Abstract
Rationale
A number of preclinical and clinical studies suggest that ketamine, a glutamate N-methyl-d-aspartate receptor antagonist, has a rapid and lasting antidepressant effect when administered either acutely or chronically. It has been postulated that this effect is due to stimulation of alpha-amino-3-hydroxy-5-methyl-4-isoxazolepropionic acid (AMPA) receptors.
Objective
In this study, we tested whether AMPA alone has an antidepressant effect and if the combination of AMPA and ketamine provides added benefit in Wistar-Kyoto rats, a putative animal model of depression.
Results
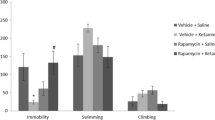
Chronic AMPA treatment resulted in a dose-dependent antidepressant effect in both the forced swim test and sucrose preference test. Moreover, chronic administration (10–11 days) of combinations of AMPA and ketamine, at doses that were ineffective on their own, resulted in a significant antidepressant effect. The behavioral effects were associated with increases in hippocampal brain-derived neurotrophic factor, synapsin, and mammalian target of rapamycin.
Conclusion
These findings are the first to provide evidence for an antidepressant effect of AMPA and suggest the usefulness of AMPA–ketamine combination in treatment of depression. Furthermore, these effects appear to be associated with increases in markers of hippocampal neurogenesis and synaptogenesis, suggesting a mechanism of their action.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
aan het Rot M, Collins KA, Murrough JW, Perez AM, Reich DL, Charney DS, Mathew SJ (2010) Safety and efficacy of repeated-dose intravenous ketamine for treatment-resistant depression. Biol Psychiatry 67:139–145
Alt A, Nisenbaum ES, Bleakman D, Witkin JM (2006) A role for AMPA receptors in mood disorders. Biochem Pharmacol 71:1273–1288
Banasr M, Soumier A, Hery M, Mocaër E, Daszuta A (2006) Agomelatine, a new antidepressant, induces regional changes in hippocampal neurogenesis. Biol Psychiatry 59:1087–1096
Berman RM, Cappiello A, Anand A, Oren DA, Heninger GR, Charney DS et al (2000) Antidepressant effects of ketamine in depressed patients. Biol Psychiatry 47:351–354
Campbell S, Macqueen G (2004) The role of the hippocampus in the pathophysiology of major depression. J Psychiatry Neurosci 29:417–426
Carrier N, Kabbaj M (2013) Sex differences in the antidepressant-like effects of ketamine. Neuropharmacology 70:27–34
Cho HS, D’Souza DC, Gueorguieva R, Perry EB, Madonick S, Karper LP et al (2005) Absence of behavioral sensitization in healthy human subjects following repeated exposure to ketamine. Psychopharmacology 179:136–143
Cornwell BR, Salvadore G, Furey M, Marquardt CA, Brutsche NE, Grillon C et al (2012) Synaptic potentiation is critical for rapid antidepressant response to ketamine in treatment-resistant major depression. Biol Psychiatry 72:555–561
Dazert E, Hall MN (2011) mTOR signaling in disease. Curr Opin Cell Biol 23:744–55
Denk MC, Rewerts C, Holsboer F, Erhardt-Lehmann A, Turck C (2011) Monitoring ketamine treatment response in a depressed patient via peripheral mammalian target of rapamycin activation. Am J Psychiatry 168:751–752
Detke MJ, Rickels M, Lucki I (1995) Active behaviors in the rat forced swimming test differentially produced by serotonergic and noradrenergic antidepressants. Psychopharmacology 121:66–72
Diniz L, dos Santos TB, Britto LRG, Céspedes IC, Garcia MC, Spadari-Bratfisch RC et al (2013) Effects of chronic treatment with corticosterone and imipramine on fos immunoreactivity and adult hippocampal neurogenesis. Behav Brain Res 238:170–177
Dugovic C, Solberg LC, Redei E, Van Reeth O, Turek FW (2000) Sleep in the Wistar-Kyoto rat, a putative genetic animal model for depression. NeuroReport 11:627–631
Duman RS, Voleti B (2012) Signaling pathways underlying the pathophysiology and treatment of depression: novel mechanisms for rapid-acting agents. Trends Neurosci 35:47–56
