Abstract
Rational
Although it has been recognized that inhibition of calcineurin induced depressive-like behavior, the underlying neural mediators have not yet been identified. Mammalian target of rapamycin (mTOR), a serine/threonine protein kinase that regulates protein synthesis in synapses, has been demonstrated to be involved in the rapid antidepressant effects of ketamine.
Objective
To investigate a potential role of mTOR signaling pathway which interferes with depressive-like behavior induced by calcineurin blockade and to determine the neurobiological mechanisms underlying mood-related disorders.
Methods
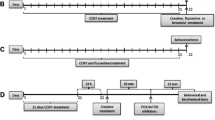
Calcineurin inhibitor cyclosporine A (CsA) and tacrolimus (FK506) were microinjected into the medial prefrontal cortex (mPFC) in rats, and the depressive-like behavior was measured in sucrose preference test and forced swim test. Additionally, mTOR activity was tested by the levels of phosphorylation of p70s6 kinase (p70s6k) and 40S ribosomal protein S6 (rps6).
Results
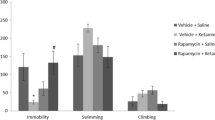
Chronic microinjection of CsA or FK506 into mPFC increased depressive-like behaviors and decreased mTOR activity, but acute CsA or FK506 had no effects on both behavioral phenotype and mTOR activity. Furthermore, activation of mTOR by NMDA reversed the depressive-like behavior induced by chronic CsA or FK506 administration. Moreover, inhibition of mTOR by rapamycin reversed the antidepressant effects of ketamine. Finally, traditional antidepressant venlafaxine prevented the depressive-like performance induced by chronic CsA or FK506 treatment.
Conclusion
These findings indicate that calcineurin-inhibition-induced depressive-like behavior is mediated by blockade of the mTOR signaling pathway and raise the possibility that stimulation of specific brain mTOR may be sufficient to decrease risk of affective disorders in patients treated with calcineurin inhibitor.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aguiar DC, Terzian AL, Guimaraes FS, Moreira FA (2009) Anxiolytic-like effects induced by blockade of transient receptor potential vanilloid type 1 (TRPV1) channels in the medial prefrontal cortex of rats. Psychopharmacology (Berl) 205:217–225
Bahi A, Mineur YS, Picciotto MR (2009) Blockade of protein phosphatase 2B activity in the amygdala increases anxiety- and depression-like behaviors in mice. Biol Psychiatry 66:1139–1146
Banasr M, Duman RS (2008) Glial loss in the prefrontal cortex is sufficient to induce depressive-like behaviors. Biol Psychiatry 64:863–870
Beretta L, Gingras AC, Svitkin YV, Hall MN, Sonenberg N (1996) Rapamycin blocks the phosphorylation of 4E-BP1 and inhibits cap-dependent initiation of translation. EMBO J 15:658–664
Budde K, Becker T, Arns W, Sommerer C, Reinke P, Eisenberger U, Kramer S, Fischer W, Gschaidmeier H, Pietruck F (2011) Everolimus-based, calcineurin-inhibitor-free regimen in recipients of de-novo kidney transplants: an open-label, randomised, controlled trial. Lancet 377:837–847
Buttini M, Limonta S, Luyten M, Boddeke H (1993) Differential distribution of calcineurin A alpha isoenzyme mRNA’s in rat brain. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol 348:679–683
Chen B, Dowlatshahi D, MacQueen GM, Wang JF, Young LT (2001) Increased hippocampal BDNF immunoreactivity in subjects treated with antidepressant medication. Biol Psychiatry 50:260–265
Chiang GG, Abraham RT (2005) Phosphorylation of mammalian target of rapamycin (mTOR) at Ser-2448 is mediated by p70S6 kinase. J Biol Chem 280:25485–25490
de Groen PC, Aksamit AJ, Rakela J, Forbes GS, Krom RA (1987) Central nervous system toxicity after liver transplantation. The role of cyclosporine and cholesterol. N Engl J Med 317:861–866
