Abstract
Rationale
Many studies have reported medication effects on alcohol cue-elicited brain activation or associations between such activation and subsequent drinking. However, few have combined the methodological rigor of a randomized clinical trial (RCT) with follow-up assessments to determine whether cue-elicited activation predicts relapse during treatment, the crux of alcoholism.
Objectives
This study analyzed functional magnetic resonance imaging (fMRI) data from 48 alcohol-dependent subjects enrolled in a 6-week RCT of an investigational pharmacotherapy.
Methods
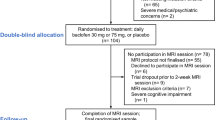
Subjects were randomized, based on their level of alcohol withdrawal (AW) at study entry, to receive either a combination of gabapentin (GBP; up to 1,200 mg for 39 days) and flumazenil (FMZ) infusions (2 days) or two placebos. Midway through the RCT, subjects were administered an fMRI alcohol cue reactivity task.
Results
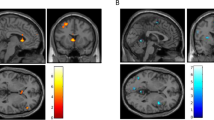
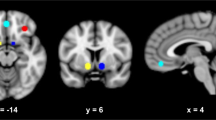
There were no main effects of medication or initial AW status on cue-elicited activation, but these factors interacted, such that the GBP/FMZ/higher AW and placebo/lower AW groups, which had previously been shown to have relatively reduced drinking, demonstrated greater dorsal anterior cingulate cortex (dACC) activation to alcohol cues. Further analysis suggested that this finding represented differences in task-related deactivation and was associated with greater control over alcohol-related thoughts. Among study completers, regardless of medication or AW status, greater left dorsolateral prefrontal cortex (DLPFC) activation predicted more post-scan heavy drinking.
Conclusions
These data suggest that alterations in task-related deactivation of dACC, a component of the default mode network, may predict better alcohol treatment response, while activation of DLPFC, an area associated with selective attention, may predict relapse drinking.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
American Psychiatric Association (2000) Diagnostic and statistical manual of mental disorders, 4th edn. American Psychiatric Association, Washington, DC
Anton RF, Moak DH, Latham PK (1996) The obsessive compulsive drinking scale: a new method of assessing outcome in alcoholism treatment studies. Arch Gen Psychiatry 53:225–231
Anton RF, Myrick H, Baros AM, Latham PK, Randall PK, Wright TM, Stewart SH, Waid R, Malcolm R (2009) Efficacy of a combination of flumazenil and gabapentin in the treatment of alcohol dependence: relationship to alcohol withdrawal symptoms. J Clin Psychopharmacol 29:334–342
Anton RF, Myrick H, Wright TM, Latham PK, Baros AM, Waid LR, Randall PK (2011) Gabapentin combined with naltrexone for the treatment of alcohol dependence. Am J Psychiatry 11:709–717
Beck A, Wustenberg T, Genauck A, Wrase J, Schlagenhauf F, Smolka MN, Mann K, Heinz A (2012) Effect of brain structure, brain function, and brain connectivity on relapse in alcohol-dependent patients. Arch Gen Psychiatry 69:842–852
Biggio F, Gorini G, Caria S, Murru L, Sanna E, Follesa P (2007) Flumazenil selectively prevents the increase in alpha(4)-subunit gene expression and an associated change in GABA(A) receptor function induced by ethanol withdrawal. J Neurochem 102:657–666
Boggio PS, Sultani N, Fecteau S, Merabet L, Mecca T, Pascual-Leone A, Basaglia A, Fregni F (2008) Prefrontal cortex modulation using transcranial DC stimulation reduces alcohol craving: a double-blind, sham-controlled study. Drug Alcohol Depend 92:55–60
Bonnet U, Banger M, Leweke FM, Maschke M, Kowalski T, Gastpar M (1999) Treatment of alcohol withdrawal syndrome with gabapentin. Pharmacopsychiatry 32:107–109
