Abstract
Rationale
We have recently shown that post-extinction exposure of rats to a sub-threshold reminder shock can reactivate extinguished context-related freezing and found that chronic treatment with fluoxetine before fear extinction prevents this phenomenon.
Objectives
In the present study, we examined whether these findings would be confirmed with auditory fear conditioning.
Methods
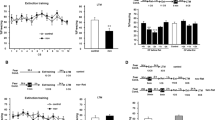
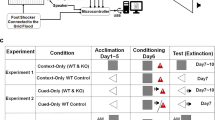
Rats were initially submitted to a session of five tone–shock pairings with either a 0.7- or 0.1-mA shock and underwent, 3 days later, a session of 20 tone-alone trials.
Results
At the beginning of this latter session, we observed cue-conditioned freezing in rats that received the strong, but not the weak, shock. At the end, both groups (strong and weak shocks) displayed similar low levels of freezing, indicating fear extinction in rats exposed to the strong shock. These rats exhibited again high levels of cue-evoked freezing when exposed to three tone–shock pairings with 0.1-mA shock. This reemergence of cue-conditioned fear was completely abolished by chronic (over a 21-day period) fluoxetine treatment which spared, when administered before the initial fear conditioning, the original tone–shock association.
Conclusions
These data extend our previous findings and suggest that chronic fluoxetine treatment favor extinction memory by dampening the reactivation of the original tone–shock association.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Alme MN, Wibrand K, Dagestad G, Bramham CR (2007) Chronic fluoxetine treatment induces brain region-specific upregulation of genes associated with BDNF-induced long-term potentiation. Neural Plast 2007:26496
Berthier ML, Kulisevsky J, Fernandez Benitez JA, Gironell A (1998) Reactivation of posttraumatic stress disorder after minor head injury. Depress Anxiety 8:43–47
Bianchi P, Ciani E, Guidi S, Trazzi S, Felice D, Grossi G, Fernandez M, Giuliani A, Calza L, Bartesaghi R (2010) Early pharmacotherapy restores neurogenesis and cognitive performance in the Ts65Dn mouse model for Down syndrome. J Neurosci 30:8769–8779
Bouton ME (2002) Context, ambiguity, and unlearning: sources of relapse after behavioral extinction. Biol Psychiatry 52:976–986
Bouton ME, Bolles RC (1979) Role of conditioned contextual stimuli in reinstatement of extinguished fear. J Exp Psychol Anim Behav Process 5:368–378
Brady K, Pearlstein T, Asnis GM, Baker D, Rothbaum B, Sikes CR, Farfel GM (2000) Efficacy and safety of sertraline treatment of posttraumatic stress disorder: a randomized controlled trial. JAMA 283:1837–1844
Cavazzuti E, Bertolini A, Vergoni AV, Arletti R, Poggioli R, Forgione A, Benelli A (1999) l-Sulpiride, at a low, non-neuroleptic dose, prevents conditioned fear stress-induced freezing behavior in rats. Psychopharmacology (Berl) 143:20–23
Connor KM, Sutherland SM, Tupler LA, Malik ML, Davidson JR (1999) Fluoxetine in post-traumatic stress disorder. Randomised, double-blind study. Br J Psychiatry 175:17–22
Dirikx T, Hermans D, Vansteenwegen D, Baeyens F, Eelen P (2007) Reinstatement of conditioned responses in human differential fear conditioning. J Behav Ther Exp Psychiatry 38:237–251
Dirikx T, Vansteenwegen D, Eelen P, Hermans D (2009) Non-differential return of fear in humans after a reinstatement procedure. Acta Psychol (Amst) 130:175–182
Dykman RA, Ackerman PT, Newton JE (1997) Posttraumatic stress disorder: a sensitization reaction. Integr Physiol Behav Sci 32:9–18
Eysenck HJ (1979) Behavioral therapy and the philosophers. Behav Res Ther 17:511–514
Farinelli M, Deschaux O, Hugues S, Thevenet A, Garcia R (2006) Hippocampal train stimulation modulates recall of fear extinction independently of prefrontal cortex synaptic plasticity and lesions. Learn Mem 13:329–334
