Abstract
Rationale
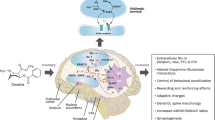
Glutaminase is considered the main glutamate (Glu)-producing enzyme. Two isoforms, liver (LGA)- and kidney (KGA)-type glutaminases, have been identified in neurons. The role of both enzymes in psychopharmacological responses to cocaine remains unknown.
Objectives
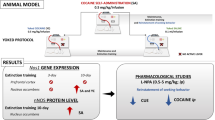
We examined both mRNA and protein expression of KGA and LGA in the brain of mice sensitized to cocaine. Additionally, total glutaminase activity was also measured.
Methods
Total glutaminase activity and mRNA and protein expression of KGA and LGA were measured on the dorsal striatum, prefrontal cortex, hippocampus and cerebellum of cocaine-sensitized mice.
Results
Cocaine-sensitized animals (20 mg/kg × 5 days, followed by 5 drug-free days) exhibited a decrease of total glutaminase activity in both the dorsal striatum and the prefrontal cortex. This was associated with an increase in KGA mRNA expression in both brain areas that was not observed when protein KGA levels were measured by western blot. LGA mRNA expression was increased as results of acute cocaine administration in sensitized animals, although protein levels were only enhanced in the prefrontal cortex of sensitized mice. These findings suggest that chronic cocaine administration modulates glutamate production through the regulation of glutaminase expression and activity. These actions are mainly observed in the prefrontal cortex–dorsal striatum circuit, the neuroanatomical target for the psychostimulant sensitization properties of cocaine.
Conclusions
The present results indicate that glutaminase enzymes (mainly KGA) are modulated by cocaine in both the prefrontal cortex and the dorsal striatum, as part of the neuroadaptions associated with behavioural sensitization to this drug of abuse.






Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- BS:
-
Behavioural sensitization
- CL:
-
Conditioned locomotion
- EAAC1:
-
Neuronal excitatory amino acid carrier 1
- GA:
-
Phosphate-activated glutaminase
- Gln:
-
Glutamine
- Glu:
-
Glutamate
- KGA:
-
Kidney-type glutaminase isoform
- LGA:
-
Liver-type glutaminase isoform
- mGluR:
-
Metabotropic glutamate receptor
- PFC:
-
Prefrontal cortex
- VTA:
-
Ventral tegmental area
References
Aledo JC, Gomez-Fabre PM, Olalla L, Marquez J (2000) Identification of two human glutaminase loci and tissue-specific expression of the two related genes. Mamm Genome 11:1107–1110
Aoyama K, Suh SW, Hamby AM, Liu J, Chan WY, Chen Y, Swanson RA (2006) Neuronal glutathione deficiency and age-dependent neurodegeneration in the EAAC1 deficient mouse. Nat Neurosci 9:119–126
Baker DA, Shen H, Kalivas PW (2002) Cystine/glutamate exchange serves as the source for extracellular glutamate: modifications by repeated cocaine administration. Amino Acids 23:161–162
Baker DA, McFarland K, Lake RW, Shen H, Tang XC, Toda S, Kalivas PW (2003) Neuroadaptations in cystine-glutamate exchange underlie cocaine relapse. Nat Neurosci 67:743–749
Choi KH, Edwards S, Graham DL, Larson EB, Whisler KN, Simmons D, Friedman AK, Walsh JJ, Rahman Z, Monteggia LM, Eisch AJ, Neve RL, Nestler EJ, Han MH, Self DW (2011) (2011) Reinforcement-related regulation of AMPA glutamate receptor subunits in the ventral tegmental area enhances motivation for cocaine. J Neurosci 31(21):7927–7937
Collingridge GL, Lester RA (1989) Excitatory amino acid receptors in the vertebrate central nervous system. Pharmacol Rev 41:143–210
Conti F, Weinberg RJ (1999) Shaping excitation at glutamatergic synapses. Trends Neurosci 22:451–458
Curthoys NP, Watford M (1995) Regulation of glutaminase activity and glutamine metabolism. Annu Rev Nutr 15:133–159
Dong Y, Nasif FJ, Tsui JJ, Ju WY, Cooper DC, Hu XT, Malenka RC, White FJ (2005) Cocaine-induced plasticity of intrinsic membrane properties in prefrontal cortex pyramidal neurons: adaptations in potassium currents. J Neurosci 25:936–940
Engblom D, Bilbao A, Sanchis-Segura C, Dahan L, Perreau-Lenz S, Balland B, Parkitna JR, Lujan R, Halbout B, Mameli M, Parlato R, Sprengel R, Luscher C, Schutz G, Spanagel R (2008) Glutamate receptors on dopamine neurons control the persistence of cocaine seeking. Neuron 59:497–508
