Abstract
Rationale
Atypical antipsychotics have been linked to weight gain and type 2 diabetes, but are also associated with diabetic ketoacidosis (DKA), which can occur more acutely and in the absence of weight gain.
Objectives
Our aim was to review current case reports of DKA in the context of atypical antipsychotic treatment to better understand (a) the scope of the problem, (b) its relationship to different atypical agents, (c) risk factors, (d) long-term outcome, and (e) putative mechanisms of action.
Method
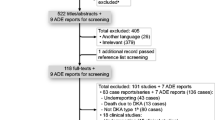
Searches in PubMed/Medline, as well as the University of Toronto’s Scholar Portal, were performed for all relevant articles/abstracts in English.
Results
Sixty reports, yielding 69 cases, affirm that DKA is a rare but serious risk with almost all atypical antipsychotics; however, liability seems to vary between agents, at least partially mirroring risk of weight gain. Mean age of onset was 36.9 years (range 12–80), with 68 % of cases occurring in males, and 41 % in individuals of African American or African Caribbean descent. Over one third of cases present with either no weight gain or weight loss, and 61 % of these require ongoing treatment for glycemic control. Death occurred in 7.25 % of cases.
Conclusion
While the underlying mechanisms are not well understood, antipsychotic-related DKA can occur soon after treatment onset and in the absence of weight gain. Although rare, clinicians must remain vigilant given its acute onset and potential lethality.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Agid O, Foussias G, Singh S, Remington G (2010) Where to position clozapine: re-examining the evidence. Can J Psychiatry Rev Can Psychiatr 55(10):677–684
Ai D, Roper TA, Riley JA (1998) Diabetic ketoacidosis and clozapine. Postgrad Med J 74(874):493–494
Albaugh VL, Singareddy R, Mauger D, Lynch CJ (2011) A double blind, placebo-controlled, randomized crossover study of the acute metabolic effects of olanzapine in healthy volunteers. PLoS One 6(8):e22662
Alessi-Severini S, Biscontri RG, Collins DM, Sareen J, Enns MW (2012) Ten years of antipsychotic prescribing to children: a Canadian population-based study. Can J Psychiatry 57(1):52–58
Allison DB, Casey DE (2001) Antipsychotic-induced weight gain: a review of the literature. J Clin Psychiatry 62(Suppl 7):22–31
Allison DB, Fontaine KR, Manson JE, Stevens J, VanItallie TB (1999a) Annual deaths attributable to obesity in the United States. JAMA 282(16):1530–1538
Allison DB, Mentore JL, Heo M, Chandler LP, Cappelleri JC, Infante MC et al (1999b) Antipsychotic-induced weight gain: a comprehensive research synthesis. Am J Psychiatry 156(11):1686–1696
American Diabetes Association (2004) Consensus development conference on antipsychotic drugs and obesity and diabetes. J Clin Psychiatry 65(2):267–272
Ananth J, Johnson KM, Levander EM, Harry JL (2004a) Diabetic ketoacidosis, neuroleptic malignant syndrome, and myocardial infarction in a patient taking risperidone and lithium carbonate. J Clin Psychiatry 65(5):724
Ananth J, Venkatesh R, Burgoyne K, Gadasalli R, Binford R, Gunatilake S (2004b) Atypical antipsychotic induced weight gain: pathophysiology and management. Ann Clin Psychiatry 16(2):75–85
