Abstract
Rationale and objective
Repeated and/or heightened elevations in glucocorticoids (e.g., repeated stress) can promote escalated drug-taking behaviors and induce compromised HPA axis function. Given that interoceptive/subjective drug cues are a fundamental factor in drug-taking behavior, we sought to determine the effects of exposure to repeated elevations in the glucocorticoid corticosterone (CORT) on the interoceptive effects of alcohol in rats using drug discrimination techniques.
Methods
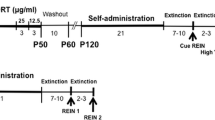
Male Long Evans rats trained to discriminate alcohol (1 g/kg, IG) vs. water were exposed to CORT (300 μg/ml) in the home cage drinking water for 7 days. The interoceptive effects of experimenter- and self-administered alcohol were assessed and HPA axis function was determined.
Results
The interoceptive effects of experimenter- and self-administered alcohol were blunted following CORT. Control experiments determined that this decreased sensitivity was unrelated to discrimination performance impairments or decreased CORT levels at the time of testing and was dependent on repeated CORT exposure. Susceptibility to compromised HPA axis function following CORT exposure was suggested by an altered pattern of CORT secretion and blunted CORT response following injection of the synthetic glucocorticoid dexamethasone.
Conclusions
These findings present a possible behavioral mechanism for escalated alcohol drinking during episodes of heightened elevations in glucocorticoids (e.g., stress). That is, during these episodes, individuals may consume more alcohol to achieve the desired interoceptive effects. Understanding these behavioral mechanisms may lead to a better understanding of factors that promote alcoholism and alcohol abuse in at risk populations.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Adinoff B, Martin PR, Bone GH, Eckardt MJ, Roehrich L, George DT, Moss HB, Eskay R, Linnoila M, Gold PW (1990) Hypothalamic–pituitary–adrenal axis functioning and cerebrospinal fluid corticotropin releasing hormone and corticotropin levels in alcoholics after recent and long-term abstinence. Arch Gen Psychiatry 47:325–330
Berman JD, Cook DM, Buchman M, Keith LD (1990) Diminished adrenocorticotropin response to insulin-induced hypoglycemia in nondepressed, actively drinking male alcoholics. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 71:712–717
Besheer J, Hodge CW (2005) Pharmacological and anatomical evidence for an interaction between mGluR5- and GABA(A) alpha1-containing receptors in the discriminative stimulus effects of ethanol. Neuropsychopharmacology 30:747–757
Besheer J, Cox AA, Hodge CW (2003) Coregulation of ethanol discrimination by the nucleus accumbens and amygdala. Alcohol Clin Exp Res 27:450–456
Besheer J, Stevenson RA, Hodge CW (2006) mGlu5 receptors are involved in the discriminative stimulus effects of self-administered ethanol in rats. Eur J Pharmacol 551:71–75
Besheer J, Schroeder JP, Stevenson RA, Hodge CW (2008) Ethanol-induced alterations of c-Fos immunoreactivity in specific limbic brain regions following ethanol discrimination training. Brain Res 1232:124–131
Besheer J, Grondin JJ, Salling MC, Spanos M, Stevenson RA, Hodge CW (2009) Interoceptive effects of alcohol require mGlu5 receptor activity in the nucleus accumbens. J Neurosci 29:9582–9591
Bowen CA, Purdy RH, Grant KA (1999) An investigation of endogenous neuroactive steroid-induced modulation of ethanol's discriminative stimulus effects. Behav Pharmacol 10:297–311
Brown ES, Varghese FP, McEwen BS (2004) Association of depression with medical illness: does cortisol play a role? Biol Psychiatry 55:1–9
Buffalari DM, Grace AA (2009) Chronic cold stress increases excitatory effects of norepinephrine on spontaneous and evoked activity of basolateral amygdala neurons. Int J Neuropsychopharmacol 12:95–107
Buwalda B, de Boer SF, Schmidt ED, Felszeghy K, Nyakas C, Sgoifo A, Van der Vegt BJ, Tilders FJ, Bohus B, Koolhaas JM (1999) Long-lasting deficient dexamethasone suppression of hypothalamic–pituitary–adrenocortical activation following peripheral CRF challenge in socially defeated rats. J Neuroendocrinol 11:513–520
