Abstract
Rationale
There is a focus on developing D3 receptor antagonists as cocaine addiction treatments.
Objective
We investigated the effects of a novel selective D3 receptor antagonist, SR 21502, on cocaine reward, cocaine-seeking, food reward, spontaneous locomotor activity and cocaine-induced locomotor activity in rats.
Methods
In Experiment 1, rats were trained to self-administer cocaine under a progressive ratio (PR) schedule of reinforcement and tested with vehicle or one of three doses of SR 21502. In Experiment 2, animals were trained to self-administer cocaine under a fixed ratio schedule of reinforcement followed by extinction of the response. Then, animals were tested with vehicle or one of the SR 21502 doses on cue-induced reinstatement of responding. In Experiment 3, animals were trained to lever press for food under a PR schedule and tested with vehicle or one dose of the compound. In Experiments 4 and 5, in separate groups of animals, the vehicle and three doses of SR 21502 were tested on spontaneous or cocaine (10 mg/kg, IP)-induced locomotor activity, respectively.
Results
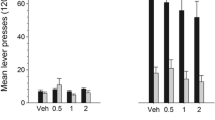
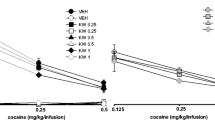
SR 21502 produced significant, dose-related (3.75, 7.5 and 15 mg/kg) reductions in breakpoint for cocaine self-administration, cue-induced reinstatement (3.75, 7.5 and 15 mg/kg) and cocaine-induced locomotor activity (3.75, 7.5 and 15 mg/kg) but failed to reduce food self-administration and spontaneous locomotor activity.
Conclusions
SR 21502 decreases cocaine reward, cocaine-seeking and locomotor activity at doses that have no effect on food reward or spontaneous locomotor activity. These data suggest SR 21502 may selectively inhibit cocaine’s rewarding, incentive motivational and stimulant effects.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ananthan S, Saini SK, Zhou G, Hobrath JV, McDowell S, Mishra Y, Griffin SA, Luedtke RR (2012) Structure–activity relationships in a novel series of DA D3 receptor selective ligands. Soc Neurosci Meet 2012. Abstract Number 780.20
Arroyo M, Markou A, Robbins TW, Everitt BJ (1998) Acquisition, maintenance and reinstatement of intravenous cocaine self-administration under a second-order schedule of reinforcement in rats: effects of conditioned cues and continuous access to cocaine. Psychopharmacology 140:331–344
Caine SB, Koob GF (1993) Modulation of cocaine self-administration in the rat through D-3 dopamine receptors. Science 260:1814–1816
Caine SB, Koob GF (1994) Effects of dopamine D-1 and D-2 antagonists on cocaine self-administration under different schedules of reinforcement in the rat. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 270:209–218
Cervo L, Burbassi S, Colovic M, Caccia S (2005) Selective antagonist at D3 receptors, but not non-selective partial agonists, influences the expression of cocaine-induced conditioned place preference in free-feeding rats. Pharmacol Biochem Behav 82:727–734
Childress AR, Ehrman RN, McLellan AT, O’Brien CP (1988) Conditioned craving and arousal in cocaine addiction: a preliminary report. NIDA Res Monogr 81:74–80
Childress AR, Hole AV, Ehrman RN, Robbins SJ, McLellan AT, O’Brien CP (1993) Cue reactivity and cue reactivity interventions in drug dependence. NIDA Res Monogr 137:73–95
de Wit H, Stewart J (1981) Reinstatement of cocaine-reinforced responding in the rat. Psychopharmacology 75:134–143
de Wit H, Wise RA (1977) Blockade of cocaine reinforcement in rats with the dopamine receptor blocker pimozide, but not with noradrenergic blockers phentolamine and phenoxybenzamine. Can J Psychol 31:195–203
Diaz J, Levesque D, Lammers CH, Griffon N, Martres MP, Schwartz JC, Sokoloff P (1995) Phenotypical characterization of neurons expressing the dopamine D3 receptor in the rat brain. Neuroscience 65:731–7345
Diaz J, Pilon C, Le Foll B, Gros C, Triller A, Schwartz JC, Sokoloff P (2000) Dopamine D3 receptors expressed by all mesencephalic dopamine neurons. J Neurosci 20:8677–8684
Ehrman RN, Robbins SJ, Childress AR, O'Brien CP (1992) Conditioned responses to cocaine-related stimuli in cocaine abuse patients. Psychopharmacology 107:523–529
