Abstract
Rationale
In psychopharmacology, researchers have been interested in the hypnotic effects of terrestrial plant polyphenols and their synthetic derivatives. Phlorotannins, a marine plant polyphenol, could have potential as a source of novel hypnotic drugs.
Objectives
The effects of phlorotannins and major phlorotannin constituent eckstolonol on sleep–wake profiles in mice were evaluated in comparison with diazepam, and their hypnotic mechanism was also investigated.
Methods
The effects of phlorotannin preparation (PRT) and eckstolonol orally given on sleep–wake profiles were measured by recording electroencephalograms (EEG) and electromyograms in C57BL/6N mice. Flumazenil, a GABAA-benzodiazepine (BZD) receptor antagonist, was injected 15 min before PRT and eckstolonol to reveal its hypnotic mechanism.
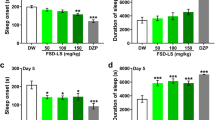
Results
PRT administration (>250 mg/kg) produced a significant decrease in sleep latency and an increase in the amount of non-rapid eye movement sleep (NREMS). Eckstolonol significantly decreased sleep latency (>12.5 mg/kg) and increased the amount of NREMS (50 mg/kg). PRT and eckstolonol had no effect on EEG power density of NREMS. The hypnotic effects of PRT or eckstolonol were completely abolished by pretreatment with flumazenil.
Conclusions
We demonstrated that phlorotannins promote NREMS by modulating the BZD site of the GABAA receptor. These results suggest that phlorotannins can be potentially used as an herbal medicine for insomnia and as a promising structure for developing novel sedative–hypnotics.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Alexandre C, Dordal A, Aixendri R, Guzman A, Hamon M, Adrien J (2008) Sleep-stabilizing effects of E-6199, compared to zopiclone, zolpidem and THIP in mice. Sleep 31:259–270
Anaclet C, Zhang M, Zhao C, Buda C, Seugnet L, Lin JS (2012) Effects of GF-015535-00, a novel α1 GABAA receptor ligand, on the sleep-wake cycle in mice, with reference to zolpidem. Sleep 35:103–111
Atack JR, Smith AJ, Emms F, McKernan RM (1999) Regional differences in the inhibition of mouse in vivo [3H]Ro 15-1788 binding reflect selectivity for α1 versus α2 and α3 subunit-containing GABAA receptors. Neuropsychopharmacology 20:255–262
Barnum D, Greene J, Smellie A, Sprague P (1996) Identification of common functional configurations among molecules. J Chem Inf Comput Sci 36:563–571
Bastien CH, LeBlanc M, Carrier J, Morin CM (2003) Sleep EEG power spectra, insomnia, and chronic use of benzodiazepines. Sleep 26:313–317
Blanco-Centurion C, Xu M, Murillo-Rodriguez E, Gerashchenko D, Shiromani AM, Salin-Pascual RJ, Hof PR, Shiromani PJ (2006) Adenosine and sleep homeostasis in the basal forebrain. J Neurosci 26:8092–8100
Bouayed J, Rammal H, Dicko A, Younos C, Soulimani R (2007) Chlorogenic acid, a polyphenol from Prunus domestica (Mirabelle), with coupled anxiolytic and antioxidant effects. J Neurol Sci 262:77–84
Chen CR, Zhou XZ, Luo YJ, Huang ZL, Urade Y, Qu WM (2012) Magnolol, a major bioactive constituent of the bark of Magnolia officinalis, induces sleep via the benzodiazepine site of GABAA receptor in mice. Neuropharmacology 63:1191–1199
Cho S, Yang H, Jeon YJ, Lee CJ, Jin YH, Back NI, Kim DS, Kang SM, Yoon M, Yong H, Shimizu M, Han D (2012) Phlorotannins of the edible brown seaweed Ecklonia cava Kjellman induce sleep via positive allosteric modulation of gamma-aminobutyric acid type A-benzodiazepine receptor: a novel neurological activity of seaweed polyphenols. Food Chem 132:1133–1142
