Abstract
Rationale
Discovery of an endocannabinoid signaling system launched the development of the blocker rimonabant, a cannabinoid CB1 receptor (CB1R) antagonist/inverse agonist. Due to untoward effects, this medication was withdrawn and efforts have been directed towards discovering chemicals with more benign profiles.
Objective
This study aims to comparatively evaluate new ligands using a rimonabant discriminated drinking aversion procedure.
Methods
Rats discriminated between rimonabant (5.6 mg/kg) and vehicle. The 30 min saccharin (0.1%) drinking after rimonabant pretreatment was followed by injection of lithium chloride (120 mg/kg) in the experimental animals. After vehicle pretreatment, experimental animals were given i.p. NaCl (10 ml/kg). Postdrinking treatment for controls was NaCl, irrespective of pretreatment condition (rimonabant or vehicle).
Results
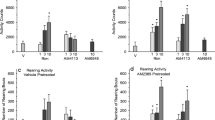
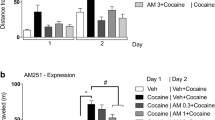
The centrally acting neutral CB1R antagonist AM4113, but not the limited brain penetrating CB1R neutral antagonist AM6545, substituted for rimonabant. The CB1R agonists THC (1–10 mg/kg), AM1346 (1–10 mg/kg) did not substitute. The rimonabant-induced conditioned suppression of saccharin drinking was attenuated when CB1R agonists AM5983 (0.01–1 mg/kg) and THC (10 mg/kg), but not the CB1R agonist AM1346 (0.1–18 mg/kg), were combined with rimonabant (5.6 mg/kg). By varying the injection-to-test interval, we gauged the relative duration of the cueing effects of rimonabant, and the in vivo functional half-life was estimated to be approximately 1.5 h.
Conclusion
A neutral CB1R antagonist (AM4113) produced cueing effects similar to those of rimonabant and generalization likely was centrally mediated. The functional cueing effects of rimonabant are relatively short-acting, pharmacologically selective, and differentially blocked by cannabinergics.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Baskfield CY, Martin BR, Wiley JL (2004) Differential effects of delta-9-tetrahydrocannabinol and methanandamide in CB1 knockout and wild-type mice. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 309:86–91
Chambers AP, Vemuri VK, Peng Y, Wood JT, Olszewska T, Pittman QJ, Makriyannis A, Sharkey KA (2007) A neutral CB1 receptor antagonist reduces weight gain in rat. Am J Physiol Regul Integr Comp Physiol 293:R2185–R2193
Cluny NL, Vemuri VK, Chambers AP, Limebeer CL, Bedard H, Wood JT, Lutz B, Zimmer A, Parker LA, Makriyannis A, Sharkey KA (2010) A novel peripherally restricted cannabinoid receptor antagonist, AM6545, reduces food intake and body weight, but does not cause malaise, in rodents. Br J Pharmacol 161:629–642
Cohen C, Perrault G, Voltz C, Steinberg R, Soubrie P (2002) SR141716, a central cannabinoid (CB(1)) receptor antagonist, blocks the motivational and dopamine-releasing effects of nicotine in rats. Behav Pharmacol 13:451–463
Colpaert FC, Niemegeers CJ, Janssen PA (1975) Differential response control by isopropamide: a peripherally induced discriminative cue. Eur J Pharmacol 34:381–384
Colpaert FC, Kuyps JJ, Niemegeers CJ, Janssen PA (1976) Discriminative stimulus properties of a low dl-amphetamine dose. Arch Int Pharmacodyn Thér 223:34–42
Davis CM, Stevenson GW, Canadas F, Ullrich T, Rice KC, Riley AL (2009) Discriminative stimulus properties of naloxone in Long–Evans rats: assessment with the conditioned taste aversion baseline of drug discrimination learning. Psychopharmacol Berl 203:421–429
Di Marzo V (2010) Anandamide serves two masters in the brain. Nat Neurosci 13:1446–1448
Hanus LO (2009) Pharmacological and therapeutic secrets of plant and brain (endo)cannabinoids. Med Res Rev 29:213–271
Huestis MA, Boyd SJ, Heishman SJ, Preston KL, Bonnet D, Le Fur G, Gorelick DA (2007) Single and multiple doses of rimonabant antagonize acute effects of smoked cannabis in male cannabis users. Psychopharmacol Berl 194:505–515
Janero DR, Vadivel SK, Makriyannis A (2009) Pharmacotherapeutic modulation of the endocannabinoid signalling system in psychiatric disorders: drug-discovery strategies. Int Rev Psychiatry 21:122–133
Järbe TUC (1989) Discrimination learning with drug stimuli: methods and applications. In: Boulten AA, Baker GB, Greenshaw AJ (eds) Neuromethods, vol 13, Psychopharmacology. Humana Press, Clifton, pp 513–563
