Abstract
Rationale
Synthetic hallucinogenic tryptamines, especially those originally described by Alexander Shulgin, continue to be abused in the USA. The range of subjective experiences produced by different tryptamines suggests that multiple neurochemical mechanisms are involved in their actions, in addition to the established role of agonist activity at serotonin 2A (5-HT2A) receptors.
Objectives
This study evaluated the interaction of a series of synthetic tryptamines with biogenic amine neurotransmitter transporters and with serotonin (5-HT) receptor subtypes implicated in psychedelic effects.
Methods
Neurotransmitter transporter activity was determined in rat brain synaptosomes. Receptor activity was determined using calcium mobilization and DiscoveRx PathHunter® assays in HEK293, Gα16-CHO, and CHOk1 cells transfected with human receptors.
Results
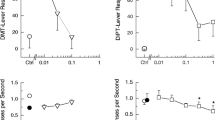
Twenty-one tryptamines were analyzed in transporter uptake and release assays, and 5-HT2A, serotonin 1A (5-HT1A), and 5-HT2A β-arrestin functional assays. Eight of the compounds were found to have 5-HT-releasing activity. Thirteen compounds were found to be 5-HT uptake inhibitors or were inactive. All tryptamines were 5-HT2A agonists with a range of potencies and efficacies, but only a few compounds were 5-HT1A agonists. Most tryptamines recruited β-arrestin through 5-HT2A activation.
Conclusions
All psychoactive tryptamines are 5-HT2A agonists, but 5-HT transporter (SERT) activity may contribute significantly to the pharmacology of certain compounds. The in vitro transporter data confirm structure-activity trends for releasers and uptake inhibitors whereby releasers tend to be structurally smaller compounds. Interestingly, two tertiary amines were found to be selective substrates at SERT, which dispels the notion that 5-HT-releasing activity is limited only to primary or secondary amines.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Baumann MH, Clark RD, Budzynski AG, Partilla JS, Blough BE, Rothman RB (2004) Effects of “Legal X” piperazine analogs on dopamine and serotonin release in rat brain. Ann N Y Acad Sci 1025:189–197
Bogenschutz MP (2013) Studying the effects of classic hallucinogens in the treatment of alcoholism: rationale, methodology, and current research with psilocybin. Curr Drug Abuse Rev 6:17–29
Braida D, Limonta V, Capurro V, Fadda P, Rubino T, Mascia P, Zani A, Gori E, Fratta W, Parolaro D, Sala M (2008) Involvement of kappa-opioid and endocannabinoid system on Salvinorin A-induced reward. Biol Psychiatry 63:286–292
Bunzow JR, Sonders MS, Arttamangkul S, Harrison LM, Zhang G, Quigley DI, Darland T, Suchland KL, Pasumamula S, Kennedy JL, Olson SB, Magenis RE, Amara SG, Grandy DK (2001) Amphetamine, 3,4-methylenedioxymethamphetamine, lysergic acid diethylamide, and metabolites of the catecholamine neurotransmitters are agonists of a rat trace amine receptor. Mol Pharmacol 60:1181–1188
Busch AK, Johnson WC (1950) L.S.D. 25 as an aid in psychotherapy; preliminary report of a new drug. Dis Nerv Syst 11:241–243
Callahan PM, Appel JB (1990) Differentiation between the stimulus effects of (+)-lysergic acid diethylamide and lisuride using a three-choice, drug discrimination procedure. Psychopharmacology 100:13–18
Callaway CW, Wing LL, Geyer MA (1990) Serotonin release contributes to the locomotor stimulant effects of 3,4-methylenedioxymethamphetamine in rats. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 254:456–464
Carroll FI, Lewin AH, Mascarella SW, Seltzman HH, Reddy PA (2012) Designer drugs: a medicinal chemistry perspective. Ann N Y Acad Sci 1248:18–38
Cozzi NV, Gopalakrishnan A, Anderson LL, Feih JT, Shulgin AT, Daley PF, Ruoho AE (2009) Dimethyltryptamine and other hallucinogenic tryptamines exhibit substrate behavior at the serotonin uptake transporter and the vesicle monoamine transporter. J Neural Transm 116:1591–1599
Delille HK, Becker JM, Burkhardt S, Bleher B, Terstappen GC, Schmidt M, Meyer AH, Unger L, Marek GJ, Mezler M (2012) Heterocomplex formation of 5-HT2A-mGlu2 and its relevance for cellular signaling cascades. Neuropharmacology 62:2184–2191