Assie MB, Carilla-Durand E, Bardin L, Maraval M, Aliaga M, Malfetes N et al (2008) The antipsychotics clozapine and olanzapine increase plasma glucose and corticosterone levels in rats: comparison with aripiprazole, ziprasidone, bifeprunox and F15063. Eur J Pharmacol 592(1–3):160–166
Avella J, Wetli C, Wilson J, Katz M, Hahn T (2004) Fatal olanzapine-induced hyperglycemic ketoacidosis. Am J Forensic Med Pathol 25(2):172–175
Avram AM, Patel V, Taylor HC, Kirwan JP, Kalhan S (2001) Euglycemic clamp study in clozapine-induced diabetic ketoacidosis. Ann Pharmacother 35(11):1381–1387
Babu K, Ganetsky M, Liang I, Bird S, Boyer E (2005) Pancreatitis and diabetic ketoacidosis associated with aripiprazole therapy. Clin Toxicol 43(6):642
Baptista T, De Mendoza S, Beaulieu S, Bermudez A, Martinez M (2004) The metabolic syndrome during atypical antipsychotic drug treatment: mechanisms and management. Metab Syndr Relat Disord 2(4):290–307
Baptista T, ElFakih Y, Uzcategui E, Sandia I, Talamo E, Araujo de Baptista E et al (2008) Pharmacological management of atypical antipsychotic-induced weight gain. CNS Drugs 22(6):477–495
Barnes TR, Paton C, Cavanagh MR, Hancock E, Taylor DM, UK Prescribing Observatory for Mental Health (2007) A UK audit of screening for the metabolic side effects of antipsychotics in community patients. Schizophr Bull 33(6):1397–1403
Boyda HN, Tse L, Procyshyn RM, Wong D, Wu TK, Pang CC et al (2010) A parametric study of the acute effects of antipsychotic drugs on glucose sensitivity in an animal model. Prog Neuro-Psychopharmacol Biol Psychiatry 34(6):945–954
Bulloch AG, Bresee LC, Beck CA, Patten SB (2012) Substantial changes in prescription recommendations for bipolar disorder in Canada: 2002–2010. Can J Psychiatry Rev Can Psychiatr 57(4):263–268
Canadian Diabetes Association (2008) Clinical practice guidelines for the prevention and management of diabetes in Canada. Can J Diabetes 32(Suppl 1):S1–S201
Chellamuth P, Kong M, Gregory R (2010) Ketosis-prone type 2 diabetes: an increasingly recognized entity. Pract Diabetes 27(3):18–19
Chintoh AF, Mann SW, Lam L, Giacca A, Fletcher P, Nobrega J et al (2009) Insulin resistance and secretion in vivo: effects of different antipsychotics in an animal model. Schizophr Res 108(1–3):127–133
Cho DY, Lindenmayer JP (2009) Aripiprazole-induced agitation after clozapine discontinuation: a case report. J Clin Psychiatry 70(1):141–143
Church CO, Stevens DL, Fugate SE (2005) Diabetic ketoacidosis associated with aripiprazole. Diabet Med 22(10):1440–1443
Cohen D (2004) Atypical antipsychotics and new onset diabetes mellitus—an overview of the literature. Pharmacopsychiatry 37(1):1–11
Colli A, Cocciolo M, Francobandiera F, Rogantin F, Cattalini N (1999) Diabetic ketoacidosis associated with clozapine treatment. Diabetes Care 22(1):176–177
Comer JS, Mojtabai R, Olfson M (2011) National trends in the antipsychotic treatment of psychiatric outpatients with anxiety disorders. Am J Psychiatry 168(10):1057–1065
Conley RR, Kelly DL (2001) Management of treatment resistance in schizophrenia. Biol Psychiatry 50(11):898–911
Croarkin PE, Jacobs KM, Bain BK (2000) Diabetic ketoacidosis associated with risperidone treatment? Psychosomatics 41(4):369–370
de Boer C, Gaete HP (1992) Neuroleptic malignant syndrome and diabetic keto-acidosis. Br J Psychiatry J Ment Sci 161:856–858
Dhamija R, Verma R (2008) Diabetic ketoacidosis induced by aripiprazole in a 12-year-old boy. Diabetes Care 31(6):e50
