. Dev Psychobiol 54:28–35
Champagne DL, Hoefnagels CC, de Kloet RE, Richardson MK (2010) Translating rodent behavioral repertoire to zebrafish (Danio rerio): relevance for stress research. Behav Brain Res 214:332–342
Chopin P, Pellow S, File SE (1986) The effects of yohimbine on exploratory and locomotor behaviour are attributable to its effects at noradrenaline and not at benzodiazepine receptors. Neuropharmacology 25:53–57
Cole JC, Burroughs GJ, Laverty CR, Sheriff NC, Sparham EA, Rodgers RJ (1995) Anxiolytic-like effects of yohimbine in the murine plus-maze: strain independence and evidence against alpha 2-adrenoceptor mediation. Psychopharmacology (Berl) 118:425–436
Colwill RM, Creton R (2011a) Imaging escape and avoidance behavior in zebrafish larvae. Rev Neurosci 22:63–73
Colwill RM, Creton R (2011b) Locomotor behaviors in zebrafish (Danio rerio) larvae. Behav Processes 86:222–229
de Esch C, van der Linde H, Slieker R, Willemsen R, Wolterbeek A, Woutersen R, De Groot D (2012) Locomotor activity assay in zebrafish larvae: influence of age, strain and ethanol. Neurotoxicol Teratol 34:425–433
De Vry J, Benz U, Schreiber R, Traber J (1993) Shock-induced ultrasonic vocalization in young adult rats: a model for testing putative anti-anxiety drugs. Eur J Pharmacol 249:331–339
Egan RJ, Bergner CL, Hart PC, Cachat JM, Canavello PR, Elegante MF, Elkhayat SI, Bartels BK, Tien AK, Tien DH, Mohnot S, Beeson E, Glasgow E, Amri H, Zukowska Z, Kalueff AV (2009) Understanding behavioral and physiological phenotypes of stress and anxiety in zebrafish. Behav Brain Res 205:38–44
Ellis LD, Soanes KH (2012) A larval zebrafish model of bipolar disorder as a screening platform for neuro-therapeutics. Behav Brain Res 233:450–457
Ellis LD, Seibert J, Soanes KH (2012) Distinct models of induced hyperactivity in zebrafish larvae. Brain Res 1449:46–59
Guo S (2004) Linking genes to brain, behavior and neurological diseases: what can we learn from zebrafish? Genes Brain Behav 3:63–74
Houtepen LC, Peterse DP, Westphal KG, Olivier B, Vinkers CH (2011) The autonomic stress-induced hyperthermia response is not enhanced by several anxiogenic drugs. Physiol Behav 102:105–109
Irons TD, MacPhail RC, Hunter DL, Padilla S (2010) Acute neuroactive drug exposures alter locomotor activity in larval zebrafish. Neurotoxicol Teratol 32:84–90
Irons TD, Kelly PE, Hunter DL, Macphail RC, Padilla S (2013) Acute administration of dopaminergic drugs has differential effects on locomotion in larval zebrafish. Pharmacol Biochem Behav 103:792–813
Johnston AL, Baldwin HA, File SE (1988) Measures of anxiety and stress in the rat following chronic treatment with yohimbine. J Psychopharmacol 2:33–38
Kily LJ, Cowe YC, Hussain O, Patel S, McElwaine S, Cotter FE, Brennan CH (2008) Gene expression changes in a zebrafish model of drug dependency suggest conservation of neuro-adaptation pathways. J Exp Biol 211:1623–1634
Kimmel CB, Ballard WW, Kimmel SR, Ullmann B, Schilling TF (1995) Stages of embryonic development of the zebrafish. Dev Dyn 203:253–310
Kokel D, Bryan J, Laggner C, White R, Cheung CY, Mateus R, Healey D, Kim S, Werdich AA, Haggarty SJ, Macrae CA, Shoichet B, Peterson RT (2010) Rapid behavior-based identification of neuroactive small molecules in the zebrafish. Nat Chem Biol 6:231–237
Levin ED, Bencan Z, Cerutti DT (2007) Anxiolytic effects of nicotine in zebrafish. Physiol Behav 90:54–58
Lopez-Patino MA, Yu L, Cabral H, Zhdanova IV (2008) Anxiogenic effects of cocaine withdrawal in zebrafish. Physiol Behav 93:160–171
MacPhail RC, Brooks J, Hunter DL, Padnos B, Irons TD, Padilla S (2009) Locomotion in larval zebrafish: Influence of time of day, lighting and ethanol. Neurotoxicology 30:52–58
Mason K, Heal DJ, Stanford SC (1998) The anxiogenic agents, yohimbine and FG 7142, disrupt the noradrenergic response to novelty. Pharmacol Biochem Behav 60:321–327
