Abstract
Background
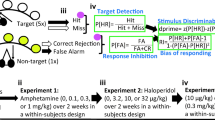
Cognitive deficits are a core feature of schizophrenia that respond minimally to existing drugs. PCP is commonly used to model schizophrenia-like deficits preclinically although different dosing protocols may affect different domains. Here we characterise the acute, and chronic intermittent effects of PCP in the 5-choice serial reaction time task (5-CSRTT) in rats, and assess the effects of clozapine. In a novel approach, we also assess the effects of increased inhibitory load and conduct clinically relevant signal detection analysis (SDA).
Materials and methods
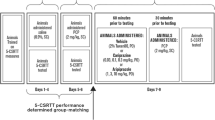
The effects of acute and repeated PCP (2.58 mg/kg) treatment on attentional processes and inhibitory control were assessed during and following the chronic treatment regime in the presence or absence of chronic clozapine (20 mg/kg/day).
Results
Thirty minutes post-PCP injection, there was an increase in anticipatory responding which disappeared after 24 h. Although, acute PCP did not change accuracy of responding or processing speed, repeated PCP revealed delayed deficits in cognitive processing speed which were partly ameliorated by clozapine. Extended inter-trial intervals increased premature responding, while SDA revealed that clozapine modified persistent PCP-induced deficits in lnBeta (a composite measure of risk taking versus caution).
Conclusion
Acute NMDA receptor antagonism impairs inhibitory control, whereas repeated treatment produces delayed deficits in cognitive processing speed. The ability of clozapine partially to restore persistent PCP-induced deficits in processing speed and in lnBeta is consistent with clinical findings. This suggests that the enduring effects of repeated PCP treatment, combined with SDA, offers a useful, translational, approach to evaluate novel cognitive enhancers in the 5-CSRTT.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abdul-Monim Z, Reynolds GP, Neill JC (2006) The effect of atypical and classical antipsychotics on sub-chronic PCP-induced cognitive deficits in a reversal-learning paradigm. Behav Brain Res 169:263–273
Allen RM, Young SJ (1978) Phencyclidine-induced psychosis. Am J Psychiatry 135:1081–1084
Amitai N, Markou A (2009) Increased impulsivity and disrupted attention induced by repeated phencyclidine are not attenuated by chronic quetiapine treatment. Pharmacol Biochem Behav 93:248–257
Amitai N, Semenova S, Markou A (2007) Cognitive-disruptive effects of the psychotomimetic phencyclidine and attenuation by atypical antipsychotic medications in rats. Psychopharmacology (Berl) 193:521–537
Andreasen NC, Rezai K, Alliger R, Swayze VW 2nd, Flaum M, Kirchner P, Cohen G, O’Leary DS (1992) Hypofrontality in neuroleptic-naive patients and in patients with chronic schizophrenia. Assessment with xenon 133 single-photon emission computed tomography and the Tower of London. Arch Gen Psychiatry 49:943–958
Auclair AL, Besnard J, Newman-Tancredi A, Depoortere R (2009) The 5-choice serial reaction time task: comparison between Sprague–Dawley and Long–Evans rats on acquisition of task, and sensitivity to phenycyclidine. Pharmacol Biochem Behav 92:363–369
Baldessarini RJ, Centorrino F, Flood JG, Volpicelli SA, Huston-Lyons D, Cohen BM (1993) Tissue concentrations of clozapine and its metabolites in the rat. Neuropsychopharmacology 9:117–124
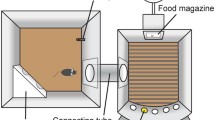
Bari A, Dalley JW, Robbins TW (2008) The application of the 5-choice serial reaction time task for the assessment of visual attentional processes and impulse control in rats. Nat Protoc 3:759–767
Bowie CR, Harvey PD (2006) Treatment of cognitive deficits in schizophrenia. Curr Opin Investig Drugs 7:608–613
Brébion G, Larøi F, Van der Linden M (2010) Associations of hallucination proneness with free-recall intrusions and response bias in a nonclinical sample. J Clin Exp Neuropsychol (in press): 1–8
Buchsbaum MS, Hazlett EA (1998) Positron emission tomography studies of abnormal glucose metabolism in schizophrenia. Schizophr Bull 24:343–364
Buchsbaum MS, Nuechterlein KH, Haier RJ, Wu J, Sicotte N, Hazlett E, Asarnow R, Potkin S, Guich S (1990) Glucose metabolic rate in normals and schizophrenics during the Continuous Performance Test assessed by positron emission tomography. Br J Psychiatry 156:216–227