Erecinska M, Silver IA (1990) Metabolism and role of glutamate in mammalian brain. Prog Neurobiol 35:245–296
Everitt BJ, Wolf ME (2002) Psychomotor stimulant addiction: a neural systems perspective. J Neurosci 22:3312–3320
Everitt BJ, Belin D, Economidou D, Pelloux Y, Dalley JW, Robbins TW (2008) Review. Neural mechanisms underlying the vulnerability to develop compulsive drug-seeking habits and addiction. Philos Trans R Soc Lond B Biol Sci 363:3125–3135
Ferrario CR, Li X, Wang X, Reimers JM, Uejima JL, Wolf ME (2010) The role of glutamate receptor redistribution in locomotor sensitization to cocaine. Neuropsychopharmacology 35:818–833
Fonnum F (1984) Glutamate: a neurotransmitter in mammalian brain. J Neurochem 42:1–11
Ghasemzadeh MB, Mueller C, Vasudevan P (2009a) Behavioral sensitization to cocaine is associated with increased glutamate receptor trafficking to the postsynaptic density after extended withdrawal period. Neuroscience 159:414–426
Ghasemzadeh MB, Vasudevan P, Mueller C, Seubert C, Mantsch JR (2009b) Neuroadaptations in the cellular and postsynaptic group 1 metabotropic glutamate receptor mGluR5 and Homer proteins following extinction of cocaine self-administration. Neurosci Lett 452:167–171
Gomez-Fabre PM, Aledo JC, Del Castillo-Olivares A, Alonso FJ, Nunez De Castro I, Campos JA, Marquez J (2000) Molecular cloning, sequencing and expression studies of the human breast cancer cell glutaminase. Biochem J 345(Pt 2):365–375
Heini HG, Gebhardt R, Brecht A, Mecke D (1987) Purification and characterization of rat liver glutaminase. Eur J Biochem 162:541–546
Ito R, Dalley JW, Robbins TW, Everitt BJ (2002) Dopamine release in the dorsal striatum during cocaine-seeking behavior under the control of a drug-associated cue. J Neurosci 22:6247–6253
Kalivas PW (2004) Glutamate systems in cocaine addiction. Curr Opin Pharmacol 4:23–29
Kalivas PW, Lalumiere RT, Knackstedt L, Shen H (2009) Glutamate transmission in addiction. Neuropharmacology 56(Suppl 1):169–173
Kanai Y, Hediger MA (1992) Primary structure and functional characterization of a high-affinity glutamate transporter. Nature 360:467–471
Kanai Y, Bhide PG, DiFiglia M, Hediger MA (1995) Neuronal high-affinity glutamate transport in the rat central nervous system. Neuroreport 6:2357–2362
Kauer JA, Malenka RC (2007) Synaptic plasticity and addiction. Nat Rev Neurosci 8:844–858
Kim M, Au E, Neve R, Yoon BJ (2009) AMPA receptor trafficking in the dorsal striatum is critical for behavioral sensitization to cocaine in juvenile mice. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 379:65–69
Kovacevic Z, McGivan JD (1983) Mitochondrial metabolism of glutamine and glutamate and its physiological significance. Physiol Rev 63:547–605
Kvamme K (1984) Glutamine metabolism in mammalian tissues. In: Häussinger D, Sies H (eds) Enzymes of cerebral glutamine metabolism. Springer, Berlin, pp 32–48
Lehre KP, Levy LM, Ottersen OP, Storm-Mathisen J, Danbolt NC (1995) Differential expression of two glial glutamate transporters in the rat brain: quantitative and immunocytochemical observations. J Neurosci 15:1835–1853
Marquez J, de la Oliva AR, Mates JM, Segura JA, Alonso FJ (2006) Glutaminase: a multifaceted protein not only involved in generating glutamate. Neurochem Int 48:465–471
McFarland K, Lapish CC, Kalivas PW (2003) Prefrontal glutamate release into the core of the nucleus accumbens mediates cocaine-induced reinstatement of drug-seeking behavior. J Neurosci 23:3531–3537
Miguens M, Crespo JA, Del Olmo N, Higuera-Matas A, Montoya GL, Garcia-Lecumberri C, Ambrosio E (2008) Differential cocaine-induced modulation of glutamate and dopamine transporters after contingent and non-contingent administration. Neuropharmacology 55:771–779
Mohn AR, Yao WD, Caron MG (2004) Genetic and genomic approaches to reward and addiction. Neuropharmacology 47(Suppl 1):101–110
Nasif FJ, Hu XT, White FJ (2005a) Repeated cocaine administration increases voltage-sensitive calcium currents in response to membrane depolarization in medial prefrontal cortex pyramidal neurons. J Neurosci 25:3674–3679