Cannady R, Grondin JJ, Fisher KR, Hodge CW, Besheer J (2011) Activation of group I metabotropic glutamate receptors inhibits the discriminative stimulus effects of alcohol via selective activity within the amygdala. Neuropsychopharmacology
Chao HM, Choo PH, McEwen BS (1989) Glucocorticoid and mineralocorticoid receptor mRNA expression in rat brain. Neuroendocrinology 50:365–371
Childs E, O'Connor S, de Wit H (2011) Bidirectional interactions between acute psychosocial stress and acute intravenous alcohol in healthy men. Alcohol Clin Exp Res
Conrad CD, LeDoux JE, Magarinos AM, McEwen BS (1999) Repeated restraint stress facilitates fear conditioning independently of causing hippocampal CA3 dendritic atrophy. Behav Neurosci 113:902–913
Conrad CD, McLaughlin KJ, Harman JS, Foltz C, Wieczorek L, Lightner E, Wright RL (2007) Chronic glucocorticoids increase hippocampal vulnerability to neurotoxicity under conditions that produce CA3 dendritic retraction but fail to impair spatial recognition memory. J Neurosci 27:8278–8285
Costa A, Bono G, Martignoni E, Merlo P, Sances G, Nappi G (1996) An assessment of hypothalamo–pituitary–adrenal axis functioning in non-depressed, early abstinent alcoholics. Psychoneuroendocrinology 21:263–275
Crum RM, Pratt LA (2001) Risk of heavy drinking and alcohol use disorders in social phobia: a prospective analysis. Am J Psychiatry 158:1693–1700
Dai X, Thavundayil J, Gianoulakis C (2002) Response of the hypothalamic–pituitary–adrenal axis to stress in the absence and presence of ethanol in subjects at high and low risk of alcoholism. Neuropsychopharmacology 27:442–452
Davidson JR, Kudler HS, Saunders WB, Smith RD (1990) Symptom and comorbidity patterns in World War II and Vietnam veterans with posttraumatic stress disorder. Compr Psychiatry 31:162–170
de Kloet ER, Joels M, Holsboer F (2005) Stress and the brain: from adaptation to disease. Nat Rev Neurosci 6:463–475
de Wit H, Soderpalm AH, Nikolayev L, Young E (2003) Effects of acute social stress on alcohol consumption in healthy subjects. Alcohol Clin Exp Res 27:1270–1277
Errico AL, Parsons OA, King AC, Lovallo WR (1993) Attenuated cortisol response to biobehavioral stressors in sober alcoholics. J Stud Alcohol 54:393–398
Filip M, Nowak E, Siwanowicz J, Przegalinski E (2000) Effects of corticosterone and its synthesis blockade on the cocaine-induced discriminative stimulus effects in rats. Pol J Pharmacol 52:411–421
Goeders NE (2002) The HPA axis and cocaine reinforcement. Psychoneuroendocrinology 27:13–33
Gold PW, Chrousos GP (2002) Organization of the stress system and its dysregulation in melancholic and atypical depression: high vs. low CRH/NE states. Mol Psychiatry 7:254–275
Gourley SL, Taylor JR (2009) Recapitulation and reversal of a persistent depression-like syndrome in rodents. Curr Protoc Neurosci Chapter 9: Unit 9 32
Griesbach GS, Hovda DA, Tio DL, Taylor AN (2011) Heightening of the stress response during the first weeks after a mild traumatic brain injury. Neuroscience 178:147–158
Harris RB, Gu H, Mitchell TD, Endale L, Russo M, Ryan DH (2004) Increased glucocorticoid response to a novel stress in rats that have been restrained. Physiol Behav 81:557–568
Hasin DS, Goodwin RD, Stinson FS, Grant BF (2005) Epidemiology of major depressive disorder: results from the National Epidemiologic Survey on Alcoholism and Related Conditions. Arch Gen Psychiatry 62:1097–1106
Hatzinger M, Reul JM, Landgraf R, Holsboer F, Neumann I (1996) Combined dexamethasone/CRH test in rats: hypothalamo–pituitary–adrenocortical system alterations in aging. Neuroendocrinology 64:349–356
Herman JP, Ostrander MM, Mueller NK, Figueiredo H (2005) Limbic system mechanisms of stress regulation: hypothalamo–pituitary–adrenocortical axis. Prog Neuropsychopharmacol Biol Psychiatry 29:1201–1213
Hernandez-Avila CA, Oncken C, Van Kirk J, Wand G, Kranzler HR (2002) Adrenocorticotropin and cortisol responses to a naloxone challenge and risk of alcoholism. Biol Psychiatry 51:652–658
Hodge CW, Aiken AS (1996) Discriminative stimulus function of ethanol: role of GABAA receptors in the nucleus accumbens. Alcohol Clin Exp Res 20:1221–1228