Drevets WC (2001) Neuroimaging and neuropathological studies of depression: implications for the cognitive–emotional features of mood disorders. Curr Opin Neurobiol 11:240–249
Dufner A, Thomas G (1999) Ribosomal S6 kinase signaling and the control of translation. Exp Cell Res 253:100–109
Foster TC, Sharrow KM, Masse JR, Norris CM, Kumar A (2001) Calcineurin links Ca2+ dysregulation with brain aging. J Neurosci 21:4066–4073
Gong R, Park CS, Abbassi NR, Tang SJ (2006) Roles of glutamate receptors and the mammalian target of rapamycin (mTOR) signaling pathway in activity-dependent dendritic protein synthesis in hippocampal neurons. J Biol Chem 281:18802–18815
Guertin DA, Sabatini DM (2005) An expanding role for mTOR in cancer. Trends Mol Med 11:353–361
Gungor O, Kircelli F, Carrero JJ, Hur E, Demirci MS, Asci G, Toz H (2011) The effect of immunosuppressive treatment on arterial stiffness and matrix Gla protein levels in renal transplant recipients. Clin Nephrol 75:491–496
Hoeffer CA, Klann E (2010) mTOR signaling: at the crossroads of plasticity, memory and disease. Trends Neurosci 33:67–75
Hou L, Klann E (2004) Activation of the phosphoinositide 3-kinase-Akt-mammalian target of rapamycin signaling pathway is required for metabotropic glutamate receptor-dependent long-term depression. J Neurosci 24:6352–6361
Jernigan CS, Goswami DB, Austin MC, Iyo AH, Chandran A, Stockmeier CA, Karolewicz B (2011) The mTOR signaling pathway in the prefrontal cortex is compromised in major depressive disorder. Prog Neuropsychopharmacol Biol Psychiatry 35:1774–1779
Juckel G, Mendlin A, Jacobs BL (1999) Electrical stimulation of rat medial prefrontal cortex enhances forebrain serotonin output: implications for electroconvulsive therapy and transcranial magnetic stimulation in depression. Neuropsychopharmacology 21:391–398
Kim DH, Sarbassov DD, Ali SM, King JE, Latek RR, Erdjument-Bromage H, Tempst P, Sabatini DM (2002) mTOR interacts with raptor to form a nutrient-sensitive complex that signals to the cell growth machinery. Cell 110:163–175
Klann E, Dever TE (2004) Biochemical mechanisms for translational regulation in synaptic plasticity. Nat Rev Neurosci 5:931–942
Lenz G, Avruch J (2005) Glutamatergic regulation of the p70S6 kinase in primary mouse neurons. J Biol Chem 280:38121-38124
Li N, Lee B, Liu RJ, Banasr M, Dwyer JM, Iwata M, Li XY, Aghajanian G, Duman RS (2010) mTOR-dependent synapse formation underlies the rapid antidepressant effects of NMDA antagonists. Science 329:959–964
Li N, Liu RJ, Dwyer JM, Banasr M, Lee B, Son H, Li XY, Aghajanian G, Duman RS (2011) Glutamate N-methyl-d-aspartate receptor antagonists rapidly reverse behavioral and synaptic deficits caused by chronic stress exposure. Biol Psychiatry 69:754–761
Lian Q, Ladner CJ, Magnuson D, Lee JM (2001) Selective changes of calcineurin (protein phosphatase 2B) activity in Alzheimer’s disease cerebral cortex. Exp Neurol 167:158–165
Lin YH, Liu AH, Xu Y, Tie L, Yu HM, Li XJ (2005) Effect of chronic unpredictable mild stress on brain–pancreas relative protein in rat brain and pancreas. Behav Brain Res 165:63–71
Lu L, Hope BT, Dempsey J, Liu SY, Bossert JM, Shaham Y (2005) Central amygdala ERK signaling pathway is critical to incubation of cocaine craving. Nat Neurosci 8:212–219
Maeng S, Zarate CA Jr, Du J, Schloesser RJ, McCammon J, Chen G, Manji HK (2008) Cellular mechanisms underlying the antidepressant effects of ketamine: role of alpha-amino-3-hydroxy-5-methylisoxazole-4-propionic acid receptors. Biol Psychiatry 63:349–352
Mansuy IM (2003) Calcineurin in memory and bidirectional plasticity. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 311:1195–1208