Ettenberg A, Pettit HO, Bloom FE, Koob GF (1982) Heroin and cocaine intravenous self-administration in rats: mediation by separate neural systems. Psychopharmacology 78:204–209
Gal K, Gyertyan I (2003) Targeting the dopamine D3 receptor cannot influence continuous reinforcement cocaine self-administration in rats. Brain Res Bull 61:595–601
Gilbert JG, Newman AH, Gardner EL, Ashby CR Jr, Heidbreder CA, Pak AC, Peng XQ, Xi ZX (2005) Acute administration of SB-277011A, NGB 2904, or BP 897 inhibits cocaine cue-induced reinstatement of drug-seeking behavior in rats: role of dopamine D3 receptors. Synapse 57:17–28
Grundt P, Carlson EE, Cao J, Bennett CJ, McElveen E, Taylor M, Luedtke RR, Newman AH (2005) Novel heterocyclic trans olefin analogues of N-{4-[4-(2,3-dichlorophenyl)piperazin-1-yl]butyl}arylcarboxamides as selective probes with high affinity for the dopamine D3 receptor. J Med Chem 48(3):839–848
Grundt P, Prevatt KM, Cao J, Taylor M, Floresca CZ, Choi JK, Jenkins BG, Luedtke RR, Newman AH (2007) Heterocyclic analogues of N-(4-(4-(2,3-dichlorophenyl)piperazin-1-yl)butyl)arylcarboxamides with functionalized linking chains as novel dopamine D3 receptor ligands: potential substance abuse therapeutic agents. J Med Chem 50:4135–4146
Gyertyan I, Gal K (2003) Dopamine D3 receptor ligands show place conditioning effect but do not influence cocaine-induced place preference. Neuroreport 14:93–98
Heidbreder C (2008) Selective antagonism at dopamine D3 receptors as a target for drug addiction pharmacotherapy: a review of preclinical evidence. CNS Neurol Disord Drug Targets 7:410–421
Heidbreder CA, Newman AH (2010) Current perspectives on selective dopamine D(3) receptor antagonists as pharmacotherapeutics for addictions and related disorders. Ann N Y Acad Sci 1187:4–34
Macdonald GJ, Branch CL, Hadley MS, Johnson CN, Nash DJ, Smith AB, Stemp G, Thewlis KM, Vong AK, Austin NE, Jeffrey P, Winborn KY, Boyfield I, Hagan JJ, Middlemiss DN, Reavill C, Riley GJ, Watson JM, Wood M, Parker SG, Ashby CR Jr (2003) Design and synthesis of trans-3-(2-(4-((3-(3-(5-methyl-1,2,4-oxadiazolyl))- phenyl)carboxamido)cyclohexyl)ethyl)-7-methylsulfonyl-2,3,4,5-tetrahydro-1 H-3-benzazepine (SB-414796): a potent and selective dopamine D3 receptor antagonist. J Med Chem 46:4952–4964
Mason CW, Hassan HE, Kim KP, Cao J, Eddington ND, Newman AH, Voulalas PJ (2010) Characterization of the transport, metabolism, and pharmacokinetics of the dopamine D3 receptor-selective fluorenyl- and 2-pyridylphenyl amides developed for treatment of psychostimulant abuse. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 333:854–864
Micheli F, Bonanomi G, Blaney FE, Braggio S, Capelli AM, Checchia A, Curcuruto O, Damiani F, Fabio RD, Donati D, Gentile G, Gribble A, Hamprecht D, Tedesco G, Terreni S, Tarsi L, Lightfoot A, Stemp G, Macdonald G, Smith A, Pecoraro M, Petrone M, Perini O, Piner J, Rossi T, Worby A, Pilla M, Valerio E, Griffante C, Mugnaini M, Wood M, Scott C, Andreoli M, Lacroix L, Schwarz A, Gozzi A, Bifone A, Ashby CR Jr, Hagan JJ, Heidbreder C (2007) 1,2,4-triazol-3-yl-thiopropyl-tetrahydrobenzazepines: a series of potent and selective dopamine D(3) receptor antagonists. J Med Chem 50:5076–5089
Murray AM, Ryoo HL, Gurevich E, Joyce JN (1994) Localization of dopamine D 3 receptors to mesolimbic and D 2 receptors to mesostriatal regions of human forebrain. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 91:11271–11275
Peng XQ, Ashby CR Jr, Spiller K, Li X, Li J, Thomasson N, Millan MJ, Mocaer E, Munoz C, Gardner EL, Xi ZX (2009) The preferential dopamine D3 receptor antagonist S33138 inhibits cocaine reward and cocaine-triggered relapse to drug-seeking behavior in rats. Neuropharmacology 56:752–760
Pierce RC, Kumaresan V (2006) The mesolimbic dopamine system: the final common pathway for the reinforcing effect of drugs of abuse? Neurosci Biobehav Rev 30:215–238
Pilla M, Perachon S, Sautel F, Garrido F, Mann A, Wermuth CG, Schwartz JC, Everitt BJ, Sokoloff P (1999) Selective inhibition of cocaine-seeking behaviour by a partial dopamine D3 receptor agonist. Nature 400:371–375