Hodge CW, Cox AA (1998) The discriminative stimulus effects of ethanol are mediated by NMDA and GABA(A) receptors in specific limbic brain regions. Psychopharmacology (Berl) 139:95–107
Hoffmann JP, Su SS (1998) Stressful life events and adolescent substance use and depression: conditional and gender differentiated effects. Subst Use Misuse 33:2219–2262
Ising M, Kunzel HE, Binder EB, Nickel T, Modell S, Holsboer F (2005) The combined dexamethasone/CRH test as a potential surrogate marker in depression. Prog Neuropsychopharmacol Biol Psychiatry 29:1085–1093
Jacobsen LK, Southwick SM, Kosten TR (2001) Substance use disorders in patients with posttraumatic stress disorder: a review of the literature. Am J Psychiatry 158:1184–1190
Karatsoreos IN, Bhagat SM, Bowles NP, Weil ZM, Pfaff DW, McEwen BS (2010) Endocrine and physiological changes in response to chronic corticosterone: a potential model of the metabolic syndrome in, ouse. Endocrinology 151:2117–2127
King A, Munisamy G, de Wit H, Lin S (2006) Attenuated cortisol response to alcohol in heavy social drinkers. Int J Psychophysiol 59:203–209
Kodl MM, Fu SS, Willenbring ML, Gravely A, Nelson DB, Joseph AM (2008) The impact of depressive symptoms on alcohol and cigarette consumption following treatment for alcohol and nicotine dependence. Alcohol Clin Exp Res 32:92–99
Koob GF (1999) Stress, corticotropin-releasing factor, and drug addiction. Ann N Y Acad Sci 897:27–45
Koros E, Kostowski W, Danysz W, Bienkowski P (1999) Ethanol discrimination in the rat: lack of modulation by restraint stress and memantine. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol 359:117–122
Kreek MJ, Koob GF (1998) Drug dependence: stress and dysregulation of brain reward pathways. Drug Alcohol Depend 51:23–47
Lovallo WR, Dickensheets SL, Myers DA, Thomas TL, Nixon SJ (2000) Blunted stress cortisol response in abstinent alcoholic and polysubstance-abusing men. Alcohol Clin Exp Res 24:651–658
Lu L, Shepard JD, Hall FS, Shaham Y (2003) Effect of environmental stressors on opiate and psychostimulant reinforcement, reinstatement and discrimination in rats: a review. Neurosci Biobehav Rev 27:457–491
Magarinos AM, Orchinik M, McEwen BS (1998) Morphological changes in the hippocampal CA3 region induced by non-invasive glucocorticoid administration: a paradox. Brain Res 809:314–318
Majumdar SK, Shaw GK, Bridges PK (1988) The dexamethasone suppression test in chronic alcoholics with and without depression and its relationship to their hepatic status. Drug Alcohol Depend 21:231–235
Makino S, Gold PW, Schulkin J (1994) Corticosterone effects on corticotropin-releasing hormone mRNA in the central nucleus of the amygdala and the parvocellular region of the paraventricular nucleus of the hypothalamus. Brain Res 640:105–112
Mantsch JR, Goeders NE (1998) Generalization of a restraint-induced discriminative stimulus to cocaine in rats. Psychopharmacology (Berl) 135:423–426
Mantsch JR, Cullinan WE, Tang LC, Baker DA, Katz ES, Hoks MA, Ziegler DR (2007) Daily cocaine self-administration under long-access conditions augments restraint-induced increases in plasma corticosterone and impairs glucocorticoid receptor-mediated negative feedback in rats. Brain Res 1167:101–111
Marti O, Armario A (1997) Influence of regularity of exposure to chronic stress on the pattern of habituation of pituitary–adrenal hormones, prolactin and glucose. Stress 1:179–189
McEwen BS (2007) Physiology and neurobiology of stress and adaptation: central role of the brain. Physiol Rev 87:873–904
McLaughlin KJ, Gomez JL, Baran SE, Conrad CD (2007) The effects of chronic stress on hippocampal morphology and function: an evaluation of chronic restraint paradigms. Brain Res 1161:56–64
Miczek KA, Mutschler NH, van Erp AM, Blank AD, McInerney SC (1999) d-amphetamine “cue” generalizes to social defeat stress: behavioral sensitization and attenuated accumbens dopamine. Psychopharmacology (Berl) 147:190–199
Mizoguchi K, Shoji H, Ikeda R, Tanaka Y, Tabira T (2008) Persistent depressive state after chronic stress in rats is accompanied by HPA axis dysregulation and reduced prefrontal dopaminergic neurotransmission. Pharmacol Biochem Behav 91:170–175
Morales-Medina JC, Sanchez F, Flores G, Dumont Y, Quirion R (2009) Morphological reorganization after repeated corticosterone administration in the hippocampus, nucleus accumbens and amygdala in the rat. J Chem Neuroanat