Maximino C, de Brito TM, Colmanetti R, Pontes AA, de Castro HM, de Lacerda RI, Morato S, Gouveia A Jr (2010) Parametric analyses of anxiety in zebrafish scototaxis. Behav Brain Res 210:1–7
Maximino C, da Silva AW, Gouveia A Jr, Herculano AM (2011) Pharmacological analysis of zebrafish (Danio rerio) scototaxis. Prog Neuropsychopharmacol Biol Psychiatry 35:624–631
Millan MJ, Newman-Tancredi A, Audinot V, Cussac D, Lejeune F, Nicolas JP, Coge F, Galizzi JP, Boutin JA, Rivet JM, Dekeyne A, Gobert A (2000) Agonist and antagonist actions of yohimbine as compared to fluparoxan at alpha(2)-adrenergic receptors (AR)s, serotonin (5-HT)(1A), 5-HT(1B), 5-HT(1D) and dopamine D(2) and D(3) receptors. Significance for the modulation of frontocortical monoaminergic transmission and depressive states. Synapse 35:79–95
Prut L, Belzung C (2003) The open field as a paradigm to measure the effects of drugs on anxiety-like behaviors: a review. Eur J Pharmacol 463:3–33
Richendrfer H, Pelkowski SD, Colwill RM, Creton R (2012) On the edge: pharmacological evidence for anxiety-related behavior in zebrafish larvae. Behav Brain Res 228:99–106
Sackerman J, Donegan JJ, Cunningham CS, Nguyen NN, Lawless K, Long A, Benno RH, Gould GG (2010) Zebrafish behavior in novel environments: effects of acute exposure to anxiolytic compounds and choice of Danio rerio line. Int J Comp Psychol 23:43–61
Schnorr SJ, Steenbergen PJ, Richardson MK, Champagne DL (2012) Measuring thigmotaxis in larval zebrafish. Behav Brain Res 228:367–374
Simon P, Dupuis R, Costentin J (1994) Thigmotaxis as an index of anxiety in mice. Influence of dopaminergic transmissions. Behav Brain Res 61:59–64
Treit D, Fundytus M (1988) Thigmotaxis as a test for anxiolytic activity in rats. Pharmacol Biochem Behav 31:959–962
Udvadia AJ, Linney E (2003) Windows into development: historic, current, and future perspectives on transgenic zebrafish. Dev Biol 256:1–17
van der Ven K, De Wit M, Keil D, Moens L, Van Leemput K, Naudts B, De Coen W (2005) Development and application of a brain-specific cDNA microarray for effect evaluation of neuro-active pharmaceuticals in zebrafish (Danio rerio). Comp Biochem Physiol B Biochem Mol Biol 141:408–417
Vignet C, Begout ML, Pean S, Lyphout L, Leguay D, Cousin X (2013) Systematic screening of behavioral responses in two zebrafish strains. Zebrafish 10:365–375
Westerfield M (1995) The zebrafish book: a guide for the laboratory use of zebrafish, Brachydanio rerio. University of Oregon Press, Eugene
Wolman MA, Jain RA, Liss L, Granato M (2011) Chemical modulation of memory formation in larval zebrafish. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 108:15468–15473
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (grant 81271509), Shanghai Pujiang Program (11PJ1401800) from the Science and Technology Commission of Shanghai Municipality, and Open Project of Key Laboratory for the Genetics of Developmental and Neuropsychiatric Disorders, Ministry of Education, P.R. China to Li Q; Innovation Program of Shanghai Municipal Education Commission (2012Z10268036) and Open Project of Key Laboratory for the Genetics of Developmental and Neuropsychiatric Disorders, Ministry of Education, P.R. China to Guo N; National Natural Science Foundation of China (grant 81070937, 81172397) to Chen XQ; and National Twelfth Five-Year Science and Technology Project (2012BAI01B09) and the 973 Program (2010CB529602) to He L.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Li, Q., Lin, J., Zhang, Y. et al. Differential behavioral responses of zebrafish larvae to yohimbine treatment. Psychopharmacology 232, 197–208 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00213-014-3656-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00213-014-3656-5