Dibben CR, Kalavalapalli SS, Linnington HE, Hynes FA, Dinneen SF, Adler AI et al (2005) Diabetes associated with atypical antipsychotic treatment may be severe but reversible: case report. Int J Psychiatry Med 35(3):307–311
Dixon L, Weiden P, Delahanty J, Goldberg R, Postrado L, Lucksted A et al (2000) Prevalence and correlates of diabetes in national schizophrenia samples. Schizophr Bull 26(4):903–912
Eder U, Mangweth B, Ebenbichler C, Weiss E, Hofer A, Hummer M et al (2001) Association of olanzapine-induced weight gain with an increase in body fat. Am J Psychiatry 158(10):1719–1722
English P, Williams G (2004) Hyperglycaemic crises and lactic acidosis in diabetes mellitus. Postgrad Med J 80(943):253–261
Fulbright A, Breedlove K (2006) Complete resolution of olanzapine-induced diabetic ketoacidosis. J Pharm Pract 19(4):255–258
Gatta B, Rigalleau V, Gin H (1999) Diabetic ketoacidosis with olanzapine treatment. Diabetes Care 22(6):1002–1003
Geddes J, Freemantle N, Harrison P, Bebbington P (2000) Atypical antipsychotics in the treatment of schizophrenia: systematic overview and meta-regression analysis. BMJ 321(7273):1371–1376
Gilles M, Hentschel F, Paslakis G, Glahn V, Lederbogen F, Deuschle M (2010) Visceral and subcutaneous fat in patients treated with olanzapine: a case series. Clin Neuropharmacol 33(5):248–249
Gilon P, Henquin JC (2001) Mechanisms and physiological significance of the cholinergic control of pancreatic beta-cell function. Endocr Rev 22(5):565–604
Goldstein LE, Sporn J, Brown S, Kim H, Finkelstein J, Gaffey GK et al (1999) New-onset diabetes mellitus and diabetic ketoacidosis associated with olanzapine treatment. Psychosomatics 40(5):438–443
Hahn M, Chintoh A, Giacca A, Xu L, Lam L, Mann S et al (2011) Atypical antipsychotics and effects of muscarinic, serotonergic, dopaminergic and histaminergic receptor binding on insulin secretion in vivo: an animal model. Schizophr Res 131(1–3):90–95
Hamanaka S, Kamijo Y (2007) New-onset diabetic ketoacidosis induced by the addition of perospirone hydrochloride in a patient treated with risperidone. Intern Med (Tokyo, Japan) 46(4):199–200
Hardy TA, Meyers AL, Yu J, Shankar SS, Steinberg HO, Porksen NK (2007) Acute insulin response and beta-cell compensation in normal subjects treated with olanzapine or risperidone for 2 weeks. Diabetes Care 30(1):157–158
Haupt DW, Fahnestock PA, Flavin KA, Schweiger JA, Stevens A, Hessler MJ et al (2007) Adiposity and insulin sensitivity derived from intravenous glucose tolerance tests in antipsychotic-treated patients. Neuropsychopharmacology 32(12):2561–2569
Haupt DW, Rosenblatt LC, Kim E, Baker RA, Whitehead R, Newcomer JW (2009) Prevalence and predictors of lipid and glucose monitoring in commercially insured patients treated with second-generation antipsychotic agents. Am J Psychiatry 166(3):345–353
Henderson DC (2008) Managing weight gain and metabolic issues in patients treated with atypical antipsychotics. J Clin Psychiatry 69(2):e04
Henderson DC, Cagliero E, Copeland PM, Louie PM, Borba CP, Fan X et al (2007) Elevated hemoglobin A1c as a possible indicator of diabetes mellitus and diabetic ketoacidosis in schizophrenia patients receiving atypical antipsychotics. J Clin Psychiatry 68(4):533–541