Otero Losada ME (1988) Changes in central GABAergic function following acute and repeated stress. Br J Pharmacol 93:483–490
Perrotti LI, Hadeishi Y, Ulery PG, Barrot M, Monteggia L, Duman RS, Nestler EJ (2004) Induction of deltaFosB in reward-related brain structures after chronic stress. J Neurosci 24:10594–10602
Piazza PV, Le Moal M (1998) The role of stress in drug self-administration. Trends Pharmacol Sci 19:67–74
Pollock VE (1992) Meta-analysis of subjective sensitivity to alcohol in sons of alcoholics. Am J Psychiatry 149:1534–1538
Pung T, Zimmerman K, Klein B, Ehrich M (2003) Corticosterone in drinking water: altered kinetics of a single oral dose of corticosterone and concentrations of plasma sodium, albumin, globulin, and total protein. Toxicol Ind Health 19:171–182
Raone A, Cassanelli A, Scheggi S, Rauggi R, Danielli B, De Montis MG (2007) Hypothalamus–pituitary–adrenal modifications consequent to chronic stress exposure in an experimental model of depression in rats. Neuroscience 146:1734–1742
Romeo RD, Bellani R, Karatsoreos IN, Chhua N, Vernov M, Conrad CD, McEwen BS (2006) Stress history and pubertal development interact to shape hypothalamic–pituitary–adrenal axis plasticity. Endocrinology 147:1664–1674
Sapolsky RM (2000) Glucocorticoids and hippocampal atrophy in neuropsychiatric disorders. Arch Gen Psychiatry 57:925–935
Schneier FR, Foose TE, Hasin DS, Heimberg RG, Liu SM, Grant BF, Blanco C (2010) Social anxiety disorder and alcohol use disorder co-morbidity in the National Epidemiologic Survey on Alcohol and Related Conditions. Psychol Med 40:977–988
Schuckit MA (2009) An overview of genetic influences in alcoholism. J Subst Abuse Treat 36:S5–S14
Schuckit MA, Smith TL (2000) The relationships of a family history of alcohol dependence, a low level of response to alcohol and six domains of life functioning to the development of alcohol use disorders. J Stud Alcohol 61:827–835
Sillaber I, Henniger MS (2004) Stress and alcohol drinking. Ann Med 36:596–605
Stolerman I (1992) Drugs of abuse: behavioural principles, methods and terms. Trends Pharmacol Sci 13:170–176
Trim RS, Schuckit MA, Smith TL (2009) The relationships of the level of response to alcohol and additional characteristics to alcohol use disorders across adulthood: a discrete-time survival analysis. Alcohol Clin Exp Res 33:1562–1570
Uhart M, Oswald L, McCaul ME, Chong R, Wand GS (2006) Hormonal responses to psychological stress and family history of alcoholism. Neuropsychopharmacology 31:2255–2263
Van Eekelen JA, Jiang W, De Kloet ER, Bohn MC (1988) Distribution of the mineralocorticoid and the glucocorticoid receptor mRNAs in the rat hippocampus. J Neurosci Res 21:88–94
Waltman C, McCaul ME, Wand GS (1994) Adrenocorticotropin responses following administration of ethanol and ovine corticotropin-releasing hormone in the sons of alcoholics and control subjects. Alcohol Clin Exp Res 18:826–830
Wand GS, Dobs AS (1991) Alterations in the hypothalamic–pituitary–adrenal axis in actively drinking alcoholics. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 72:1290–1295
Wang W, Sun D, Pan B, Roberts CJ, Sun X, Hillard CJ, Liu QS (2010) Deficiency in endocannabinoid signaling in the nucleus accumbens induced by chronic unpredictable stress. Neuropsychopharmacology
Acknowledgments
The authors would like to thank Dr. Cynthia Kuhn for discussions on corticosterone data interpretation, and Drs. Sarah Holstein and Sara Faccidomo, and Kelly Psilos for help with blood collection and/or blood analyses. This work was supported in part by funds from the National Institutes of Health AA016009 (JB), AA019682 (JB), AA014983 (CWH), ABMRF/The Foundation for Alcohol Research (JB), and by the Bowles Center for Alcohol Studies.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Besheer, J., Fisher, K.R., Grondin, J.J.M. et al. The effects of repeated corticosterone exposure on the interoceptive effects of alcohol in rats. Psychopharmacology 220, 809–822 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00213-011-2533-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00213-011-2533-8