Järbe TUC (2011) Perceptual drug discriminative aspects of the endocannabinoid signaling system in animals and man. In: Glennon RA, Young R (eds) Drug discrimination: applications to medicinal chemistry and drug studies. Wiley Publ. Co., Hoboken
Järbe TUC, Lamb RJ (1995) Discriminated conditioned taste aversion for studying multi-element stimulus control. Behav Pharmacol 6:149–155
Järbe TUC, Lamb RJ (1999) Effects of lithium dose (UCS) on the acquisition and extinction of a discriminated morphine aversion: tests with morphine and delta-9-THC. Behav Pharmacol 10:349–358
Järbe TUC, Sheppard R, Lamb RJ, Makriyannis A, Lin S, Goutopoulos A (1998) Effects of delta-9-tetrahydrocannabinol and (R)-methanandamide on open-field behavior in rats. Behav Pharmacol 9:169–174
Järbe TUC, Lamb RJ, Lin S, Makriyannis A (2001) (R)-methanandamide and Δ9-THC as discriminative stimuli in rats: tests with the cannabinoid antagonist SR-141716 and the endogenous ligand anandamide. Psychopharmacol Berl 156:369–380
Järbe TUC, Andrzejewski ME, DiPatrizio NV (2002) Interactions between the CB1 receptor agonist delta-9-THC and the CB1 receptor antagonist SR-141716 in rats: open-field revisited. Pharmacol Biochem Behav 73:911–919
Järbe TUC, DiPatrizio NV, Li C, Makriyannis A (2003) The cannabinoid receptor antagonist SR-141716 does not readily antagonize open-field effects induced by the cannabinoid receptor agonist (R)-methanandamide in rats. Pharmacol Biochem Behav 75:809–821
Järbe TUC, Harris MY, Li C, Liu Q, Makriyannis A (2004) Discriminative stimulus effects in rats of SR-141716 (rimonabant), a cannabinoid CB1 receptor antagonist. Psychopharmacol Berl 177:35–45
Järbe TUC, Lamb RJ, Liu Q, Makriyannis A (2006a) Discriminative stimulus functions of AM-1346, a CB1R selective anandamide analog, in rats trained with ∆9-THC or (R)-methanandamide (AM-356). Psychopharmacol Berl 188:315–323
Järbe TUC, Liu Q, Makriyannis A (2006b) Antagonism of discriminative stimulus effects of delta-9-THC and (R)-methanandamide in rats. Psychopharmacol Berl 184:36–45
Järbe TUC, DiPatrizio NV, Li C, Makriyannis A (2007) Effects of AM1346, a high-affinity CB1 receptor selective anandamide analog, on open-field behavior in rats. Behav Pharmacol 18:673–680
Järbe TUC, LeMay BJ, Olszewska T, Vemuri VK, Wood JT, Makriyannis A (2008a) Intrinsic effects of AM4113, a putative neutral CB1 receptor selective antagonist, on open-field behaviors in rats. Pharmacol Biochem Behav 91:84–90
Järbe TUC, Li C, Vadivel SK, Makriyannis A (2008b) Discriminative stimulus effects of the cannabinoid CB1 receptor antagonist rimonabant in rats. Psychopharmacol Berl 198:467–478
Järbe TUC, Li C, Liu Q, Makriyannis A (2009) Discriminative stimulus functions in rats of AM1346, a high-affinity CB1R selective anandamide analog. Psychopharmacol Berl 203:229–239
Järbe TUC, Gifford RS, Makriyannis A (2010) Antagonism of THC-induced behavioral effects by rimonabant: time course studies in rats. Eur J Pharmacol 648:133–138
Kirk RE (1968) Experimental design: procedures for the behavioral sciences, 2nd edn. Brooks/Cole, Belmont, CA
Le Foll B, Goldberg SR (2004) Rimonabant, a CB1 antagonist, blocks nicotine-conditioned place preferences. NeuroReport 15:2139–2143
Limebeer CL, Vemuri VK, Bedard H, Lang ST, Ossenkopp KP, Makriyannis A, Parker LA (2010) Inverse agonism of cannabinoid CB1 receptors potentiates LiCl-induced nausea in the conditioned gaping model in rats. Br J Pharmacol 161:336–349
Mansbach RS, Rovetti CC, Winston EN, Lowe JA 3rd (1996) Effects of the cannabinoid CB1 receptor antagonist SR141716A on the behavior of pigeons and rats. Psychopharmacol Berl 124:315–322
McLaughlin PJ, Winston K, Swezey L, Wisniecki A, Aberman J, Tardif DJ, Betz AJ, Ishiwari K, Makriyannis A, Salamone JD (2003) The cannabinoid CB1 antagonists SR 141716A and AM 251 suppress food intake and food-reinforced behavior in a variety of tasks in rats. Behav Pharmacol 14:583–588
McLaughlin PJ, Winston KM, Limebeer CL, Parker LA, Makriyannis A, Salamone JD (2005) The cannabinoid CB1 antagonist AM 251 produces food avoidance and behaviors associated with nausea but does not impair feeding efficiency in rats. Psychopharmacol Berl 180:286–293
McMahon LR (2006) Discriminative stimulus effects of the cannabinoid CB1 antagonist SR 141716A in rhesus monkeys pretreated with Δ9-tetrahydrocannabinol. Psychopharmacol Berl 188:306–314
McMahon LR, Ginsburg BC, Lamb RJ (2008) Cannabinoid agonists differentially substitute for the discriminative stimulus effects of Δ9-tetrahydrocannabinol in C57BL/6J mice. Psychopharmacol Berl 198:487–495