Hollingworth SA, Siskind DJ, Nissen LM, Robinson M, Hall WD (2010) Patterns of antipsychotic medication use in Australia 2002–2007. Aust NZ J Psychiatry 44(4):372–377
Houseknecht KL, Robertson AS, Zavadoski W, Gibbs EM, Johnson DE, Rollema H (2007) Acute effects of atypical antipsychotics on whole-body insulin resistance in rats: implications for adverse metabolic effects. Neuropsychopharmacology 32(2):289–297
Howes OD, Rifkin L (2004) Diabetic keto-acidotic (DKA) coma following olanzapine initiation in a previously euglycaemic woman and successful continued therapy with olanzapine. J Psychopharmacol 18(3):435–437
Jassim G, Skrede S, Vazquez MJ, Wergedal H, Vik-Mo AO, Lunder N et al (2012) Acute effects of orexigenic antipsychotic drugs on lipid and carbohydrate metabolism in rat. Psychopharmacology 219(3):783–794
Jin H, Meyer JM, Jeste DV (2002) Phenomenology of and risk factors for new-onset diabetes mellitus and diabetic ketoacidosis associated with atypical antipsychotics: an analysis of 45 published cases. Ann Clin Psychiatry 14(1):59–64
Johnson RP, Al-Taher MT, Madlock LE, Guo M, Nasdahl CS (2002) Increasing insulin dose for olanzapine-related diabetes. Am J Psychiatry 159(1):150–151
Joseph AM, Venkatasubramanian G, Sharma PS (2011) A six-to-ten weeks’ follow-up study on the effects of olanzapine on abdominal fat and other metabolic parameters in patients with psychoses—an imaging-based study with controls. East Asian Arch Psychiatry 21(1):10–16
Kahn D, Bourgeois JA (2007) Acute pancreatitis and diabetic ketoacidosis in a schizophrenic patient taking olanzapine. J Clin Psychopharmacol 27(4):397–400
Kane JM (2011) A user’s guide to clozapine. Acta Psychiatr Scand 123(6):407–408
Kibbey KJ, Roberts AM, Nicholson GC (2010) Diabetic ketoacidosis and elevated serum lipase in the setting of aripiprazole therapy. Diabetes Care 33(7):e96
Kitabchi AE, Umpierrez GE, Miles JM, Fisher JN (2009) Hyperglycemic crises in adult patients with diabetes. Diabetes Care 32(7):1335–1343
Kohen D (2004) Diabetes mellitus and schizophrenia: historical perspective. Br J Psychiatry Suppl 47:S64–S66
Koller EA, Doraiswamy PM (2002) Olanzapine-associated diabetes mellitus. Pharmacotherapy 22(7):841–852
Koller E, Malozowski S, Doraiswamy PM (2001) Atypical antipsychotic drugs and hyperglycemia in adolescents. JAMA 286(20):2547–2548
Koller EA, Cross JT, Doraiswamy PM, Schneider BS (2003) Risperidone-associated diabetes mellitus: a pharmacovigilance study. Pharmacotherapy 23(6):735–744
Koller EA, Weber J, Doraiswamy PM, Schneider BS (2004) A survey of reports of quetiapine-associated hyperglycemia and diabetes mellitus. J Clin Psychiatry 65(6):857–863
Kondziela JR, Kaufmann MW, Klein MJ (1985) Diabetic ketoacidosis associated with lithium: case report. J Clin Psychiatry 46(11):492–493
Kostakoglu AE, Yazici KM, Erbas T, Guvener N (1996) Ketoacidosis as a side-effect of clozapine: a case report. Acta Psychiatr Scand 93(3):217–218
Koval MS, Rames LJ, Christie S (1994) Diabetic ketoacidosis associated with clozapine treatment. Am J Psychiatry 151(10):1520–1521
Krentz A, Nattrass M (2003) Acute metabolic complications of diabetes: diabetic ketoacidosis, hyperosmolar non-ketotic hyperglycaemia and lactic acidosis. In: Pickup JC, Williams G (eds) Textbook of diabetes. Blackwell Science, Oxford
