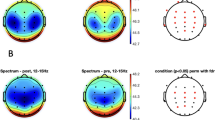
Abstract
Introduction
Antagonists of histamine H1 receptors (antihistamines) are widely used for the treatment of allergic disorders in children. These drugs' sedative effect on brain function, however, has been mostly examined in adults.
Objective
The objective of this study was to examine the effects of anitihistamines on prefrontal cortex activity in young children using near-infrared spectroscopy (NIRS), a novel brain-imaging method.
Materials and methods
In 15 healthy children (mean age, 7.7 years), we examined changes of oxygenated hemoglobin concentration in the prefrontal cortex while they performed a verbal fluency task 3 h after taking a sedating antihistamine (ketotifen), nonsedating antihistamine (epinastine), or placebo.
Results
Ketotifen significantly impaired behavioral performance and cortical activation at the lateral prefrontal cortex compared with placebo. There were no sedative effects on neural response or behavioral performance after epinastine administration.
Conclusions
NIRS revealed that sedating and nonsedating antihistamines exert differential effects on brain hemodynamic response in young children.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Allison T, Puce A, McCarthy G (2000) Social perception from visual cues: role of the STS region. Trends Cogn Sci 4:267–278
Clark VP, Fannon S, Lai S, Benson R, Bauer L (2000) Responses to rare visual target and distractor stimuli using event-related fMRI. J Neurophysiol 83:3133–3139
Ehlis AC, Herrmann MJ, Plichta MM, Fallgatter AJ (2007) Cortical activation during two verbal fluency tasks in schizophrenic patients and healthy controls as assessed by multi-channel near-infrared spectroscopy. Psychiatry Res 156:1–13
Folstein MF, Luria R (1973) Reliability, validity, and clinical application of the Visual Analogue Mood Scale. Psychol Med 3:479-486
Hebden JC (2003) Advances in optical imaging of the newborn infant brain. Psychophysiology 40:501–510
Herrmann MJ, Ehlis AC, Fallgatter AJ (2003) Frontal activation during a verbal-fluency task as measured by near-infrared spectroscopy. Brain Res Bull 61:51–56
Herrmann MJ, Langer JB, Jacob C, Ehlis AC, Fallgatter AJ (2008) Reduced prefrontal oxygenation in Alzheimer disease during verbal fluency tasks. Am J Geriatr Psychiatry 16:125–135
Hindmarch I, Shamsi Z (1999) Antihistamines: models to assess sedative properties, assessment of sedation, safety and other side-effects. Clin Exp Allergy 3:133–142
Koizumi H, Yamamoto T, Maki A, Yamashita Y, Sato H, Kawaguchi H, Ichikawa N (2003) Optical topography: practical problems and new applications. Appl Opt 42:3054-3062
Kuwabara H, Kasai K, Takizawa R, Kawakubo Y, Yamasue H, Rogers MA, Ishijima M, Watanabe K, Kato N (2006) Decreased prefrontal activation during letter fluency task in adults with pervasive developmental disorders: a near-infrared spectroscopy study. Behav Brain Res 172:272-277
Matsuda G, Hiraki K (2006) Sustained decrease in oxygenated hemoglobin during video games in the dorsal prefrontal cortex: a NIRS study of children. NeuroImage 29:706–711
Mochizuki H, Tashiro M, Tagawa M, Kano M, Itoh M, Okamura N, Watanabe T, Yanai K (2002) The effects of a sedative antihistamine, d-chlorpheniramine, on visuomotor spatial discrimination and regional brain activity as measured by positron emission tomography (PET). Hum Psychopharmacol 17:413–418
Mochizuki H, Kimura Y, Ishii K, Oda K, Sasaki T, Tashiro M, Yanai K, Ishiwata K (2004) Quantitative measurement of histamine H1 receptors in human brains by PET and [11C]doxepin. Nucl Med Biol 31:165–171
Nagamitsu S, Nagano M, Yamashita Y, Takashima S, Matsuishi T (2006) Prefrontal cerebral blood volume patterns while playing video games—a near-infrared spectroscopy study. Brain and Development 28:315–321
Ng KH, Chong D, Wong CK, Ong HT, Lee CY, Lee BW, Shek LP (2004) Central nervous system side effects of first- and second-generation antihistamines in school children with perennial allergic rhinitis: a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled comparative study. Pediatrics 113:e116–e121
Okamoto M, Dan H, Sakamoto K, Takeo K, Shimizu K, Kohno S, Oda I, Isobe S, Suzuki T, Kohyama K, Dan I (2004) Three-dimensional probabilistic anatomical cranio-cerebral correlation via the international 10–20 system oriented for transcranial functional brain mapping. NeuroImage 21:99–111
Otsuka Y, Nakato E, Kanazawa S, Yamaguchi MK, Watanabe S, Kakigi R (2007) Neural activation to upright and inverted faces in infants measured by near infrared spectroscopy. NeuroImage 34:399–406
Shamsi Z, Hindmarch I (2000) Sedation and antihistamines: a review of inter-drug differences using proportional impairment ratios. Hum Psychopharmacol 15:S3–S30
Simons FE, Simons KJ (2005) Levocetirizine: pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamics in children age 6 to 11 years. J Allergy Clin Immunol 116:355–361
Simons FE, Reggin JD, Roberts JR, Simons KJ (1994) Benefit/risk ratio of the antihistamines (H1-receptor antagonists) terfenadine and chlorpheniramine in children. J Pediatr 124:979–983
Simons FE, Fraser TG, Reggin JD, Roberts JR, Simons KJ (1996) Adverse central nervous system effects of older antihistamines in children. Pediatr Allergy Immunol 7:22–27
