Abstract
Rationale
Effect of cannabinoid CB1 receptor deletion on cocaine’s actions is controversial. This is partly based on findings in CB1-receptor-knockout (CB1−/−) mice with CD1 genetic background.
Objectives
In the present study, we used CB1−/− mice with a C57BL/6J genetic background to further investigate the role of CB1 receptors in cocaine’s action.
Materials and methods
Locomotor activity was assessed using AccuScan locomotor chambers. Brain extracellular dopamine (DA) levels were measured by in vivo microdialysis and by fast-scan cyclic voltammetry in the nucleus accumbens (NAc).
Results
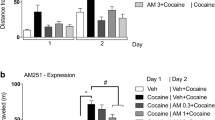
CB1−/− mice displayed a significant reduction in basal levels of locomotion and extracellular DA, as well as in cocaine-enhanced locomotion and extracellular DA, as compared to their wild-type (CB1+/+) littermates. The reduction in basal and cocaine-enhanced DA appears to be related to a reduction in basal DA release, not to an increase in DA clearance, as indicated by fast-scan cyclic voltammetry in brain slices. Pharmacological blockade of CB1 receptors by SR141716 inhibited locomotion and NAc DA release in CB1+/+ mice.
Conclusions
The present findings suggest an important role for CB1 receptors in mediating cocaine’s behavioral and neurochemical effects.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abel EL (1970) Effects of the marihuana-homologue, parahexyl, on open field behaviour in the rat. J Pharm Pharmacol 22:785
Ballesteros-Yáñez I, Valverde O, Ledent C, Maldonado R, DeFelipe J (2007) Chronic cocaine treatment alters dendritic arborization in the adult motor cortex through a CB1 cannabinoid receptor-dependent mechanism. Neuroscience 146:1536–1545
Cahill PS, Walker QD, Finnegan JM, Mickelson GE, Travis ER, Wightman RM (1996) Microelectrodes for the measurement of catecholamines in biological systems. Anal Chem 68:3180–3186
Caillé S, Parsons LH (2006) Cannabinoid modulation of opiate reinforcement through the ventral striatopallidal pathway. Neuropsychopharmacology 31:804–813
Centonze D, Battista N, Rossi S, Mercuri NB, Finazzi-Agrò A, Bernardi G, Calabresi P, Maccarrone M (2004) A critical interaction between dopamine D2 receptors and endocannabinoids mediates the effects of cocaine on striatal GABAergic transmission. Neuropsychopharmacology 29:1488–1497
Chaperon F, Soubrié P, Puech AJ, Thiébot MH (1998) Involvement of central cannabinoid (CB1) receptors in the establishment of place conditioning in rats. Psychopharmacology 135:324–332
Cheer JF, Wassum KM, Sombers LA, Heien MLAV, Ariansen JL, Aragona BJ, Phillips PEM, Wightman RM (2007) Phasic dopamine release evoked by abused substances requires cannabinoid receptor activation. J Neurosci 27:791–795
Chen J, Paredes W, Li J, Smith D, Lowinson J, Gardner EL (1990) Δ9-tetrahydrocannabinol produces naloxone-blockable enhancement of presynaptic basal dopamine efflux in nucleus accumbens of conscious, freely-moving rats as measured by intracerebral microdialysis. Psychopharmacology 102:156–162
Compton DR, Aceto MD, Lowe J, Martin BR (1996) In vivo characterization of a specific cannabinoid receptor antagonist (SR141716A): inhibition of delta Δ9-tetrahydrocannabinol-induced responses and apparent agonist activity. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 277:586–594
Corbillé AG, Valjent E, Marsicano G, Ledent C, Lutz B, Hervé D, Girault JA (2007) Role of cannabinoid type 1 receptors in locomotor activity and striatal signaling in response to psychostimulants. J Neurosci 27:6937–6947
Cornish JL, Kalivas PW (2001) Cocaine sensitization and craving: differing roles for dopamine and glutamate in the nucleus accumbens. J Addict Dis 20:43–54
Cossu G, Ledent C, Fattore L, Imperato A, Böhme GA, Parmentier M, Fratta W (2001) Cannabinoid CB1 receptor knockout mice fail to self-administer morphine but not other drugs of abuse. Behav Brain Res 118:61–65