Kristensen SH, Porksen NK (2003) Clozapine and diabetic ketoacidosis. Ugeskr Laeger 165(5):475–476
Kroeze WK, Hufeisen SJ, Popadak BA, Renock SM, Steinberg S, Ernsberger P et al (2003) H1-histamine receptor affinity predicts short-term weight gain for typical and atypical antipsychotic drugs. Neuropsychopharmacology 28(3):519–526
Kyriazis IA, Korovesis K, Bashir S, Liakouras A, Partheniou C (2006) Diabetic ketoacidosis and severe dyslipidemia in an adult psychotic man with olanzapine treatment. J Clin Psychopharmacol 26(1):92–94
Lafayette JM, Pirl WF, Henderson DC (2003) Low-dose clozapine and diabetic ketoacidosis. Psychosomatics 44(3):249–252
Laghate VD, Gupta SB (2004) Acute pancreatitis and diabetic ketoacidosis in non-diabetic person while on treatment with sodium valproate, chlorpromazine and haloperidol. J Assoc Physicians India 52:257–258
Leslie DL, Rosenheck RA (2004) Incidence of newly diagnosed diabetes attributable to atypical antipsychotic medications. Am J Psychiatry 161(9):1709–1711
Leslie DL, Rosenheck R (2012) Off-label use of antipsychotic medications in medicaid. Am J Manage Care 18(3):e109–e117
Leucht S, Kissling W, Davis JM (2009a) Second-generation antipsychotics for schizophrenia: can we resolve the conflict? Psychol Med 39(10):1591–1602
Leucht S, Corves C, Arbter D, Engel RR, Li C, Davis JM (2009b) Second-generation versus first-generation antipsychotic drugs for schizophrenia: a meta-analysis. Lancet 373(9657):31–41
Lieberman JA, Stroup TS, McEvoy JP, Swartz MS, Rosenheck RA, Perkins DO et al (2005) Effectiveness of antipsychotic drugs in patients with chronic schizophrenia. N Engl J Med 353(12):1209–1223
Lindenmayer JP, Patel R (1999) Olanzapine-induced ketoacidosis with diabetes mellitus. Am J Psychiatry 156(9):1471
Lu CH, Yan YH (2009) Risperidone-associated newly diagnosed diabetes and fatal diabetes ketoacidosis in a young schizophrenic patient. Diabetes Res Clin Pract 83(2):e66–e67
Macfarlane D, Fisher M (2006) A combination of atypical antipsychotics and diabetic ketoacidosis. Pract Diabetes Care 23(5):205–206
Makhzoumi ZH, McLean LP, Lee JH, Ibe AI (2008) Diabetic ketoacidosis associated with aripiprazole. Pharmacotherapy 28(9):1198–1202
Marder SR, Essock SM, Miller AL, Buchanan RW, Casey DE, Davis JM et al (2004) Physical health monitoring of patients with schizophrenia. Am J Psychiatry 161(8):1334–1349
Marlowe KF, Howard D, Chung A (2007) New onset diabetes with ketoacidosis attributed to quetiapine. South Med J 100(8):829–831
Martins PJ, Haas M, Obici S (2010) Central nervous system delivery of the antipsychotic olanzapine induces hepatic insulin resistance. Diabetes 59(10):2418–2425
Matsui-Sakata A, Ohtani H, Sawada Y (2005) Receptor occupancy-based analysis of the contributions of various receptors to antipsychotics-induced weight gain and diabetes mellitus. Drug Metab Pharmacokinet 20(5):368–378
Maule S, Giannella R, Lanzio M, Villari V (1999) Diabetic ketoacidosis with clozapine treatment. Diabetes Nutr Metab 12(2):187–188
Meltzer HY (2007) Illuminating the molecular basis for some antipsychotic drug-induced metabolic burden. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 104(9):3019–3020
Mitchell AJ, Delaffon V, Vancampfort D, Correll CU, De Hert M (2012) Guideline concordant monitoring of metabolic risk in people treated with antipsychotic medication: systematic review and meta-analysis of screening practices. Psychol Med 42(1):125–147