Brody AL, Mandelkern MA, Olmstead RE, Jou J, Tiongson E, Allen V, Scheibal D, London ED, Monterosso JR, Tiffany ST, Korb A, Gan JJ, Cohen MS (2007) Neural substrates of resisting craving during cigarette cue exposure. Biol Psychiatry 62:642–651
Bush G, Luu P, Posner MI (2000) Cognitive and emotional influences in anterior cingulate cortex. Trends Cogn Sci 4:215–222
Caetano R, Clark CL, Greenfield TK (1998) Prevalence, trends, and incidence of alcohol withdrawal symptoms: analysis of general population and clinical samples. Alcohol Health Res World 22:73–79
Cagetti E, Liang J, Spigelman I, Olsen RW (2003) Withdrawal from chronic intermittent ethanol treatment changes subunit composition, reduces synaptic function, and decreases behavioral responses to positive allosteric modulators of GABAA receptors. Mol Pharmacol 63:53–64
Cardenas VA, Durazzo TC, Gazdzinski S, Mon A, Studholme C, Meyerhoff DJ (2011) Brain morphology at entry into treatment for alcohol dependence is related to relapse propensity. Biol Psychiatry 70:561–567
Claus ED, Kiehl KA, Hutchison KE (2011) Neural and behavioral mechanisms of impulsive choice in alcohol use disorder. Alcohol Clin Exp Res 35:1209–1219
Durazzo TC, Gazdzinski S, Mon A, Meyerhoff DJ (2010) Cortical perfusion in alcohol-dependent individuals during short-term abstinence: relationships to resumption of hazardous drinking after treatment. Alcohol 44:201–210
First MB, Spitzer RL, Gibbon M, Williams JBW (2002) Structured Clinical Interview for DSM-IV-TR axis I disorders, research version, non-patient edition. Biometrics Research, New York State Psychiatric Institute, New York
Fox MD, Snyder AZ, Vincent JL, Corbetta M, Van Essen DC, Raichle ME (2005) The human brain is intrinsically organized into dynamic, anticorrelated functional networks. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 102:9673–9678
Garavan H, Ross TJ, Murphy K, Roche RA, Stein EA (2002) Dissociable executive functions in the dynamic control of behavior: inhibition, error detection, and correction. NeuroImage 17:1820–1829
Gilman JM, Ramchandani VA, Crouss T, Hommer DW (2012) Subjective and neural responses to intravenous alcohol in young adults with light and heavy drinking patterns. Neuropsychopharmacology 37:467–477
Goldstein RZ, Alia-Klein N, Tomasi D, Carrillo JH, Maloney T, Woicik PA, Wang R, Telang F, Volkow ND (2009) Anterior cingulate cortex hypoactivations to an emotionally salient task in cocaine addiction. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 106:9453–9458
Grüsser SM, Wrase J, Klein S, Hermann D, Smolka MN, Ruf M, Weber-Fahr W, Flor H, Mann K, Braus DF, Heinz A (2004) Cue-induced activation of the striatum and medial prefrontal cortex is associated with subsequent relapse in abstinent alcoholics. Psychopharmacology (Berl) 175:296–302
Heinz A, Wrase J, Kahnt T, Beck A, Bromand Z, Grüsser SM, Kienast T, Smolka MN, Flor H, Mann K (2007) Brain activation elicited by affectively positive stimuli is associated with a lower risk of relapse in detoxified alcoholic subjects. Alcohol Clin Exp Res 31:1138–1147
Hendrich J, Van Minh AT, Heblich F, Nieto-Rostro M, Watschinger K, Striessnig J, Wratten J, Davies A, Dolphin AC (2008) Pharmacological disruption of calcium channel trafficking by the α2δ ligand gabapentin. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 105:3628–3633
Hermann D, Smolka MN, Wrase J, Klein S, Nikitopoulos J, Georgi A, Braus DF, Flor H, Mann K, Heinz A (2006) Blockade of cue-induced brain activation of abstinent alcoholics by a single administration of amisulpride as measured with fMRI. Alcohol Clin Exp Res 30:1349–1354