Nasif FJ, Sidiropoulou K, Hu XT, White FJ (2005b) Repeated cocaine administration increases membrane excitability of pyramidal neurons in the rat medial prefrontal cortex. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 312:1305–1313
Nicklas WJ, Zeevalk G, Hyndman A (1987) Interactions between neurons and glia in glutamate/glutamine compartmentation. Biochem Soc Trans 15:208–210
Nieoullon A, Canolle B, Masmejean F, Guillet B, Pisano P, Lortet S (2006) The neuronal excitatory amino acid transporter EAAC1/EAAT3: does it represent a major actor at the brain excitatory synapse? J Neurochem 98:1007–1018
Olalla L, Gutierrez A, Campos JA, Khan ZU, Alonso FJ, Segura JA, Marquez J, Aledo JC (2002) Nuclear localization of L-type glutaminase in mammalian brain. J Biol Chem 277:38939–38944
Olalla L, Gutierrez A, Jimenez AJ, Lopez-Tellez JF, Khan ZU, Perez J, Alonso FJ, de la Rosa V, Campos-Sandoval JA, Segura JA, Aledo JC, Marquez J (2008) Expression of the scaffolding PDZ protein glutaminase-interacting protein in mammalian brain. J Neurosci Res 86:281–292
Paxinos G, Franklin KBJ (2001) The mouse brain in stereotaxic coordinates, 2nd edn. Academic, New York
Pierce RC, Bell K, Duffy P, Kalivas PW (1996) Repeated cocaine augments excitatory amino acid transmission in the nucleus accumbens only in rats having developed behavioral sensitization. J Neurosci 16:1550–1560
Pradet-Balade B, Boulmé F, Beug H, Müllner EW, Garcia-Sanz JA (2001) Translation control: bridging the gap between genomics and proteomics? Trends Biochem Sci 26:225–229
Rothstein JD, Martin L, Levey AI, Dykes-Hoberg M, Jin L, Wu D, Nash N, Kuncl RW (1994) Localization of neuronal and glial glutamate transporters. Neuron 13:713–725
Schmidt HD, Pierce RC (2010) Cocaine-induced neuroadaptations in glutamate transmission: potential therapeutic targets for craving and addiction. Ann N Y Acad Sci 1187:35–75
Shashidharan P, Huntley GW, Meyer T, Morrison JH, Plaitakis A (1994) Neuron-specific human glutamate transporter: molecular cloning, characterization and expression in human brain. Brain Res 662:245–250
Velaz-Faircloth M, McGraw TS, Alandro MS, Fremeau RT Jr, Kilberg MS, Anderson KJ (1996) Characterization and distribution of the neuronal glutamate transporter EAAC1 in rat brain. Am J Physiol 270:C67–C75
Xi ZX, Ramamoorthy S, Baker DA, Shen H, Samuvel DJ, Kalivas PW (2002) Modulation of group II metabotropic glutamate receptor signaling by chronic cocaine. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 303:608–615
Xie X, Steketee JD (2008) Repeated exposure to cocaine alters the modulation of mesocorticolimbic glutamate transmission by medial prefrontal cortex group II metabotropic glutamate receptors. J Neurochem 107:186–196
Zhang GC, Vu K, Parelkar NK, Mao LM, Stanford IM, Fibuch EE, Wang JQ (2009) Acute administration of cocaine reduces metabotropic glutamate receptor 8 protein expression in the rat striatum in vivo. Neurosci Lett 449:224–227
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by grants of excellence P07-CTS-03324 (to F.R.F) and CVI-1543 (to J.M.) from the Consejería de Innovación, Ciencia y Empresa, and a grant from the Consejería de Salud of the Regional Andalusian Government, grants RD06/0001/0000 (to F.R.F.) and RD06/0001/1012 (to J.M.) of the RTA RETICS network from the Spanish Health Institute Carlos III, grant SAF2007-61953 from the Spanish Ministry of Education and Science (to J.M.) and grant 049/2009 from the Plan Nacional sobre Drogas 2009–2011 (to F.R.F.). E. Blanco is a recipient of a postdoctoral fellowship (Juan de la Cierva, 2008) from the Spanish Ministry of Education and Science. J.A. Campos-Sandoval is a recipient of a Marie Curie Post Doctoral Fellowship from the European Union.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Additional information
Eduardo Blanco and José Ángel Campos-Sandoval contributed equally to the present study.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Blanco, E., Campos-Sandoval, J.Á., Palomino, A. et al. Cocaine modulates both glutaminase gene expression and glutaminase activity in the brain of cocaine-sensitized mice. Psychopharmacology 219, 933–944 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00213-011-2418-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00213-011-2418-x