Mithat B, Alpaslan T, Bulent C, Cengiz T (2005) Risperidone-associated transient diabetic ketoacidosis and diabetes mellitus type 1 in a patient treated with valproate and lithium. Pharmacopsychiatry 38(2):105–106
Mohan D, Gordon H, Hindley N, Barker A (1999) Schizophrenia and diabetes mellitus. Br J Psychiatry J Ment Sci 174:180–181
Monshat K, Carty B, Olver J, Castle D, Bosanac P (2010) Trends in antipsychotic prescribing practices in an urban community mental health clinic. Australas Psychiatry 18(3):238–241
Moore TA, Buchanan RW, Buckley PF, Chiles JA, Conley RR, Crismon ML et al (2007) The Texas Medication Algorithm Project antipsychotic algorithm for schizophrenia: 2006 update. J Clin Psychiatry 68(11):1751–1762
Muench J, Carey M (2001) Diabetes mellitus associated with atypical antipsychotic medications: new case report and review of the literature. J Am Board Fam Pract 14(4):278–282
Muller DJ, Kennedy JL (2006) Genetics of antipsychotic treatment emergent weight gain in schizophrenia. Pharmacogenomics 7(6):863–887
Murashita M, Kusumi I, Hosoda H, Kangawa K, Koyama T (2007) Acute administration of clozapine concurrently increases blood glucose and circulating plasma ghrelin levels in rats. Psychoneuroendocrinology 32(7):777–784
Newcomer JW (2005) Second-generation (atypical) antipsychotics and metabolic effects: a comprehensive literature review. CNS Drugs 19(Suppl 1):1–93
Newcomer JW, Haupt DW (2006) The metabolic effects of antipsychotic medications. Can J Psychiatry Rev Can Psychiatr 51(8):480–491
Niazy M, Neyyarapally T, Baidas G (2009) Severe diabetic ketoacidosis precipitated by an atypical antipsychotic drug. Kuwait Med J 41(3):240–242
NICE (2009) Schizophrenia: core interventions in the treatment and management of schizophrenia in adults in primary and secondary care. NICE Clinical Guideline 82
Nicolai J, Smith SJ, Keunen RW (2001) Simultaneous side effects of both clozapine and valproate. Intensive Care Med 27(5):943
Pascual JC, Martin-Blanco A, Soler J, Ferrer A, Tiana T, Alvarez E et al (2010) A naturalistic study of changes in pharmacological prescription for borderline personality disorder in clinical practice: from APA to NICE guidelines. Int Clin Psychopharmacol 25(6):349–355
Peterson GA, Byrd SL (1996) Diabetic ketoacidosis from clozapine and lithium cotreatment. Am J Psychiatry 153(5):737–738
Pierides M (1997) Clozapine monotherapy and ketoacidosis. Br J Psychiatry J Ment Sci 171:90–91
Ragucci KR, Wells BJ (2001) Olanzapine-induced diabetic ketoacidosis. Ann Pharmacother 35(12):1556–1558
Ramaswamy K, Kozma CM, Nasrallah H (2007) Risk of diabetic ketoacidosis after exposure to risperidone or olanzapine. Drug Saf 30(7):589–599
Rashid J, Starer PJ, Javaid S (2009) Pancreatitis and diabetic ketoacidosis with quetiapine use. Psychiatry (Edgmont) 6(5):34–37
Reddymasu S, Bahta E, Levine S, Manas K, Slay LE (2006) Elevated lipase and diabetic ketoacidosis associated with aripiprazole. JOP 7(3):303–305
Reis JS, Alvarenga T, Rosario PW, Menezes PA, Rocha Rdos S, Purisch S (2007) Diabetes mellitus associated with atypical antipsychotic medications: case report and review of the literature. Arq Bras Endocrinol Metabol 51(3):488–493