Carter CS, Barch DM, Buchanan RW, Bullmore E, Krystal JH, Cohen J, Geyer M, Green M, Nuechterlein KH, Robbins T, Silverstein S, Smith EE, Strauss M, Wykes T, Heinssen R (2008) Identifying cognitive mechanisms targeted for treatment development in schizophrenia: an overview of the first meeting of the Cognitive Neuroscience Treatment Research to Improve Cognition in Schizophrenia Initiative. Biol Psychiatry 64:4–10
Chudasama Y, Passetti F, Rhodes SE, Lopian D, Desai A, Robbins TW (2003) Dissociable aspects of performance on the 5-choice serial reaction time task following lesions of the dorsal anterior cingulate, infralimbic and orbitofrontal cortex in the rat: differential effects on selectivity, impulsivity and compulsivity. Behav Brain Res 146:105–119
Cochran SM, Kennedy M, McKerchar CE, Steward LJ, Pratt JA, Morris BJ (2003) Induction of metabolic hypofunction and neurochemical deficits after chronic intermittent exposure to phencyclidine: differential modulation by antipsychotic drugs. Neuropsychopharmacology 28:265–275
Cohen RM, Nordahl TE, Semple WE, Andreason P, Litman RE, Pickar D (1997) The brain metabolic patterns of clozapine- and fluphenazine-treated patients with schizophrenia during a continuous performance task. Arch Gen Psychiatry 54:481–486
Cornblatt BA, Lenzenweger MF, Erlenmeyer-Kimling L (1989) The continuous performance test, identical pairs version: II. Contrasting attentional profiles in schizophrenic and depressed patients. Psychiatry Res 29:65–85
Daban C, Martinez-Aran A, Torrent C, Tabares-Seisdedos R, Balanza-Martinez V, Salazar-Fraile J, Selva-Vera G, Vieta E (2006) Specificity of cognitive deficits in bipolar disorder versus schizophrenia. A systematic review. Psychother Psychosom 75:72–84
Egan MF, Goldberg TE, Gscheidle T, Weirich M, Bigelow LB, Weinberger DR (2000) Relative risk of attention deficits in siblings of patients with schizophrenia. Am J Psychiatry 157:1309–1316
Egerton A, Reid L, McGregor S, Cochran SM, Morris BJ, Pratt JA (2008) Subchronic and chronic PCP treatment produces temporally distinct deficits in attentional set shifting and prepulse inhibition in rats. Psychopharmacology (Berl) 198:37–49
Epstein JI, Keefe RS, Roitman SL, Harvey PD, Mohs RC (1996) Impact of neuroleptic medications on continuous performance test measures in schizophrenia. Biol Psychiatry 39:902–905
Fleck DE, Sax KW, Strakowski SM (2001) Reaction time measures of sustained attention differentiate bipolar disorder from schizophrenia. Schizophr Res 52:251–259
Galletly C (2008) Recent advances in treating cognitive impairment in schizophrenia. Psychopharmacology (Berl). doi:10.1007/s00213-008-1302-9
Galletly CA, Clark CR, McFarlane AC, Weber DL (2000) The effect of clozapine on the speed and accuracy of information processing in schizophrenia. Prog Neuropsychopharmacol Biol Psychiatry 24:1329–1338
Green MF (1996) What are the functional consequences of neurocognitive deficits in schizophrenia? Am J Psychiatry 153:321–330
Green MF, Kern RS, Heaton RK (2004) Longitudinal studies of cognition and functional outcome in schizophrenia: implications for MATRICS. Schizophr Res 72:41–51
Grier JB (1971) Nonparametric indexes for sensitivity and bias. Psychol Bull 75:424–429
Hazlett EA, Buchsbaum MS, Jeu LA, Nenadic I, Fleischman MB, Shihabuddin L, Haznedar MM, Harvey PD (2000) Hypofrontality in unmedicated schizophrenia patients studied with PET during performance of a serial verbal learning task. Schizophr Res 43:33–46
Henry JD, Crawford JR (2005) A meta-analytic review of verbal fluency deficits in schizophrenia relative to other neurocognitive deficits. Cognit Neuropsychiatry 10:1–33
Higgins GA, Ballard TM, Huwyler J, Kemp JA, Gill R (2003) Evaluation of the NR2B-selective NMDA receptor antagonist Ro 63-1908 on rodent behaviour: evidence for an involvement of NR2B NMDA receptors in response inhibition. Neuropharmacology 44:324–341
Hill K, Mann L, Laws KR, Stephenson CM, Nimmo-Smith I, McKenna PJ (2004) Hypofrontality in schizophrenia: a meta-analysis of functional imaging studies. Acta Psychiatr Scand 110:243–256
Hughes C, Kumari V, Soni W, Das M, Binneman B, Drozd S, O’Neil S, Mathew V, Sharma T (2003) Longitudinal study of symptoms and cognitive function in chronic schizophrenia. Schizophr Res 59:137–146