Parker LA, Limebeer CL, Rock EM, Litt DL, Kwiatkowska M, Piomelli D (2009) The FAAH inhibitor URB-597 interferes with cisplatin- and nicotine-induced vomiting in the Suncus murinus (house musk shrew). Physiol Behav 97:121–124
Pério A, Rinaldi-Carmona M, Maruani J, Barth F, Le Fur G, Soubrié P (1996) Central mediation of the cannabinoid cue: activity of a selective CB1 antagonist, SR 141716A. Behav Pharmacol 7:65–71
Pertwee RG (2010) Receptors and channels targeted by synthetic cannabinoid receptor agonists and antagonists. Curr Med Chem 17:1360–1381
Sink KS, McLaughlin PJ, Wood JA, Brown C, Fan P, Vemuri VK, Peng Y, Olszewska T, Thakur GA, Makriyannis A, Parker LA, Salamone JD (2008) The novel cannabinoid CB1 receptor neutral antagonist AM4113 suppresses food intake and food-reinforced behavior but does not induce signs of nausea in rats. Neuropsychopharmacology 33:946–955
Sink KS, Segovia KN, Sink J, Randall PA, Collins LE, Correa M, Markus EJ, Vemuri VK, Makriyannis A, Salamone JD (2009a) Potential anxiogenic effects of cannabinoid CB1 receptor antagonists/inverse agonists in rats: comparisons between AM4113, AM251, and the benzodiazepine inverse agonist FG-7142. Eur Neuropsychopharmacol 20:112–122
Sink KS, Vemuri VK, Wood J, Makriyannis A, Salamone JD (2009b) Oral bioavailability of the novel cannabinoid CB1 antagonist AM6527: effects on food-reinforced behavior and comparisons with AM4113. Pharmacol Biochem Behav 91:303–306
Sink KS, Segovia KN, Collins LE, Markus EJ, Vemuri VK, Makriyannis A, Salamone JD (2010) The CB1 inverse agonist AM251, but not the CB1 antagonist AM4113, enhances retention of contextual fear conditioning in rats. Pharmacol Biochem Behav 95:479–484
Solinas M, Panlilio LV, Antoniou K, Pappas LA, Goldberg SR (2003) The cannabinoid CB1 antagonist N-piperidinyl-5-(4-chlorophenyl)-1-(2, 4-dichlorophenyl) -4-methylpyrazole-3-carboxamide (SR-141716A) differentially alters the reinforcing effects of heroin under continuous reinforcement, fixed ratio, and progressive ratio schedules of drug self-administration in rats. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 306:93–102
Solinas M, Goldberg SR, Piomelli D (2008) The endocannabinoid system in brain reward processes. Br J Pharmacol 154:369–383
Tai S, Järbe TUC, Li C, Vadivel SK, Makriyannis A (2009) Discriminative stimulus functions of methanandamide and ∆9-THC in rats: tests with aminoalkylindoles (WIN55,212-2 and AM678) and ethanol. International Cannabinoid Research Society
Tam J, Vemuri VK, Liu J, Batkai S, Mukhopadhyay B, Godlewski G, Osei-Hyiaman D, Ohnuma S, Ambudkar SV, Pickel J, Makriyannis A, Kunos G (2010) Peripheral CB1 cannabinoid receptor blockade improves cardiometabolic risk in mouse models of obesity. J Clin Invest 120:2953–2966
Thakur GA, Nikas SP, Li C, Makriyannis A (2005) Structural requirements for cannabinoid receptor probes. Hand Exp Pharm 168:209–246
Vemuri VK, Janero DR, Makriyannis A (2008) Pharmacotherapeutic targeting of the endocannabinoid signaling system: drugs for obesity and the metabolic syndrome. Physiol Behav 93:671–686
Welzl H, D'Adamo P, Lipp HP (2001) Conditioned taste aversion as a learning and memory paradigm. Behav Brain Res 125:205–213
Acknowledgments
We thank the National Institute on Drug Abuse (NIDA), Bethesda, MD, USA for supplies of Δ9-THC and rimonabant, and also thanking Roger S. Gifford as well as three anonymous reviewers for their comments on earlier drafts of this manuscript. The studies were supported by NIDA Grants DA 09064, 03801, 9158, 7215, and 00493.
Disclosure Statement
All authors declare that there is no actual or potential conflict of interest related to this manuscript. 'Role of the funding source': Authors declare that the study sponsor did not have any role in study design; in the collection, analysis, and interpretation of data; in the writing of the report; and in the decision to submit the paper for publication.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Järbe, T.U.C., LeMay, B.J., Vemuri, V.K. et al. Central mediation and differential blockade by cannabinergics of the discriminative stimulus effects of the cannabinoid CB1 receptor antagonist rimonabant in rats. Psychopharmacology 216, 355–365 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00213-011-2226-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00213-011-2226-3