Rigalleau V, Gatta B, Bonnaud S, Masson M, Bourgeois ML, Vergnot V et al (2000) Diabetes as a result of atypical anti-psychotic drugs—a report of three cases. Diabet Med 17(6):484–486
Roth BL, Sheffler DJ, Kroeze WK (2004) Magic shotguns versus magic bullets: selectively non-selective drugs for mood disorders and schizophrenia. Nat Rev Drug Discov 3(4):353–359
Sacher J, Mossaheb N, Spindelegger C, Klein N, Geiss-Granadia T, Sauermann R et al (2008) Effects of olanzapine and ziprasidone on glucose tolerance in healthy volunteers. Neuropsychopharmacology 33(7):1633–1641
Saeverud HA, Gerlyng P (2010) From prison with coma. Tidsskr Nor Laegeforen 130(3):284–285
Sato Y, Yasui-Furukori N, Kaneko S, Moriyama T (2008) New-onset diabetic ketoacidosis in a schizophrenic patient with multiple autoimmune disease during treatment with risperidone. Prog Neuro-Psychopharmacol Biol Psychiatry 32(2):577–578
Savoy YE, Ashton MA, Miller MW, Nedza FM, Spracklin DK, Hawthorn MH et al (2010) Differential effects of various typical and atypical antipsychotics on plasma glucose and insulin levels in the mouse: evidence for the involvement of sympathetic regulation. Schizophr Bull 36(2):410–418
Seaburg HL, McLendon BM, Doraiswamy PM (2001) Olanzapine-associated severe hyperglycemia, ketonuria, and acidosis: case report and review of literature. Pharmacotherapy 21(11):1448–1454
Selva KA, Scott SM (2001) Diabetic ketoacidosis associated with olanzapine in an adolescent patient. J Pediatr 138(6):936–938
Shah SM, Carey IM, Harris T, Dewilde S, Cook DG (2011) Antipsychotic prescribing to older people living in care homes and the community in England and Wales. Int J Geriatr Psychiatry 26(4):423–434
Silvestre JS, Prous J (2005) Research on adverse drug events. I. Muscarinic M3 receptor binding affinity could predict the risk of antipsychotics to induce type 2 diabetes. Methods Find Exp Clin Pharmacol 27(5):289–304
Sirois F (2008) New-onset diabetic ketoacidosis associated with quetiapine: a case report. Gen Hosp Psychiatry 30(6):587–588
Smith H, Kenney-Herbert J, Knowles L (1999) Clozapine-induced diabetic ketoacidosis. Aust NZ J Psychiatry 33(1):120–121
Smith GC, Chaussade C, Vickers M, Jensen J, Shepherd PR (2008) Atypical antipsychotic drugs induce derangements in glucose homeostasis by acutely increasing glucagon secretion and hepatic glucose output in the rat. Diabetologia 51(12):2309–2317
Smith GC, Vickers MH, Shepherd PR (2011) Olanzapine effects on body composition, food preference, glucose metabolism and insulin sensitivity in the rat. Arch Physiol Biochem 117(4):241–249
Sowell MO, Mukhopadhyay N, Cavazzoni P, Shankar S, Steinberg HO, Breier A et al (2002) Hyperglycemic clamp assessment of insulin secretory responses in normal subjects treated with olanzapine, risperidone, or placebo. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 87(6):2918–2923
Sowell M, Mukhopadhyay N, Cavazzoni P, Carlson C, Mudaliar S, Chinnapongse S et al (2003) Evaluation of insulin sensitivity in healthy volunteers treated with olanzapine, risperidone, or placebo: a prospective, randomized study using the two-step hyperinsulinemic, euglycemic clamp. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 88(12):5875–5880
Straker D, Mendelowitz A, Karlin L (2002) Near fatal ketoacidosis with olanzapine treatment. Psychosomatics 43(4):339–340