De Vries TJ, Shaham Y, Homberg JR, Crombag H, Schuurman K, Dieben J, Vanderschuren LJMJ, Schoffelmeer ANM (2001) A cannabinoid mechanism in relapse to cocaine seeking. Nat Med 7:1151–1154
Fattore L, Martellotta MC, Cossu G, Mascia MS, Fratta W (1999) CB1 cannabinoid receptor agonist WIN 55,212-2 decreases intravenous cocaine self-administration in rats. Behav Brain Res 104:141–146
Fattore L, Fadda P, Fratta W (2007) Endocannabinoid regulation of relapse mechanisms. Pharmacol Res 56:418–427
Ferrari F, Ottani A, Giuliani D (1999) Influence of the cannabinoid agonist HU 210 on cocaine- and CQP 201-403-induced behavioural effects in rat. Life Sci 65:823–831
Filip M, Goxda A, Zaniewska M, McCreary AC, Nowak E, Kolasiewicz W, Przegaliński E (2006) Involvement of cannabinoid CB1 receptors in drug addiction: effects of rimonabant on behavioral responses induced by cocaine. Pharmacol Rep 58:806–819
French ED (1997) Δ9-Tetrahydrocannabinol excites rat VTA dopamine neurons through activation of cannabinoid CB1 but not opioid receptors. Neurosci Lett 226:159–162
Gardner A, Mallet PE (2006) Suppression of feeding, drinking, and locomotion by a putative cannabinoid receptor ‘silent antagonist’. Eur J Pharmacol 530:103–106
Gerdeman GL, Schechter JB, French ED (2008) Context-specific reversal of cocaine sensitization by the CB(1) cannabinoid receptor antagonist rimonabant. Neuropsychopharmacology 33:2747–2759
Giuffrida A, Parsons LH, Kerr TM, Rodríguez de Fonseca F, Navarro M, Piomelli D (1999) Dopamine activation of endogenous cannabinoid signaling in dorsal striatum. Nat Neurosci 2:358–363
Heien ML, Johnson MA, Wightman RM (2004) Resolving neurotransmitters detected by fast-scan cyclic voltammetry. Anal Chem 76:5697–5704
Järbe TUC, Andrzejewski ME, DiPatrizio NV (2002) Interactions between the CB1 receptor agonist Δ9-THC and the CB1 receptor antagonist SR-141716 in rats: open-field revisited. Pharmacol Biochem Behav 73:911–919
Järbe TUC, Ross T, DiPatrizio NV, Pandarinathan L, Makriyannis A (2006) Effects of the CB1R agonist WIN-55,212-2 and the CB1R antagonists SR-141716 and AM-1387: open-field examination in rats. Pharmacol Biochem Behav 85:243–252
Jones SR, Garris PA, Wightman RM (1995) Different effects of cocaine and nomifensine on dopamine uptake in the caudate-putamen and nucleus accumbens. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 274:396–403
Julian MD, Martin AB, Cuellar B, Rodríguez de Fonseca F, Navarro M, Moratalla R, Garcia-Segura LM (2003) Neuroanatomical relationship between type 1 cannabinoid receptors and dopaminergic systems in the rat basal ganglia. Neuroscience 119:309–318
Köfalvi A, Rodrigues RJ, Ledent C, Mackie K, Vizi ES, Cunha RA, Sperlágh B (2005) Involvement of cannabinoid receptors in the regulation of neurotransmitter release in the rodent striatum: a combined immunochemical and pharmacological analysis. J Neurosci 25:2874–2884
Ledent C, Valverde O, Cossu G, Petitet F, Aubert JF, Beslot F, Böhme GA, Imperato A, Pedrazzini T, Roques BP, Vassart G, Fratta W, Parmentier M (1999) Unresponsiveness to cannabinoids and reduced addictive effects of opiates in CB1 receptor knockout mice. Science 283:401–404
Lesscher HMB, Hoogveld E, Burbach JPH, van Ree JM, Gerrits MAFM (2005) Endogenous cannabinoids are not involved in cocaine reinforcement and development of cocaine-induced behavioural sensitization. Eur Neuropsychopharmacol 15:31–37
Lupica CR, Riegel AC (2005) Endocannabinoid release from midbrain dopamine neurons: a potential substrate for cannabinoid receptor antagonist treatment of addiction. Neuropharmacology 48:1105–1116
Lupica CR, Riegel AC, Hoffman AF (2004) Marijuana and cannabinoid regulation of brain reward circuits. Br J Pharmacol 143:227–234
Mailleux P, Vanderhaeghen JJ (1992) Distribution of neuronal cannabinoid receptor in the adult rat brain: a comparative receptor binding radioautography and in situ hybridization histochemistry. Neuroscience 48:655–668