Emanuele E, Colombo R, Martinelli V, Brondino N, Marini M, Boso M, Barale F, Politi P (2010) Elevated urine levels of bufotenine in patients with autistic spectrum disorders and schizophrenia. Neuro Endocrinol Lett 31:117–121
Faurbye A, Pind K (1968) Occurrence of bufotenin in the urine of schizophrenic patients and normal persons. Nature 220:489
Fontanilla D, Johannessen M, Hajipour AR, Cozzi NV, Jackson MB, Ruoho AE (2009) The hallucinogen N,N-dimethyltryptamine (DMT) is an endogenous sigma-1 receptor regulator. Science 323:934–937, New York, NY
Freedland CS, Mansbach RS (1999) Behavioral profile of constituents in ayahuasca, an Amazonian psychoactive plant mixture. Drug Alcohol Depend 54:183–194
Fribourg M, Moreno JL, Holloway T, Provasi D, Baki L, Mahajan R, Park G, Adney SK, Hatcher C, Eltit JM, Ruta JD, Albizu L, Li Z, Umali A, Shim J, Fabiato A, MacKerell AD Jr, Brezina V, Sealfon SC, Filizola M, Gonzalez-Maeso J, Logothetis DE (2011) Decoding the signaling of a GPCR heteromeric complex reveals a unifying mechanism of action of antipsychotic drugs. Cell 147:1011–1023
Gonzalez-Maeso J, Ang RL, Yuen T, Chan P, Weisstaub NV, Lopez-Gimenez JF, Zhou M, Okawa Y, Callado LF, Milligan G, Gingrich JA, Filizola M, Meana JJ, Sealfon SC (2008) Identification of a serotonin/glutamate receptor complex implicated in psychosis. Nature 452:93–97
Gonzalez-Maeso J, Weisstaub NV, Zhou M, Chan P, Ivic L, Ang R, Lira A, Bradley-Moore M, Ge Y, Zhou Q, Sealfon SC, Gingrich JA (2007) Hallucinogens recruit specific cortical 5-HT(2A) receptor-mediated signaling pathways to affect behavior. Neuron 53:439–452
Griffiths R, Richards W, Johnson M, McCann U, Jesse R (2008) Mystical-type experiences occasioned by psilocybin mediate the attribution of personal meaning and spiritual significance 14 months later. J Psychopharmacol 22:621–632, Oxford, England
Griffiths RR, Johnson MW, Richards WA, Richards BD, McCann U, Jesse R (2011) Psilocybin occasioned mystical-type experiences: immediate and persisting dose-related effects. Psychopharmacology 218:649–665
Grinspoon L, Bakalar JB (1981) The psychedelic drug therapies. Curr Psychiatr Ther 20:275–283
Grinspoon L, Bakalar JB (1986) Can drugs be used to enhance the psychotherapeutic process? Am J Psychother 40:393–404
Halberstadt AL, Buell MR, Masten VL, Risbrough VB, Geyer MA (2008) Modification of the effects of 5-methoxy-N,N-dimethyltryptamine on exploratory behavior in rats by monoamine oxidase inhibitors. Psychopharmacology 201:55–66
Halberstadt AL, Geyer MA (2013) Characterization of the head-twitch response induced by hallucinogens in mice: detection of the behavior based on the dynamics of head movement. Psychopharmacology 227:727–739
Johnson MW (2013) Facilitation of cognitive behavioral therapy for smoking cessation using the 5-HT2A agonist psilocybin. College on Problems of Drug Dependence, San Diego
Johnson MW, Sewell RA, Griffiths RR (2012) Psilocybin dose-dependently causes delayed, transient headaches in healthy volunteers. Drug Alcohol Depend 123:132–140
MacLean KA, Johnson MW, Griffiths RR (2011) Mystical experiences occasioned by the hallucinogen psilocybin lead to increases in the personality domain of openness. J Psychopharmacol 25:1453–1461, Oxford, England
Marona-Lewicka D, Chemel BR, Nichols DE (2009) Dopamine D4 receptor involvement in the discriminative stimulus effects in rats of LSD, but not the phenethylamine hallucinogen DOI. Psychopharmacology 203:265–277
Marona-Lewicka D, Thisted RA, Nichols DE (2005) Distinct temporal phases in the behavioral pharmacology of LSD: dopamine D2 receptor-mediated effects in the rat and implications for psychosis. Psychopharmacology 180:427–435
Moreno JL, Holloway T, Albizu L, Sealfon SC, Gonzalez-Maeso J (2011) Metabotropic glutamate mGlu2 receptor is necessary for the pharmacological and behavioral effects induced by hallucinogenic 5-HT2A receptor agonists. Neurosci Lett 493:76–79
Nagai F, Nonaka R, Satoh Hisashi Kamimura K (2007) The effects of non-medically used psychoactive drugs on monoamine neurotransmission in rat brain. Eur J Pharmacol 559:132–137
