Abstract
Background and rationale
Despite the popularity of polysubstance abuse among recreational methylendioxymethamphetamine (MDMA) users, relatively few controlled experimental studies have documented the neurobehavioral effects of MDMA in combination with other abused substances.
Objective
In this study, the combined acute effects of MDMA and cocaine were examined by conducting in vivo microdialysis in the rat nucleus accumbens while simultaneously monitoring locomotor activity.
Methods
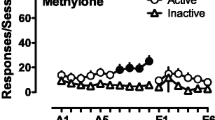
Male Sprague–Dawley rats were administered cocaine (10 or 20 mg/kg, i.p.), MDMA (1.5 or 3.0 mg/kg, i.p.), or one of four combinations of cocaine and MDMA during microdialysis experiments. Locomotor activity was monitored, and dialysis samples were collected every 30 min for 3 h prior to injections, for one 30-min period following saline injections, and for an additional 3-h period following drug injections. Samples were analyzed for dopamine content by high-performance liquid chromatography with electrochemical detection.
Results
Significant differences in locomotor activity and dopamine efflux were found among treatment groups, with some MDMA/cocaine combinations producing significantly greater increases compared to single doses of cocaine or MDMA within the first 30 min after injection.
Conclusion
Considering the popularity of polysubstance use among recreational MDMA users, the clinical implications of the current findings warrant further investigation.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aberg M, Wade D, Wall E, Izenwasser S (2007) Effect of MDMA (ecstasy) on activity and cocaine conditioned place preference in adult and adolescent rats. Neurotoxicol Teratol 29(1):37–46
Barret SP, Darredeau C, Pihl RO (2006) Patterns of simultaneous polysubstance use in drug using university students. Hum Psychopharmacol 21(4):255–263
Bozarth MA (1986) Neural basis of psychomotor stimulant and opiate reward: evidence suggesting the involvement of a common dopaminergic system. Behav Brain Res 22(2):107–116
Bozarth MA, Wise RA (1986) Involvement of the ventral tegmental dopamine system in opioid and psychomotor stimulant reinforcement. NIDA Research Monograph Series NO. 67:190–196
Bradberry CW (1994) Microdialysis assessment of the impact of (+)3, 4-methylenedioxymethamphetamine, cocaine, and cocaethylene on serotonergic neurons. Drug Dev Res 33(1):1–9
Bradberry CW (2002) Dynamics of extracellular dopamine in the acute and chronic actions of cocaine. Neuroscientist 8(4):315–322
Burmeister JJ, Lungren EM, Kirschner KF, Neisewander JL (2004) Differential roles of 5-HT receptor subtypes in cue and cocaine reinstatement of cocaine-seeking behavior in rats. Neuropsychopharmacology 29(4):660–668
Cadoni C, Solinas M, Pisanu A, Zernig G, Acquas E, Di Chiara G (2005) Effect of 3, 4-methylendioxymethamphetamine (MDMA, “ecstasy”) on dopamine transmission in the nucleus accumbens shell and core. Brain Res 1055(1–2):143–148
Chinet L, Stephan P, Zobel F, Halfon O (2007) Party drug use in techno nights: a field survey among French-speaking Swiss attendees. Pharmacol Biochem Behav 86(2):284–289
Cole JC, Sumnall HR, O’Shea E, Marsden CA (2003) Effects of MDMA exposure on the conditioned place preference produced by other drugs of abuse. Psychopharmacology 166(4):383–390
Daza-Losada M, Rodríguez-Arias M, Maldonado C, Aguilar MA, Guerri C, Miñarro J (2009) Acute behavioural and neurotoxic effects of MDMA plus cocaine in adolescent mice. Neurotoxicol Teratol 31(1):49–59
Diller AJ, Rocha A, Cardon AL, Valles R, Wellman PJ, Nation JR (2007) The effects of concurrent administration of (±)3, 4-methylenedioxymethamphetamine and cocaine on conditioned place preference in the adult male rat. Pharmacol Biochem Behav 88(2):165–170
Fletcher PJ, Sinyard J, Higgins GA (2006) The effects of the 5-HT2C receptor antagonist SB242084 on locomotor activity induced by selective, or mixed, indirect serotonergic and dopaminergic agonists. Psychopharmacology 187(4):515–525
Gouzoulis-Mayfrank E, Daumann J (2006) The confounding problem of polydrug use in recreational ecstasy/MDMA users: a brief overview. J Psychopharmacol (Oxford, England) 20(2):188–193