Garcia R (2002) Postextinction of conditioned fear: between two CS-related memories. Learn Mem 9:361–363
Garcia R, Spennato G, Nilsson-Todd L, Moreau JL, Deschaux O (2008) Hippocampal low-frequency stimulation and chronic mild stress similarly disrupt fear extinction memory in rats. Neurobiol Learn Mem 89:560–566
Hermans D, Craske MG, Mineka S, Lovibond PF (2006) Extinction in human fear conditioning. Biol Psychiatry 60:361–368
Hugues S, Chessel A, Lena I, Marsault R, Garcia R (2006) Prefrontal infusion of PD098059 immediately after fear extinction training blocks extinction-associated prefrontal synaptic plasticity and decreases prefrontal ERK2 phosphorylation. Synapse 60:280–287
Martenyi F, Soldatenkova V (2006) Fluoxetine in the acute treatment and relapse prevention of combat-related post-traumatic stress disorder: analysis of the veteran group of a placebo-controlled, randomized clinical trial. Eur Neuropsychopharmacol 16:340–349
Martenyi F, Brown EB, Zhang H, Koke SC, Prakash A (2002) Fluoxetine v. placebo in prevention of relapse in post-traumatic stress disorder. Br J Psychiatry 181:315–320
Milad MR, Pitman RK, Ellis CB, Gold AL, Shin LM, Lasko NB, Zeidan MA, Handwerger K, Orr SP, Rauch SL (2009) Neurobiological basis of failure to recall extinction memory in posttraumatic stress disorder. Biol Psychiatry 66:1075–1082
Onder E, Tural U, Aker T (2006) A comparative study of fluoxetine, moclobemide, and tianeptine in the treatment of posttraumatic stress disorder following an earthquake. Eur Psychiatry 21:174–179
Pavlov I (1927) Conditioned reflexes. Oxford University Press, Oxford
Peters J, Dieppa-Perea LM, Melendez LM, Quirk GJ (2010) Induction of fear extinction with hippocampal–infralimbic BDNF. Science 328:1288–1290
Rau V, Fanselow MS (2009) Exposure to a stressor produces a long lasting enhancement of fear learning in rats. Stress 12:125–133
Rau V, DeCola JP, Fanselow MS (2005) Stress-induced enhancement of fear learning: an animal model of posttraumatic stress disorder. Neurosci Biobehav Rev 29:1207–1223
Rau V, Oh I, Laster M, Eger EI 2nd, Fanselow MS (2009) Isoflurane suppresses stress-enhanced fear learning in a rodent model of post-traumatic stress disorder. Anesthesiology 110:487–495
Rescorla RA, Heth CD (1975) Reinstatement of fear to an extinguished conditioned stimulus. J Exp Psychol Anim Behav Process 1:88–96
Rocher C, Spedding M, Munoz C, Jay TM (2004) Acute stress-induced changes in hippocampal/prefrontal circuits in rats: effects of antidepressants. Cereb Cortex 14:224–229
Siegmund A, Wotjak CT (2006) Toward an animal model of posttraumatic stress disorder. Ann NY Acad Sci 1071:324–334
Spennato G, Zerbib C, Mondadori C, Garcia R (2008) Fluoxetine protects hippocampal plasticity during conditioned fear stress and prevents fear learning potentiation. Psychopharmacology (Berl) 196:583–589
Tucker P, Zaninelli R, Yehuda R, Ruggiero L, Dillingham K, Pitts CD (2001) Paroxetine in the treatment of chronic posttraumatic stress disorder: results of a placebo-controlled, flexible-dosage trial. J Clin Psychiatry 62:860–868
Acknowledgments
This study was supported by F. Hoffmann-La Roche (J.L.M) and the University of Nice-Sophia Antipolis (O.D., G.S., R.G.). We thank Dr. Scott Edwards for reviewing the English style of the manuscript.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Deschaux, O., Spennato, G., Moreau, JL. et al. Chronic treatment with fluoxetine prevents the return of extinguished auditory-cued conditioned fear. Psychopharmacology 215, 231–237 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00213-010-2134-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00213-010-2134-y