Takahashi M, Ohishi S, Katsumi C, Moriya T, Miyaoka H (2005) Rapid onset of quetiapine-induced diabetic ketoacidosis in an elderly patient: a case report. Pharmacopsychiatry 38(4):183–184
Tavakoli SA, Arguisola MS (2003) Diabetic ketoacidosis in a patient treated with olanzapine, valproic acid, and venlafaxine. South Med J 96(7):729–730
Torrey EF, Swalwell CI (2003) Fatal olanzapine-induced ketoacidosis. Am J Psychiatry 160(12):2241
Trachtenbarg DE (2005) Diabetic ketoacidosis. Am Fam Physician 71(9):1705–1714
Tsolaki M, Symeonides G, Kazis A (2001) Olanzapine induced diabetic ketoacidosis. Psychiatriki 13(3):222–227
Tsuchiyama N, Ando H, Ota T, Sakurai M, Takamura T (2004) Modulating effects of olanzapine on the development of diabetic ketoacidosis. Diabet Med 21(3):300–301
Tulipano G, Rizzetti C, Bianchi I, Fanzani A, Spano P, Cocchi D (2007) Clozapine-induced alteration of glucose homeostasis in the rat: the contribution of hypothalamic–pituitary–adrenal axis activation. Neuroendocrinology 85(2):61–70
Umpierrez GE, Kitabchi AE (2003) Diabetic ketoacidosis: risk factors and management strategies. Treat Endocrinol 2(2):95–108
Varma MK, Connolly K, Fulton B (2007) Life-threatening hyperglycemia and acidosis related to olanzapine: a case report and review of the literature. J Intensive Care Med 22(1):52–55
Vidarsdottir S, Vlug P, Roelfsema F, Frolich M, Pijl H (2010a) Orally disintegrating and oral standard olanzapine tablets similarly elevate the homeostasis model assessment of insulin resistance index and plasma triglyceride levels in 12 healthy men: a randomized crossover study. J Clin Psychiatry 71(9):1205–1211
Vidarsdottir S, de Leeuw van Weenen JE, Frolich M, Roelfsema F, Romijn JA, Pijl H (2010b) Effects of olanzapine and haloperidol on the metabolic status of healthy men. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 95(1):118–125
Waldman JC, Yaren S (2002) Atypical antipsychotics and glycemia: a case report. Can J Psychiatry 47(7):686–687
Watson KE (2008) Cardiovascular risk reduction among African Americans: a call to action. J Natl Med Assoc 100(1):18–26
Wilson DR, D’Souza L, Sarkar N, Newton M, Hammond C (2003) New-onset diabetes and ketoacidosis with atypical antipsychotics. Schizophr Res 59(1):1–6
Wirshing DA, Spellberg BJ, Erhart SM, Marder SR, Wirshing WC (1998) Novel antipsychotics and new onset diabetes. Biol Psychiatry 44(8):778–783
Wirshing DA, Wirshing WC, Kysar L, Berisford MA, Goldstein D, Pashdag J et al (1999) Novel antipsychotics: comparison of weight gain liabilities. J Clin Psychiatry 60(6):358–363
Wong JO, Fu JC, Hung GB (2007) Olanzapine-induced diabetic ketoacidosis in a Chinese man. Hong Kong Med J 13(1):73–74
Yang SH, McNeely MJ (2002) Rhabdomyolysis, pancreatitis, and hyperglycemia with ziprasidone. Am J Psychiatry 159(8):1435
Zipursky RB, Gu H, Green AI, Perkins DO, Tohen MF, McEvoy JP et al (2005) Course and predictors of weight gain in people with first-episode psychosis treated with olanzapine or haloperidol. Br J Psychiatry J Ment Sci 187:537–543
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Guenette, M.D., Hahn, M., Cohn, T.A. et al. Atypical antipsychotics and diabetic ketoacidosis: a review. Psychopharmacology 226, 1–12 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00213-013-2982-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00213-013-2982-3