Ishigaki T, Tanno Y (1999) The signal detection ability of patients with auditory hallucination: analysis using the continuous performance test. Psychiatry Clin Neurosci 53:471–476
Ito M, Kanno M, Mori Y, Niwa S-I (1997) Attention deficits assessed by continuous performance test and span of apprehension test in Japanese schizophrenic patients. Schizophr Res 23:205–211
Jentsch JD, Roth RH (1999) The neuropsychopharmacology of phencyclidine: from NMDA receptor hypofunction to the dopamine hypothesis of schizophrenia. Neuropsychopharmacology 20:201–225
Jentsch JD, Tran A, Le D, Youngren KD, Roth RH (1997) Subchronic phencyclidine administration reduces mesoprefrontal dopamine utilization and impairs prefrontal cortical-dependent cognition in the rat. Neuropsychopharmacology 17(2):92–99
Jones LA, Cardno AG, Sanders RD, Owen MJ, Williams J (2001) Sustained and selective attention as measures of genetic liability to schizophrenia. Schizophr Res 48:263–272
Keefe RS, Poe M, Walker TM, Kang JW, Harvey PD (2006) The Schizophrenia Cognition Rating Scale: an interview-based assessment and its relationship to cognition, real-world functioning, and functional capacity. Am J Psychiatry 163:426–432
Kerns JG, Nuechterlein KH, Braver TS, Barch DM (2008) Executive functioning component mechanisms and schizophrenia. Biol Psychiatry 64:26–33
Laurent A, Saoud M, Bougerol T, d’Amato T, Anchisi AM, Biloa-Tang M, Dalery J, Rochet T (1999) Attentional deficits in patients with schizophrenia and in their non-psychotic first-degree relatives. Psychiatry Res 89:147–159
Le Pen G, Grottick AJ, Higgins GA, Moreau JL (2003) Phencyclidine exacerbates attentional deficits in a neurodevelopmental rat model of schizophrenia. Neuropsychopharmacology 28:1799–1809
Lewis DA (2000) GABAergic local circuit neurons and prefrontal cortical dysfunction in schizophrenia. Brain Res Brain Res Rev 31:270–276
Lieberman JA (2006) Comparative effectiveness of antipsychotic drugs. A commentary on: cost utility of the latest antipsychotic drugs in schizophrenia study (CUtLASS 1) and clinical antipsychotic trials of intervention effectiveness (CATIE). Arch Gen Psychiatry 63:1069–1072
Liu SK, Hwu H-G, Chen WJ (1997) Clinical symptom dimensions and deficits on the continuous performance test in schizophrenia. Schizophr Res 25:211–219
Lopez AD, Mathers CD, Ezzati M, Jamison DT, Murray CJ (2006) Global and regional burden of disease and risk factors, 2001: systematic analysis of population health data. Lancet 367:1747–1757
Luby ED, Cohen BD, Rosenbaum G, Gottlieb JS, Kelley R (1959) Study of a new schizophrenomimetic drug; sernyl. AMA Arch Neurol Psychiatry 81:363–369
Mass R, Wolf K, Wagner M, Haasen C (2000) Differential sustained attention/vigilance changes over time in schizophrenics and controls during a degraded stimulus Continuous Performance Test. Eur Arch Psychiatry Clin Neurosci 250:24–30
Meltzer HY, McGurk SR (1999) The effects of clozapine, risperidone, and olanzapine on cognitive function in schizophrenia. Schizophr Bull 25:233–255
Minzenberg MJ, Laird AR, Thelen S, Carter CS, Glahn DC (2009) Meta-analysis of 41 functional neuroimaging studies of executive function in schizophrenia. Arch Gen Psychiatry 66:811–822
Molina V, Solera S, Sanz J, Sarramea F, Luque R, Rodríguez R, Jiménez-Arriero MA, Palomo T (2009) Association between cerebral metabolic and structural abnormalities and cognitive performance in schizophrenia. Psychiatry Res 173:88–93
Morice R (1990) Cognitive inflexibility and pre-frontal dysfunction in schizophrenia and mania. Br J Psychiatry 157:50–54
Morris BJ, Cochran SM, Pratt JA (2005) PCP: from pharmacology to modelling schizophrenia. Curr Opin Pharmacol 5:101–106
Murphy ER, Dalley JW, Robbins TW (2005) Local glutamate receptor antagonism in the rat prefrontal cortex disrupts response inhibition in a visuospatial attentional task. Psychopharmacology (Berl) 179:99–107
Navarra R, Graf R, Huang Y, Logue S, Comery T, Hughes Z, Day M (2008) Effects of atomoxetine and methylphenidate on attention and impulsivity in the 5-choice serial reaction time test. Prog Neuropsychopharmacol Biol Psychiatry 32:34–41
Neuchterlein KH, Dawson ME, Ventura J, Miklowitz D, Konishi G (1991) Information-processing anomalies in the early course of schizophrenia and bipolar disorder. Schizophr Res 5:195–196