Martin KA, Merenick BL, Ding M, Fetalvero KM, Rzucidlo EM, Kozul CD, Brown DJ, Chiu HY, Shyu M, Drapeau BL, Wagner RJ, Powell RJ (2007) Rapamycin promotes vascular smooth muscle cell differentiation through insulin receptor substrate-1/phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase/Akt2 feedback signaling. J Biol Chem 282:36112–36120
Mayberg HS (1997) Limbic–cortical dysregulation: a proposed model of depression. J Neuropsychiatry Clin Neurosci 9:471–481
Mitsuhashi S, Shima H, Kikuchi K, Igarashi K, Hatsuse R, Maeda K, Yazawa M, Murayama T, Okuma Y, Nomura Y (2000) Development of an assay method for activities of serine/threonine protein phosphatase type 2B (calcineurin) in crude extracts. Anal Biochem 278:192–197
Nathan CO, Amirghahari N, Abreo F, Rong X, Caldito G, Jones ML, Zhou H, Smith M, Kimberly D, Glass J (2004) Overexpressed eIF4E is functionally active in surgical margins of head and neck cancer patients via activation of the Akt/mammalian target of rapamycin pathway. Clin Cancer Res 10:5820–5827
Nowak G, Ordway GA, Paul IA (1995) Alterations in the N-methyl-d-aspartate (NMDA) receptor complex in the frontal cortex of suicide victims. Brain Res 675:157–164
Paxinos G, Watson CR, Emson PC (1980) AChE-stained horizontal sections of the rat brain in stereotaxic coordinates. J Neurosci Methods 3:129–149
Polli JW, Billingsley ML, Kincaid RL (1991) Expression of the calmodulin-dependent protein phosphatase, calcineurin, in rat brain: developmental patterns and the role of nigrostriatal innervation. Brain Res Dev Brain Res 63:105–119
Porsolt RD, Anton G, Blavet N, Jalfre M (1978) Behavioural despair in rats: a new model sensitive to antidepressant treatments. Eur J Pharmacol 47:379–391
Proud CG (2007) Cell signaling. mTOR, unleashed. Science 318:926–927
Sekulic A, Hudson CC, Homme JL, Yin P, Otterness DM, Karnitz LM, Abraham RT (2000) A direct linkage between the phosphoinositide 3-kinase-AKT signaling pathway and the mammalian target of rapamycin in mitogen-stimulated and transformed cells. Cancer Res 60:3504–3513
Shirayama Y, Chen AC, Nakagawa S, Russell DS, Duman RS (2002) Brain-derived neurotrophic factor produces antidepressant effects in behavioral models of depression. J Neurosci 22:3251–3261
Swanson CJ, Bures M, Johnson MP, Linden AM, Monn JA, Schoepp DD (2005) Metabotropic glutamate receptors as novel targets for anxiety and stress disorders. Nat Rev Drug Discov 4:131–144
Wang X, Luo YX, He YY, Li FQ, Shi HS, Xue LF, Xue YX, Lu L (2010) Nucleus accumbens core mammalian target of rapamycin signaling pathway is critical for cue-induced reinstatement of cocaine seeking in rats. J Neurosci 30:12632–12641
Willner P, Towell A, Sampson D, Sophokleous S, Muscat R (1987) Reduction of sucrose preference by chronic unpredictable mild stress, and its restoration by a tricyclic antidepressant. Psychopharmacology (Berl) 93:358–364
Yoon SC, Seo MS, Kim SH, Jeon WJ, Ahn YM, Kang UG, Kim YS (2008) The effect of MK-801 on mTOR/p70S6K and translation-related proteins in rat frontal cortex. Neurosci Lett 434:23–28
Zhu WL, Shi HS, Wang SJ, Wu P, Ding ZB, Lu L (2011) Hippocampal CA3 calcineurin activity participates in depressive-like behavior in rats. J Neurochem 117:1075–1086
Acknowledgments
This work was supported in part by a grant from the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 30870895 to J.L.Y).
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yu, JJ., Zhang, Y., Wang, Y. et al. Inhibition of calcineurin in the prefrontal cortex induced depressive-like behavior through mTOR signaling pathway. Psychopharmacology 225, 361–372 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00213-012-2823-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00213-012-2823-9