Green AR, Mechan AO, Elliott JM, O’Shea E, Colado MI (2003) The pharmacology and clinical pharmacology of 3, 4-methylenedioxymethamphetamine (MDMA, “ecstasy”). Pharmacol Rev 55(3):463–508
Horan B, Gardner EL, Ashby CR Jr (2000) Enhancement of conditioned place preference response to cocaine in rats following subchronic administration of 3, 4-methylenedioxymethamphetamine (MDMA). Synapse 35(2):160–162
Kalivas PW, Duffy P, White SR (1998) MDMA elicits behavioral and neurochemical sensitization in rats. Neuropsychopharmacology 18(6):469–479
Khorana N, Pullagurla MR, Young R, Glennon RA (2004) Comparison of the discriminative stimulus effects of 3, 4-methylenedioxymethamphetamine (MDMA) and cocaine: asymmetric generalization. Drug Alcohol Depend 74(3):281–287
Koch S, Galloway MP (1997) MDMA induced dopamine release in vivo: role of endogenous serotonin. J Neural Transm 104(2–3):135–146
Lua AC, Lin HR, Tseng YT, Hu AR, Yeh PC (2003) Profiles of urine samples from participants at rave party in Taiwan: prevalence of ketamine and MDMA abuse. Forensic Sci Int 136(1–3):47–51
Marsden J, Stillwell G, Barlow H, Boys A, Taylor C, Hunt N et al (2006) An evaluation of a brief motivational intervention among young ecstasy and cocaine users: no effect on substance and alcohol use outcomes. Addiction 101(7):1014–1026
Metzger RR, Hanson GR, Gibb JW, Fleckenstein AE (1998) 3, 4-methylenedioxymethamphetamine-induced acute changes in dopamine transporter function. Eur J Pharmacol 349(2–3):205–210
Montgomery C, Fisk JE, Newcombe R, Murphy PN (2005) The differential effects of ecstasy/polydrug use on executive components: shifting, inhibition, updating and access to semantic memory. Psychopharmacology 182(2):262–276
Morgan AE, Horan B, Dewey SL, Ashby CR Jr (1997a) Repeated administration of 3, 4-methylenedioxymethamphetamine augments cocaine’s action on dopamine in the nucleus accumbens: a microdialysis study. Eur J Pharmacol 331(1):R1–R3
Morgan AE, Porter SP, Clarkson FA, Volkow ND, Fowler JS, Dewey SL (1997b) Direct approach for attenuating cocaine’s effects on extracellular dopamine: targeting the dopamine transporter. Synapse 26(4):423–427
Parrott AC, Milani RM, Parmar R, Turner JD (2001) Recreational ecstasy/MDMA and other drug users from the UK and Italy: psychiatric symptoms and psychobiological problems. Psychopharmacology 159:77–82
Paxinos G, Watson C (1998) The rat brain in stereotaxic coordinates. Academic, New York
Reay JL, Hamilton C, Kennedy DO, Scholey AB (2006) MDMA polydrug users show process-specific central executive impairments coupled with impaired social and emotional judgment processes. J Psychopharmacol 20:385–388
Riley SCE, James C, Gregory D, Dingle H, Cadger M (2001) Patterns of recreational drug use at dance events in Edinburgh, Scotland. Addiction 96(7):1035–1047
Scholey AB, Parrott AC, Buchanan T, Heffernan TM, Ling J, Rodgers J (2004) Increased intensity of Ecstasy and polydrug usage in the more experienced recreational Ecstasy/MDMA users: a WWW study. Addict Behav 29(4):743–752
Shimada A, Yamaguchi K, Yanagita T (1996) Neurochemical analysis of the psychotoxicity of methamphetamine and cocaine by microdialysis in the rat brain. Ann N Y Acad Sci 801:361–370
Williams H, Dratcu L, Taylor R, Roberts M, Oyefeso A (1998) “Saturday night fever”: ecstasy related problems in a London accident and emergency department. J Accid Emerg Med 15(5):322–326
Winstock AR, Griffiths P, Stewart D (2001) Drugs and the dance music scene: a survey of current drug use patterns among a sample of dance music enthusiasts in the UK. Drug Alcohol Depend 64(1):9–17
Wish ED, Fitzelle DB, O’Grady KE, Hsu MH, Arria AM (2006) Evidence for significant polydrug use among ecstasy-using college students. J Am Coll Health 55(2):99–104
Acknowledgements
This research was funded by awards from the Monroe-Brown Foundation of Kalamazoo, MI, USA, and the Graduate College of Western Michigan University.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Panos, J.J., Baker, L.E. An in vivo microdialysis assessment of concurrent MDMA and cocaine administration in Sprague–Dawley rats. Psychopharmacology 209, 95–102 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00213-009-1774-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00213-009-1774-2