Hong LE, Gu H, Yang Y, Ross TJ, Salmeron BJ, Buchholz B, Thaker GK, Stein EA (2009) Association of nicotine addiction and nicotine's actions with separate cingulate cortex functional circuits. Arch Gen Psychiatry 66:431–441
Koob GF, Roberts AJ, Schulteis G, Parsons LH, Heyser CJ, Hyytia P, Merlo-Pich E, Weiss F (1998) Neurocircuitry targets in ethanol reward and dependence. Alcohol Clin Exp Res 22:3–9
Lancaster JL, Woldorff MG, Parsons LM, Liotti M, Freitas CS, Rainey L, Kochunov PV, Nickerson D, Mikiten SA, Fox PT (2000) Automated Talairach atlas labels for functional brain mapping. Hum Brain Mapp 10:120–131
Langosch JM, Spiegelhalder K, Jahnke K, Feige B, Regen W, Kiemen A, Hennig J, Olbrich HM (2012) The impact of acamprosate on cue reactivity in alcohol dependent individuals: a functional magnetic resonance imaging study. J Clin Psychopharmacol 32:661–665
Mason BJ, Light JM, Williams LD, Drobes DJ (2009) Proof-of-concept human laboratory study for protracted abstinence in alcohol dependence: effects of gabapentin. Addict Biol 14:73–83
Matthews SC, Paulus MP, Simmons AN, Nelesen RA, Dimsdale JE (2004) Functional subdivisions within anterior cingulate cortex and their relationship to autonomic nervous system function. NeuroImage 22:1151–1156
Miller WR (2004) Combined behavioral intervention manual. National Institute on Alcohol Abuse and Alcoholism, Bethesda
Monti PM, Rohsenow DJ, Hutchison KE (2000) Toward bridging the gap between biological, psychobiological and psychosocial models of alcohol craving. Addiction 95(Suppl 2):S229–S236
Myrick H, Anton RF, Li X, Henderson S, Drobes D, Voronin K, George MS (2004) Differential brain activity in alcoholics and social drinkers to alcohol cues: relationship to craving. Neuropsychopharmacology 29:393–402
Myrick H, Anton RF, Li X, Henderson S, Randall PK, Voronin K (2008) Effect of naltrexone and ondansetron on alcohol cue-induced activation of the ventral striatum in alcohol-dependent people. Arch Gen Psychiatry 65:466–475
Myrick H, Malcolm R, Randall PK, Boyle E, Anton RF, Becker HC, Randall CL (2009) A double-blind trial of gabapentin versus lorazepam in the treatment of alcohol withdrawal. Alcohol Clin Exp Res 33:1582–1588
Myrick H, Li X, Randall PK, Henderson S, Voronin K, Anton RF (2010) The effect of aripiprazole on cue-induced brain activation and drinking parameters in alcoholics. J Clin Psychopharmacol 30:365–372
O'Daly OG, Trick L, Scaife J, Marshall J, Ball D, Phillips ML, Williams SS, Stephens DN, Duka T (2012) Withdrawal-associated increases and decreases in functional neural connectivity associated with altered emotional regulation in alcoholism. Neuropsychopharmacology 37:2267–2276
Park SQ, Kahnt T, Beck A, Cohen MX, Dolan RJ, Wrase J, Heinz A (2010) Prefrontal cortex fails to learn from reward prediction errors in alcohol dependence. J Neurosci 30:7749–7753
Paus T (2001) Primate anterior cingulate cortex: where motor control, drive and cognition interface. Nat Rev Neurosci 2:417–424
Petrides M (2005) Lateral prefrontal cortex: architectonic and functional organization. Philos Trans R Soc Lond B Biol Sci 360:781–795
Rando K, Hong KI, Bhagwagar Z, Li CS, Bergquist K, Guarnaccia J, Sinha R (2011) Association of frontal and posterior cortical gray matter volume with time to alcohol relapse: a prospective study. Am J Psychiatry 168:183–192
Roberts JS, Anton RF, Latham PK, Moak DH (1999) Factor structure and predictive validity of the Obsessive Compulsive Drinking Scale. Alcohol Clin Exp Res 23:1484–1491
Sanna E, Mostallino MC, Busonero F, Talani G, Tranquilli S, Mameli M, Spiga S, Follesa P, Biggio G (2003) Changes in GABA(A) receptor gene expression associated with selective alterations in receptor function and pharmacology after ethanol withdrawal. J Neurosci 23:11711–11724