Nichols DE (1986) Differences between the mechanism of action of MDMA, MBDB, and the classic hallucinogens. Identification of a new therapeutic class: entactogens. J Psychoactive Drugs 18:305–313
Nichols DE (2004) Hallucinogens. Pharmacology & therapeutics 101:131–181
Oehen P, Traber R, Widmer V, Schnyder U (2013) A randomized, controlled pilot study of MDMA (± 3,4-Methylenedioxymethamphetamine)-assisted psychotherapy for treatment of resistant, chronic Post-Traumatic Stress Disorder (PTSD). J Psychopharmacol 27:40–52, Oxford, England
Parrott AC (2007) The psychotherapeutic potential of MDMA (3,4-methylenedioxymethamphetamine): an evidence-based review. Psychopharmacology 191:181–193
Reimann W, Schneider F (1993) The serotonin receptor agonist 5-methoxy-N,N-dimethyltryptamine facilitates noradrenaline release from rat spinal cord slices and inhibits monoamine oxidase activity. Gen Pharmacol 24:449–453
Roth BL, Baner K, Westkaemper R, Siebert D, Rice KC, Steinberg S, Ernsberger P, Rothman RB (2002) Salvinorin A: a potent naturally occurring nonnitrogenous kappa opioid selective agonist. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 99:11934–11939
Rothman RB, Ayestas MA, Dersch CM, Baumann MH (1999) Aminorex, fenfluramine, and chlorphentermine are serotonin transporter substrates. Implications for primary pulmonary hypertension. Circulation 100:869–875
Rothman RB, Baumann MH, Dersch CM, Romero DV, Rice KC, Carroll FI, Partilla JS (2001) Amphetamine-type central nervous system stimulants release norepinephrine more potently than they release dopamine and serotonin. Synapse 39:32–41
Rothman RB, Katsnelson M, Vu N, Partilla JS, Dersch CM, Blough BE, Baumann MH (2002) Interaction of the anorectic medication, phendimetrazine, and its metabolites with monoamine transporters in rat brain. Eur J Pharmacol 447:51–57
Schmid CL, Bohn LM (2010) Serotonin, but not N-methyltryptamines, activates the serotonin 2A receptor via a β-arrestin2/Src/Akt signaling complex in vivo. J Neurosci 30:13513–13524
Schmid CL, Raehal KM, Bohn LM (2008) Agonist-directed signaling of the serotonin 2A receptor depends on beta-arrestin-2 interactions in vivo. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 105:1079–1084
Seeman P, Ko F, Tallerico T (2005) Dopamine receptor contribution to the action of PCP, LSD and ketamine psychotomimetics. Mol Psychiatry 10:877–883
Shen HW, Jiang XL, Yu AM (2011) Nonlinear pharmacokinetics of 5-methoxy-N,N-dimethyltryptamine in mice. Drug metabolism and disposition: the biological fate of chemicals 39:1227–1234
Shulgin A, Shulgin A (1997) TiHKAL the continuation. Transform Press, Berkeley
Shulgin AT, Carter MF (1980) N,N-Diisopropyltryptamine (DIPT) and 5-methoxy-N,N-diisopropyltryptamine (5-MeO-DIPT). Two orally active tryptamine analogs with CNS activity. Commun Psychopharmacol 4:363–369
Sogawa C, Sogawa N, Tagawa J, Fujino A, Ohyama K, Asanuma M, Funada M, Kitayama S (2007) 5-Methoxy-N,N-diisopropyltryptamine (Foxy), a selective and high affinity inhibitor of serotonin transporter. Toxicol Lett 170:75–82
Su TP, Hayashi T, Vaupel DB (2009) When the endogenous hallucinogenic trace amine N,N-dimethyltryptamine meets the sigma-1 receptor. Sci Signal 2:pe12
Walentiny DM, Vann RE, Warner JA, King LS, Seltzman HH, Navarro HA, Twine CE Jr, Thomas BF, Gilliam AF, Gilmour BP, Carroll FI, Wiley JL (2010) Kappa opioid mediation of cannabinoid effects of the potent hallucinogen, salvinorin A, in rodents. Psychopharmacology 210:275–284
White FJ, Appel JB (1982) Lysergic acid diethylamide (LSD) and lisuride: differentiation of their neuropharmacological actions. Science 216:535–537, New York, NY
Acknowledgments
We would like to thank NIDA for their financial support (DA12970). Portions of this work were supported by the Intramural Research Program, National Institute on Drug Abuse, NIH, DHHS.
Conflict of interest
None.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Blough, B.E., Landavazo, A., Decker, A.M. et al. Interaction of psychoactive tryptamines with biogenic amine transporters and serotonin receptor subtypes. Psychopharmacology 231, 4135–4144 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00213-014-3557-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00213-014-3557-7