Duman RS, Li N, Liu R-J, Duric V, Aghajanian G (2012) Signaling pathways underlying the rapid antidepressant actions of ketamine. Neuropharmacology 62:35–41
Freitas AE, Machado DG, Budni J, Neis VB, Balen GO, Lopes MW et al (2013) Fluoxetine modulates hippocampal cell signaling pathways implicated in neuroplasticity in olfactory bulbectomized mice. Behav Brain Res 237:176–184
Fumagalli F, Calabrese F, Luoni A, Shahid M, Racagni G, Riva MA (2012) The AMPA receptor potentiator Org 26576 modulates stress-induced transcription of BDNF isoforms in rat hippocampus. Pharmacol Res 65:176–181
Garcia LS, Comim CM, Valvassori SS, Réus GZ, Barbosa LM, Andreazza AC et al (2008) Acute administration of ketamine induces antidepressant-like effects in the forced swimming test and increases BDNF levels in the rat hippocampus. Prog Neuropsychopharmacol Biol Psychiatry 32:140–144
Griebel G, Moreau JL, Jenck F, Misslin R, Martin JR (1994) Acute and chronic treatment with 5-HT uptake inhibitors differentially modulates emotional responses in anxiety models in rodents. Psychopharmacology 113:463–470
Grippo AJ, Mofitt JA, Johnson AK (2002) Cardiovascular alterations and autonomic imbalance in an experimental model of depression. Am J Physiol Regul Integr Comp Physiol 282:R1333–R1341
Jernigan CS, Goswami DB, Austin MC, Iyo AH, Chandran A, Stockmeier CA et al (2011) The mTOR signaling pathway in the prefrontal cortex is compromised in major depressive disorder. Prog Neuropsychopharmacol Biol Psychiatry 35:1774–1779
Knapp RJ, Goldenberg R, Shuck C, Cecil A, Watkins J, Miller C et al (2002) Antidepressant activity of memory-enhancing drugs in the reduction of submissive behavior model. Eur J Pharmacol 440:27–35
Kodama M, Fujioka T, Duman RS (2004) Chronic olanzapine or fluoxetine administration increases cell proliferation in hippocampus and prefrontal cortex of adult rat. Biol Psychiatry 56:570–580
Koike H, Iijima M, Chaki S (2011) Involvement of AMPA receptor in both the rapid and sustained antidepressant-like effects of ketamine in animal models of depression. Behav Brain Res 224:107–111
Lahmame A, del Arco C, Pazos A, Yritia M, Amario A (1997) Are Wistar-Kyoto rats a genetic model of depression resistant to antidepressants? Eur J Pharmacol 337:115–123
Larsen MH, Mikkelsen JD, Hay-Schmidt A, Sandi C (2010) Regulation of brain-derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF) in the chronic unpredictable stress rat model and the effects of chronic antidepressant treatment. J Psychiatr Res 44:808–816
Li X, Tizzano JP, Griffey K, Clay M, Lindstrom T, Skolnick P (2001) Antidepressant-like actions of an AMPA receptor potentiator (LY392098). Neuropharmacology 40:1028–1033
Li N, Lee B, Liu RJ, Banasr M, Dwyer JM, Iwata M et al (2010) mTOR-dependent synapse formation underlies the rapid antidepressant effects of NMDA antagonists. Science 29:959–964
Lindholm JSO, Autio H, Vesa L, Antila H, Lindemann L, Hoener MC et al (2012) The antidepressant-like effects of glutamatergic drugs ketamine and AMPA receptor potentiator LY 451646 are preserved in bdnf+/− heterozygous null mice. Neuropharmacology 62:391–397
Liu R-J, Lee FS, Li X-Y, Bambico F, Duman RS, Aghajanian GK (2012) Brain-derived neurotrophic factor Val66Met allele impairs basal and ketamine-stimulated synaptogenesis in prefrontal cortex. Biol Psychiatry 71:996–1005
Lopez-Rubalcaava C, Lucki I (2000) Strain differences in the behavioral effects of antidepressant drugs in the rat forced swimming test. Neuropsychopharmacology 22:191–199
Machado-Vieira R, Yuan P, Brutsche N, DiazGranados N, Luckenbaugh D, Manji HK et al (2009) Brain-derived neurotrophic factor and initial antidepressant response to an N-methyl-d-aspartate antagonist. J Clin Psychiatry 70:662–1666