Erman MK (2005) Therapeutic options in the treatment of insomnia. J Clin Psychiatry 66:18–23
Goutman JD, Waxemberg MD, Doñate-Oliver F, Pomata PE, Calvo DJ (2003) Flavonoid modulation of ionic currents mediated by GABAA and GABAC receptors. Eur J Pharmacol 461:79–87
Greene J, Kahn S, Savoj H, Sprague P, Teig S (1994) Chemical function queries for 3D database search. J Chem Inf Com Sci 34:1297–1308
Hambrecht-Wiedbusch VS, Gauthier EA, Baghdoyan HA, Lydic R (2010) Benzodiazepine receptor agonists cause drug-specific and state-specific alterations in EEG power and acetylcholine release in rat pontine reticular formation. Sleep 33:909–918
Huen MS, Leung JW, Ng W, Lui WS, Chan MN, Wong JT, Xue H (2003) 5,7-Dihydroxy-6-methoxyflavone, a benzodiazepine site ligand isolated from Scutellaria baicalensis Georgi, with selective antagonistic properties. Biochem Pharmacol 66:125–132
Ioannou E, Roussis V (2009) Natural products from seaweeds. In: Osbourn AE, Lanzotti V (eds) Plant-derived natural products. Springer, New York, pp 51–81
Ishida T, Obara Y, Kamei C (2009) Effects of some antipsychotics and a benzodiazepine hypnotic on the sleep-wake pattern in an animal model of schizophrenia. J Pharmacol Sci 111:44–52
Jäger AK, Saaby L (2011) Flavonoids and the CNS. Molecules 16:1471–1485
Jin YH, Cahill EA, Fernandes LG, Wang X, Chen W, Smith SM, Andresen MC (2010) Optical tracking of phenotypically diverse individual synapses on solitary tract nucleus neurons. Brain Res 1312:54–66
Jin Z, Kim S, Cho S, Kim IH, Han D, Jin YH (2013) Potentiating effect of glabridin on GABAA receptor-mediated responses in dorsal raphe neurons. Planta Med 79:1408–1412
Johnston GA (2005) GABAA receptor channel pharmacology. Curr Pharm Des 11:1867–1885
Kahnberg P, Lager E, Rosenberg C, Schougaard J, Camet L, Sterner O, Østergaard Nielsen E, Nielsen M, Liljefors T (2002) Refinement and evaluation of a pharmacophore model for flavone derivatives binding to the benzodiazepine site of the GABAA receptor. J Med Chem 45:4188–4201
Kemp JA, Marshall GR, Wong EH, Woodruff GN (1987) The affinities, potencies and efficacies of some benzodiazepine-receptor agonists, antagonists and inverse-agonists at rat hippocampal GABAA-receptors. Br J Pharmacol 91:601–608
Koivikko R, Loponen J, Pihlaja K, Jormalainen V (2007) High-performance liquid chromatographic analysis of phlorotannins from the brown alga Fucus vesiculosus. Phytochem Anal 18:326–332
Korpi ER, Mattila MJ, Wisden W, Lüddens H (1997) GABAA-receptor subtypes: clinical efficacy and selectivity of benzodiazepine site ligands. Ann Med 29:275–282
Kim AR, Shin TS, Lee MS, Park JY, Park KE, Yoon NY, Kim JS, Choi JS, Jang BC, Byun DS, Park NK, Kim HR (2009) Isolation and identification of phlorotannins from Ecklonia stolonifera with antioxidant and anti-inflammatory properties. J Agric Food Chem 57:3483–3489
Kopp C, Rudolph U, Keist R, Tobler I (2003) Diazepam-induced changes on sleep and the EEG spectrum in mice: role of the α3-GABAA receptor subtype. Eur J Neurosci 17:2226–2230
Kopp C, Rudolph U, Low K, Tobler I (2004) Modulation of rhythmic brain activity by diazepam: GABAA receptor subtype and state specificity. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 101:3674–3679
Marder M, Viola H, Wasowski C, Wolfman C, Waterman PG, Cassels BK, Medina JG, Paladini AC (1996) 6-Bromoflavone, a high affinity ligand for the central benzodiazepine receptors is a member of a family of active flavonoids. Biochem Biophys Res Comm 223:384–389