Platt DM, Rowlett JK, Spealman RD (2002) Behavioral effects of cocaine and dopaminergic strategies for preclinical medication development. Psychopharmacology (Berl) 163:265–282
Ranaldi R, Wise RA (2001) Blockade of D1 dopamine receptors in the ventral tegmental area decreases cocaine reward: possible role for dendritically released dopamine. J Neurosci 21:5841–5846
Ranaldi R, Kest K, Zellner M, Hachimine-Semprebom P (2011) Environmental enrichment, administered after establishment of cocaine self-administration, reduces lever pressing in extinction and during a cocaine context renewal test. Behav Pharmacol 22:347–353
Richardson NR, Roberts DCS (1996) Progressive ratio schedules in drug self-administration studies in rats: a method to evaluate reinforcing efficacy. J Neurosci Methods 66:1–11
Ritchie TJ, Macdonald SJF, Peace S, Pickett SD, Luscombe CN (2013) Increasing small molecule drug devolopability in sub-optimal chemical space. Med Chem Commun 4:673–680
Shalev U, Grimm JW, Shaham Y (2002) Neurobiology of relapse to heroin and cocaine seeking: a review. Pharmacol Rev 54:1–42
Sokoloff P, Giros B, Martres MP, Bouthenet ML, Scwartz JC (1990) Molecular cloning and characterization of a novel dopamine receptor (D 3) as a target for neuroleptics. Nature 347:146–150
Song R, Yang RF, Wu N, Su RB, Li J, Peng XQ, Li X, Gaal J, Xi ZX, Gardner EL (2011) YQA14: a novel dopamine D(3) receptor antagonist that inhibits cocaine self-administration in rats and mice, but not in D(3) receptor-knockout mice. Addict Biol 17:14
Vorel SR, Ashby CR Jr, Paul M, Liu X, Hayes R, Hagan JJ, Middlemiss DN, Stemp G, Gardner EL (2002) Dopamine D3 receptor antagonism inhibits cocaine-seeking and cocaine-enhanced brain reward in rats. J Neurosci 22:9595–9603
Willuhn I, Wanat MJ, Clark JJ, Phillips PE (2010) Dopamine signaling in the nucleus accumbens of animals self-administering drugs of abuse. Curr Top Behav Neurosci 3:29–71
Wise RA (1996) Neurobiology of addiction. Curr Opin Neurobiol 6:243–251
Wise RA (2004) Dopamine, learning and motivation. Nat Rev Neurosci 5:483–494
Wise RA (2005) Forebrain substrates of reward and motivation. J Comp Neurol 493:115–1121
Woolverton WL, Virus RM (1989) The effects of a D1 and a D2 dopamine antagonist on behavior maintained by cocaine or food. Pharmacol Biochem Behav 32:691–697
Xi ZX, Gardner EL (2007) Pharmacological actions of NGB 2904, a selective dopamine D3 receptor antagonist, in animal models of drug addiction. CNS Drug Rev 13:240–259
Xi ZX, Gilbert J, Campos AC, Kline N, Ashby CR Jr, Hagan JJ, Heidbreder CA, Gardner EL (2004) Blockade of mesolimbic dopamine D3 receptors inhibits stress-induced reinstatement of cocaine-seeking in rats. Psychopharmacology (Berl) 176:57–65
Xi ZX, Gilbert JG, Pak AC, Ashby CR Jr, Heidbreder CA, Gardner EL (2005) Selective dopamine D3 receptor antagonism by SB-277011A attenuates cocaine reinforcement as assessed by progressive-ratio and variable-cost-variable-payoff fixed-ratio cocaine self-administration in rats. Eur J Neurosci 21:3427–3438
Xi ZX, Newman AH, Gilbert JG, Pak AC, Peng XQ, Ashby CR Jr, Gitajn L, Gardner EL (2006) The novel dopamine D3 receptor antagonist NGB 2904 inhibits cocaine’s rewarding effects and cocaine-induced reinstatement of drug-seeking behavior in rats. Neuropsychopharmacology 31:1393–1405
Yuan J, Chen X, Brodbeck R, Primus R, Braun J, Wasley JW, Thurkauf A (1998) NGB 2904 and NGB 2849: two highly selective dopamine D3 receptor antagonists. Bioorg Med Chem Lett 8(19):2715–2718
Acknowledgments
We want to thank Adjoa Anor and Myriam Waheed for their technical assistance in conducting these studies.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Galaj, E., Ananthan, S., Saliba, M. et al. The effects of the novel DA D3 receptor antagonist SR 21502 on cocaine reward, cocaine seeking and cocaine-induced locomotor activity in rats. Psychopharmacology 231, 501–510 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00213-013-3254-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00213-013-3254-y