Nuechterlein KH, Robbins TW, Einat H (2005) Distinguishing separable domains of cognition in human and animal studies: what separations are optimal for targeting interventions? A summary of recommendations from breakout group 2 at the measurement and treatment research to improve cognition in schizophrenia new approaches conference. Schizophr Bull 31:870–874
Nordahl TE, Kusubov N, Carter C, Salamat S, Cummings AM, O’Shora-Celaya L, Eberling J, Robertson L, Huesman RH, Jagust W, Budinger TF (1996) Temporal lobe metabolic differences in medication-free outpatients with schizophrenia via the PET-600. Neuropsychopharmacology 15:541–554
Paine TA, Carlezon WA (2009) Effects of antipsychotic drugs on MK801-induced attentional and motivational deficits in rats. Neuropharmacology 56:788–797
Perlstein WM, Carter CS, Noll DC, Cohen JD (2001) Relation of prefrontal cortex dysfunction to working memory and symptoms in schizophrenia. Am J Psychiatry 158:1105–1113
Potkin SG, Buchsbaum MS, Jin Y, Tang C, Telford J, Friedman G, Lottenberg S, Najafi A, Gulasekaram B, Costa J et al (1994) Clozapine effects on glucose metabolic rate in striatum and frontal cortex. J Clin Psychiatry 55(Suppl B):63–66
Pratt JA, Winchester C, Egerton A, Cochran SM, Morris BJ (2008) Modelling prefrontal cortex deficits in schizophrenia: implications for treatment. Br J Pharmacol 153(Suppl 1):S465–S470
Robbins TW (2002) The 5-choice serial reaction time task: behavioural pharmacology and functional neurochemistry. Psychopharmacology (Berl) 163:362–380
Salgado-Pineda P, Junque C, Vendrell P, Baeza I, Bargallo N, Falcon C, Bernardo M (2004) Decreased cerebral activation during CPT performance: structural and functional deficits in schizophrenic patients. Neuroimage 21:840–847
Schroder J, Buchsbaum MS, Siegel BV, Geider FJ, Lohr J, Tang C, Wu J, Potkin SG (1996) Cerebral metabolic activity correlates of subsyndromes in chronic schizophrenia. Schizophr Res 19:41–53
Seidman LJ, Van Manen K-J, Turner WM, Gamser DM, Faraone SV, Goldstein JM, Tsuang MT (1998) The effects of increasing resource demand on vigilance performance in adults with schizophrenia or developmental attentional/learning disorders: a preliminary study. Schizophr Res 34:101–112
Steward LJ, Kennedy MD, Morris BJ, Pratt JA (2004) The atypical antipsychotic drug clozapine enhances chronic PCP-induced regulation of prefrontal cortex 5-HT2A receptors. Neuropharmacology 47:527–537
Suwa H, Matsushima E, Ohta K, Mori K (2004) Attention disorders in schizophrenia. Psychiatry Clin Neurosci 58:249–256
Swets JA (1973) The relative operating characteristic in psychology: a technique for isolating effects of response bias finds wide use in the study of perception and cognition. Science 182:990–1000
Tamminga CA, Thaker GK, Buchanan R, Kirkpatrick B, Alphs LD, Chase TN, Carpenter WT (1992) Limbic system abnormalities identified in schizophrenia using positron emission tomography with fluorodeoxyglucose and neocortical alterations with deficit syndrome. Arch Gen Psychiatry 49:522–530
Thaden E, Rhinewine JP, Lencz T, Kester H, Cervellione KL, Henderson I, Roofeh D, Burdick KE, Napolitano B, Cornblatt BA, Kumra S (2006) Early-onset schizophrenia is associated with impaired adolescent development of attentional capacity using the identical pairs continuous performance test. Schizophr Res 81:157–166
Wolkin A, Sanfilipo M, Wolf AP, Angrist B, Brodie JD, Rotrosen J (1992) Negative symptoms and hypofrontality in chronic schizophrenia. Arch Gen Psychiatry 49:959–965
Wykes T, Reeder C, Corner J (2000) The prevalence and stability of an executive processing deficit, response inhibition, in people with chronic schizophrenia. Schizophr Res 46:241–253
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by former Mitsubishi Pharma Co. (currently Mitsubishi Tanabe Pharma Co).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Thomson, D.M., McVie, A., Morris, B.J. et al. Dissociation of acute and chronic intermittent phencyclidine-induced performance deficits in the 5-choice serial reaction time task: influence of clozapine. Psychopharmacology 213, 681–695 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00213-010-2020-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00213-010-2020-7