Marder M, Zinczuk J, Colombo MI, Wasowski C, Viola H, Wolfman C, Medina JH, Rúveda EA, Paladini AC (1997) Synthesis of halogenated/nitrated flavone derivatives and evaluation of their affinity for the central benzodiazepine receptor. Bioorg Med Chem Lett 7:2003–2008
Martínez JHI, Castañeda HGT (2013) Preparation and chromatographic analysis of phlorotannins. J Chromatogr Sci 51:825–838
Masaki M, Aritake K, Tanaka H, Shoyama Y, Huang ZL, Urade Y (2012) Crocin promotes non-rapid eye movement sleep in mice. Mol Nutr Food Res 56:304–308
Meletis CD, Zabriskie N (2008) Natural approaches for optimal sleep. Altern Complement Ther 14:181–188
Meolie AL, Rosen C, Kristo D, Kohrman M, Gooneratne N, Aguillard RN, Fayle R, Troell R, Townsend D, Claman D, Hoban T, Mahowald M (2005) Oral nonprescription treatment for insomnia: an evaluation of products with limited evidence. J Clin Sleep Med 1:173–187
Murase K, Ryu PD, Randic M (1989) Excitatory and inhibitory amino acids and peptide-induced responses in acutely isolated rat spinal dorsal horn neurons. Neurosci Lett 103:56–63
Myung CS, Shin HC, Bao HY, Yeo SJ, Lee BH, Kang JS (2005) Improvement of memory by dieckol and phlorofucofuroeckol in ethanol-treated mice: possible involvement of the inhibition of acetylcholinesterase. Arch Pharm Res 28:691–698
Nazar M, Jessa M, Plaznik A (1997) Benzodiazepine-GABAA receptor complex ligands in two models of anxiety. J Neural Transm 104:733–746
Omori K, Kagami Y, Yokoyama C, Moriyama T, Matsumoto N, Masaki M, Nakamura H, Kamasaka H, Shiraishi K, Kometani T, Kuriki T, Huang ZL, Urade Y (2012) Promotion of non-rapid eye movement sleep in mice after oral administration of ornithine. Sleep Biol Rhythms 10:38–45
Ovaskainen ML, Törrönen R, Koponen JM, Sinkko H, Hellström J, Reinivuo H, Mattila P (2008) Dietary intake and major food sources of polyphenols in Finnish adults. J Nutr 138:562–566
Pérez-Jiménez J, Hubert J, Hooper L, Cassidy A, Manach C, Williamson G, Scalbert A (2010) Urinary metabolites as biomarkers of polyphenol intake in humans: a systematic review. Am J Clin Nutr 92:801–809
Qu WM, Yue XF, Sun Y, Fan K, Chen CR, Hou YP, Urade Y, Huang ZL (2012) Honokiol promotes non-rapid eye movement sleep via the benzodiazepine site of the GABAA receptor in mice. Br J Pharmacol 167:587–598
Shibata T, Kawaguchi S, Hama Y, Inagaki M, Yamaguchi K, Nakamura T (2004) Local and chemical distribution of phlorotannins in brown algae. J Appl Phycol 16:291–296
Shim SY, Quang-To L, Lee SH, Kim SK (2009) Ecklonia cava extract suppresses the high-affinity IgE receptor FcεRI expression. Food Chem Toxicol 47:555–560
Shinomiya K, Inoue T, Utsu Y, Tokunaga S, Masuoka T, Ohmori A, Kamei C (2005) Effects of kava-kava extract on the sleep-wake cycle in sleep-disturbed rats. Psychopharmacology 180:564–569
Smit AJ (2004) Medicinal and pharmaceutical uses of seaweed natural products: a review. J Appl Phycol 16:245–262
Sprenger KJ, Aneiro L, Fung L, Liu Y, Changchit A, Rajachandran L, Kehne JH, Xie L (2007) III Clinical trial data demonstrating sedative-hypnotic efficacy of the α3-subunit preferring GABAA receptor partial allosteric activator, NG2–73: translational validity of pharmacokinetic/pharmacodynamic (PK/PD) relationships derived from preclinical studies. Program no. AAA17. Neuroscience Meeting Planner. Society for Neuroscience Online, San Diego.