Simons FER, Semus MJ, Goritz SS, Simons KJ (2003) H1-antihistaminic activity of cetirizine and fexofenadine in allergic children. Pediatr Allergy Immunol 14:207–211
Stevenson J, Cornah D, Evrard P, Vanderheyden V, Billard C, Bax M, Van Hout A (2002) Long-term evaluation of the impact of the H1-receptor antagonist cetirizine on the behavioral, cognitive, and psychomotor development of very young children with atopic dermatitis. Pediatr Res 52:251–257
Suda M, Sato T, Kameyama M, Ito M, Suto T, Yamagishi Y, Uehara T, Fukuda M, Mikuni M (2008) Decreased cortical reactivity underlies subjective daytime light sleepiness in healthy subjects: a multichannel near-infrared spectroscopy study. Neurosci Res 60:319–326
Taga G, Asakawa K, Maki A, Konishi Y, Koizumi H (2003) Brain imaging in awake infants by near-infrared optical topography. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 100:10722–10727
Tashiro M, Sakurada Y, Iwabuchi K, Mochizuki H, Kato M, Aoki M, Funaki Y, Itoh M, Iwata R, Wong DF, Yanai K (2004) Central effects of fexofenadine and cetirizine: measurement of psychomotor performance, subjective sleepiness, and brain histamine H1-receptor occupancy using 11C-doxepin positron emission tomography. J Clin Pharmacol 44:890–900
Tashiro M, Horikawa E, Mochizuki H, Sakurada Y, Kato M, Inokuchi T, Ridout F, Hindmarch I, Yanai K (2005) Effects of fexofenadine and hydroxyzine on brake reaction time during car-driving with cellular phone use. Hum Psychopharmacol 20:501–509
Tashiro M, Mochizuki H, Sakurada Y, Ishii K, Oda K, Kimura Y, Sasaki T, Ishiwata K, Yanai K (2006) Brain histamine H1 receptor occupancy of orally administered antihistamines measured by positron emission tomography with (11)C-doxepin in a placebo-controlled crossover study design in healthy subjects: a comparison of olopatadine and ketotifen. Br J Clin Pharmacol 61:16–26
Theunissen EL, Jonkman LM, Kuypers KP, Ramaekers JG (2006a) A combined neurophysiological and behavioural study into the stimulating effects of fexofenadine on performance. J Psychopharmacol 20:496–505
Theunissen EL, Vermeeren A, Ramaekers JG (2006b) Repeated-dose effects of mequitazine, cetirizine and dexchlorpheniramine on driving and psychomotor performance. Br J Clin Pharmacol 61:79–86
Theunissen EL, van Kroonenburgh MJ, van Deursen JA, Blom-Coenjaerts C, Ramaekers JG (2006c) Stimulating effects of the antihistamine fexofenadine: testing the dopamine transporter hypothesis. Psychopharmacology 187:95–102
Tsujii T, Watanabe S (2009) Neural correlates of dual-task effect on belief-bias syllogistic reasoning: a near-infrared spectroscopy study. Brain Res 1287:118-125
Tsujii T, Yamamoto E, Ohira T, Saito N, Watanabe S (2007) Effects of sedative and non-sedative H1 antagonists on cognitive tasks: behavioral and near-infrared spectroscopy (NIRS) examinations. Psychopharmacology 194:83–91
Tsujii T, Yamamoto E, Masuda S, Watanabe S (2009) Longitudinal study of spatial working memory development in young children. NeuroReport 20:759–763
Tsujimoto S, Yamamoto T, Kawaguchi H, Koizumi H, Sawaguchi T (2004) Prefrontal cortical activation associated with working memory in adults and preschool children: an event-related optical topography study. Cereb Cortex 14:703–712
Tukey JW (1953) The problem of multiple comparisons. Princeton University, Firestone Library, Princeton
Turner C, Handford AD, Nicholson AN (2006) Sedation and memory: studies with a histamine H-1 receptor antagonist. J Psychopharmacol 20:506–517
Yanai K, Tashiro M (2007) The physiological and pathophysiological roles of neuronal histamine: an insight from human positron emission tomography studies. Pharmacol Ther 113:1–15
Yoshiura T, Zhong J, Shibata DK, Kwok WE, Shrier DA, Numaguchi Y (1999) Functional MRI study of auditory and visual oddball tasks. NeuroReport 10:1683–1688
Acknowledgments
Our thanks go to the 15 young children who participated in the study, as well as to their parents. We also thank Masahito Kobayashi, MD (Department of Neurosurgery, Keio University), Kenjiro Kosaki, MD (Department of Pediatrics, Keio University), and Shozo Kojima, PhD (Department of Psychology, Keio University) for valuable contributions toward the design and execution of this study. Funding for the study was provided by the Japanese Public Health Research Foundation (JPHRF). The study was conducted at Center for Advanced Research on Logic and Sensibility (CARLS) at Keio University and was supported by grants of the Global COE program from the Ministry of Education, Culture, Sports, Science, and Technology of Japan, as well as by Boehringer Ingelheim, which also provided test agents (ketotifen, epinastine, and identical placebos).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Tsujii, T., Masuda, S., Yamamoto, E. et al. Effects of sedative and nonsedative antihistamines on prefrontal activity during verbal fluency task in young children: a near-infrared spectroscopy (NIRS) study. Psychopharmacology 207, 127–132 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00213-009-1640-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00213-009-1640-2