Mackowiak M, O’Neill MJ, Hicks CA, Bleakman D, Skolnick P (2002) An AMPA receptor potentiator modulates hippocampal expression of BDNF: an in vivo study. Neuropharmacology 43:1–10
Maeng S, Zarate CA Jr, Du J, Schloesser RJ, McCammon J, Chen G et al (2008) Cellular mechanisms underlying the antidepressant effects of ketamine: role of α-amino-3-hydroxy-5-methylisoxazole-4-propionic acid receptors. Biol Psychiatry 63:349–352
Malberg JE, Eische AJ, Nestler EJ, Duman RS (2000) Chronic antidepressant treatment increases neurogenesis in adult rat hippocampus. J Neurosci 20:9104–9110
Messer MM, Haller IV (2010) Maintenance ketamine treatment produces long-term recovery from depression. Prim Psychiatry 17:48–50
Miyamoto S, Leipzig JN, Lieberman JA, Duncan GE (2000) Effects of ketamine, MK-801, and amphetamine on regional brain 2-deoxyglucose uptake in freely moving mice. Neuropsychopharmacology 22:400–412
Nestler EJ, Barrot M, DiLeone RJ, Eisch AJ, Gold SJ, Monteggia LM (2002) Neurobiology of depression. Neuron 34:13–25
Paré WP (1994) Open field, learned helplessness, conditioned defensive burying, and forced swim tests in WKY rats. Physiol Behav 55:433–439
Paré WP, Redei E (1993) Sex differences and stress response of WKY rats. Physiol Behav 54:1179–1185
Penn E, Tracy DK (2012) The drugs don’t work? Antidepressants and the current and future pharmacological management of depression. Ther Adv Psychopharmacol 5:179–188
Pini S, Cassano GB, Simonini E, Savino M, Russo A, Montgomery SA (1997) Prevalence of anxiety disorders comorbidity in bipolar depression, unipolar depression, and dysthymia. J Affect Disord 42:145–153
Ricci V, Martinotti G, Gelfo F, Tonioni F, Caltagirone C, Bria P et al (2011) Chronic ketamine use increases serum levels of brain-derived neurotrophic factor. Psychopharmcology 215:143–148
Russo-Neustadt AM, Alejandre H, Garcia C, Ivy AS, Chen MJ (2004) Hippocampal brain-derived neurotrophic factor expression following treatment with reboxetine, citalopram, and physical exercise. Neuropsychopharmacology 29:2189–2199
Sen S, Sanacora G (2008) Major depression: emerging therapeutics. Mt Sinai J Med 75:204–225
Söderpalm B (1989) The SHR exhibits less “anxiety” but increased sensitivity to the anticonflict effect of clonidine compared to normotensive controls. Pharmacol Toxicol 65:381–386
Tejani-Butt S, Kluczynski J, Paré WP (2003) Strain-dependent modification of behavior following antidepressant treatment. Prog Neuropsychopharmacol Biol Psychiatry 27:7–14
Tizabi Y (2007) Nicotine and nicotinic system in hypoglutamatergic models of schizophrenia. Neurotox Res 12:233–246
Tizabi Y, Hauser SR, Tyler KY, Getachew B, Madani R, Sharma Y et al (2010) Effects of nicotine on depressive-like behavior and hippocampal volume of female WKY rats. Prog Neuropsychopharmacol Biol Psychiatry 34:62–69
Tizabi Y, Bhatti BH, Manaye KF, Das JR, Akinfiresoye L (2012) Antidepressant-like effects of low ketamine dose is associated with increased hippocampal AMPA/NMDA receptor density ratio in female Wistar-Kyoto rats. Neuroscience 213:72–80
Treadway MT, Zald DH (2011) Reconsidering anhedonia in depression: lessons from translational neuroscience. Neurosci Biobehav Rev 35:537–555
Zarate CA Jr, Singh JB, Carlson PJ, Brutsche NE, Ameli R, Luckenbaugh DA et al (2006) A randomized trial of an N-methyl-d-aspartate antagonist in treatment-resistant major depression. Arch Gen Psychiatry 63:856–864
Acknowledgments
This study was supported by NIH/NIGMS (2 SO6 GM08016-39).
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Akinfiresoye, L., Tizabi, Y. Antidepressant effects of AMPA and ketamine combination: role of hippocampal BDNF, synapsin, and mTOR. Psychopharmacology 230, 291–298 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00213-013-3153-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00213-013-3153-2