Stephenson FA (1995) The GABAA receptors. Biochem J 310:1–9
Stewart SA (2005) The effects of benzodiazepines on cognition. J Clin Psychiatry 66:9–13
Tokunaga S, Takeda Y, Niimoto T, Nishida N, Kubo T, Ohno T, Matsuura Y, Kawahara Y, Shinomiya K, Kamei C (2007) Effect of valerian extract preparation (BIM) on the sleep-wake cycle in rats. Biol Pharm Bull 30:363–366
Trevor AJ, Way WL, Katzung BG (2007) Sedative-hypnotic drugs. McGraw-Hill Medical, New York
Vanini G, Lydic R, Baghdoyan HA (2012) GABA-to-ACh ratio in basal forebrain and cerebral cortex varies significantly during sleep. Sleep 35:1325–1334
Vignes M, Maurice T, Lanté F, Nedjar M, Thethi K, Guiramand J, Récasens M (2006) Anxiolytic properties of green tea polyphenol (−)-epigallocatechin gallate (EGCG). Brain Res 1110:102–115
Walsh JK, Thacker S, Knowles LJ, Tasker T, Hunneyball IM (2009) The partial positive allosteric GABAA receptor modulator EVT 201 is efficacious and safe in the treatment of adult primary insomnia patients. Sleep Med 10:859–864
Wolfman C, Viola H, Marder M, Ardenghi P, Wasowski C, Schroder N, Izquierdo I, Ruveda E, Paladini A, Medina JH (1998) Pharmacological characterization of 6-bromo-3′-nitroflavone, a synthetic flavonoid with high affinity for the benzodiazepine receptors. Pharmacol Biochem Behav 61:239–246
Xiang YZ, Shang HC, Gao XM, Zhang BL (2008) A comparison of the ancient use of ginseng in traditional Chinese medicine with modern pharmacological experiments and clinical trials. Phytother Res 22:851–858
Yang S-Y (2010) Pharmacophore modeling and applications in drug discovery: challenges and recent advances. Drug Discov Today 15:444–450
Yoon NY, Chung HY, Kim HR, Choi JS (2008) Acetyl- and butyrylcholinesterase inhibitory activities of sterols and phlorotannins from Ecklonia stolonifera. Fish Sci 74:200–207
Zhang W, Koehler KF, Zhang P, Cook JM (1995) Development of a comprehensive pharmacophore model for the benzodiazepine receptor. Drug Des Discov 12:193–248
Zou Y, Qian ZJ, Li Y, Kim MM, Lee SH, Kim SK (2008) Antioxidant effects of phlorotannins isolated from Ishige okamurae in free radical mediated oxidative systems. J Agric Food Chem 56:7001–7009
Acknowledgments
This study was supported by grants from the Korea Food Research Institute (E0131402), Small and Medium Business Administration (G01981), the National Basic Research Program of China (2011CB711000, 2009ZX09303-006), the National Natural Science Foundation of China (31171010, 31121061, 31271164), the Shanghai Committee of Science and Technology (13140903100, 13dz2260700), and the Shanghai Leading Academic Discipline Project (B119).
Conflict of interest
All authors declare no conflicts of interest and had no disclosures.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Additional information
Suengmok Cho, Minseok Yoon, Makoto Shimizu and Zhi-Li Huang contributed equally to this work.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Cho, S., Yoon, M., Pae, A.N. et al. Marine polyphenol phlorotannins promote non-rapid eye movement sleep in mice via the benzodiazepine site of the GABAA receptor. Psychopharmacology 231, 2825–2837 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00213-014-3445-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00213-014-3445-1