Schacht JP, Anton RF, Randall PK, Li X, Henderson S, Myrick H (2011a) Stability of fMRI striatal response to alcohol cues: a hierarchical linear modeling approach. NeuroImage 56:61–68
Schacht JP, Randall PK, Waid LR, Baros AM, Latham PK, Wright TM, Myrick H, Anton RF (2011b) Neurocognitive performance, alcohol withdrawal, and effects of a combination of flumazenil and gabapentin in alcohol dependence. Alcohol Clin Exp Res 35:2030–2038
Schacht JP, Anton RF, Myrick H (2013a) Functional neuroimaging studies of alcohol cue reactivity: a quantitative meta-analysis and systematic review. Addict Biol 18:121–133
Schacht JP, Anton RF, Voronin KE, Randall PK, Li X, Henderson S, Myrick H (2013b) Interacting effects of naltrexone and OPRM1 and DAT1 variation on the neural response to alcohol cues. Neuropsychopharmacology 38:414–422
Schultz W, Dayan P, Montague PR (1997) A neural substrate of prediction and reward. Science 275:1593–1599
Skinner HA, Allen BA (1982) Alcohol dependence syndrome: measurement and validation. J Abnorm Psychol 91:199–209
Sobell LC, Sobell MB (1992) Timeline follow-back: a technique for assessing self-reported alcohol consumption. In: Allen JP, Litten RZ (eds) Measuring alcohol consumption: psychosocial and biochemical methods. Humana, Totowa, pp 41–72
Stout RL, Wirtz PW, Carbonari JP, Del Boca FK (1994) Ensuring balanced distribution of prognostic factors in treatment outcome research. J Stud Alcohol Suppl 12:70–75
Stritzke WG, Breiner MJ, Curtin JJ, Lang AR (2004) Assessment of substance cue reactivity: advances in reliability, specificity, and validity. Psychol Addict Behav 18:148–159
Sullivan JT, Sykora K, Schneiderman J, Naranjo CA, Sellers EM (1989) Assessment of alcohol withdrawal: the revised clinical institute withdrawal assessment for alcohol scale (CIWA-Ar). Br J Addict 84:1353–1357
Tsai GE, Ragan P, Chang R, Chen S, Linnoila VM, Coyle JT (1998) Increased glutamatergic neurotransmission and oxidative stress after alcohol withdrawal. Am J Psychiatry 155:726–732
Urschel HC, Hanselka LL, Gromov I, White L, Baron M (2007) Open-label study of a proprietary treatment program targeting type A gamma-aminobutyric acid receptor dysregulation in methamphetamine dependence. Mayo Clin Proc 82:1170–1178
Vollstädt-Klein S, Wichert S, Rabinstein J, Bühler M, Klein O, Ende G, Hermann D, Mann K (2010) Initial, habitual and compulsive alcohol use is characterized by a shift of cue processing from ventral to dorsal striatum. Addiction 105:1741–1749
Wilson SJ, Sayette MA, Fiez JA (2004) Prefrontal responses to drug cues: a neurocognitive analysis. Nat Neurosci 7:211–214
Acknowledgments
This work was conducted under an unrestricted grant from Hythiam, Inc. This funding source had no involvement in the study design, in the collection, analysis, and interpretation of data, in the writing of the paper, or in the decision to submit for publication. Drs. Schacht and Anton are supported by grants from the National Institute on Alcohol Abuse and Alcoholism (T32 AA007474 and K05 AA017435). Portions of this work were presented as a poster at the 34th Annual Meeting of the Research Society on Alcoholism (June 2011, Atlanta, GA, USA).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Schacht, J.P., Anton, R.F., Randall, P.K. et al. Effects of a GABA-ergic medication combination and initial alcohol withdrawal severity on cue-elicited brain activation among treatment-seeking alcoholics. Psychopharmacology 227, 627–637 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00213-013-2996-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00213-013-2996-x