Maldonado R, Valverde O, Berrendero F (2006) Involvement of the endocannabinoid system in drug addiction. Trends Neurosci 29:225–232
Martin M, Ledent C, Parmentier M, Maldonado R, Valverde O (2000) Cocaine, but not morphine, induces conditioned place preference and sensitization to locomotor responses in CB1 knockout mice. Eur J Neurosci 12:4038–4046
Mátyás F, Yanovsky Y, Mackie K, Kelsch W, Misgeld U, Freund TF (2006) Subcellular localization of type 1 cannabinoid receptors in the rat basal ganglia. Neuroscience 137:337–361
Mátyás F, Urbán GM, Watanabe M, Mackie K, Zimmer A, Freund TF, Katona I (2008) Identification of the sites of 2-arachidonoylglycerol synthesis and action imply retrograde endocannabinoid signaling at both GABAergic and glutamatergic synapses in the ventral tegmental area. Neuropharmacology 54:95–107
Melis M, Gessa GL, Diana M (2000) Different mechanisms for dopaminergic excitation induced by opiates and cannabinoids in the rat midbrain. Prog Neuropsychopharmacol Biol Psychiatry 24:993–1006
Miller LL, Ward SJ, Dykstra LA (2008) Chronic unpredictable stress enhances cocaine-conditioned place preference in type 1 cannabinoid receptor knockout mice. Behav Pharmacol 19:575–581
Muschamp JW, Siviy SM (2002) Behavioral sensitization to amphetamine follows chronic administration of the CB1 agonist WIN 55,212-2 in Lewis rats. Pharmacol Biochem Behave 73:835–842
Pandolfo P, Pamplona FA, Prediger RD, Takahashi RN (2007) Increased sensitivity of adolescent spontaneously hypertensive rats, an animal model of attention deficit hyperactivity disorder, to the locomotor stimulation induced by the cannabinoid receptor agonist WIN 55,212-2. Eur J Pharmacol 563:141–148
Parolaro D, Rubino T (2008) The role of the endogenous cannabinoid system in drug addiction. Drug News Perspect 21:149–157
Patel S, Rademacher DJ, Hillard CJ (2003) Differential regulation of the endocannabinoids anandamide and 2-arachidonylglycerol within the limbic forebrain by dopamine receptor activity. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 306:880–888
Paxinos G, Watson C (1998) The rat brain in stereotaxic coordinates, 4th edn. Academic, San Diego
Pertwee RG (2005) Pharmacological actions of cannabinoids. Handb Exp Pharmacol 168:1–51
Przegaliński E, Göthert M, Frankowska M, Filip M (2005) WIN 55,212-2-induced reduction of cocaine hyperlocomotion: possible inhibition of 5-HT3 receptor function. Eur J Pharmacol 517:68–73
Riegel AC, Lupica CR (2004) Independent presynaptic and postsynaptic mechanisms regulate endocannabinoid signaling at multiple synapses in the ventral tegmental area. J Neurosci 24:11070–11078
Robbe D, Alonso G, Duchamp F, Bockaert J, Manzoni OJ (2001) Localization and mechanisms of action of cannabinoid receptors at the glutamatergic synapses of the mouse nucleus accumbens. J Neurosci 21:109–116
Robbe D, Kopf M, Remaury A, Bockaert J, Manzoni OJ (2002) Endogenous cannabinoids mediate long-term synaptic depression in the nucleus accumbens. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 99:8384–8388
Sabeti J, Adams CE, Burmeister J, Gerhardt GA, Zahniser NR (2002) Kinetic analysis of striatal clearance of exogenous dopamine recorded by chronoamperometry in freely-moving rats. J Neurosci Methods 121:41–52
Sañudo-Peña MC, Romero J, Seale GE, Fernandez-Ruiz JJ, Walker JM (2000) Activational role of cannabinoids on movement. Eur J Pharmacol 391:269–274
Shi LH, Luo F, Woodward DJ, Chang JY (2005) Dose and behavioral context dependent inhibition of movement and basal ganglia neural activity by Δ−9-tetrahydrocannabinol during spontaneous and treadmill locomotion tasks in rats. Synapse 55:1–16
Soria G, Mendizábal V, Touriño C, Robledo P, Ledent C, Parmentier M, Maldonado R, Valverde O (2005) Lack of CB1 cannabinoid receptor impairs cocaine self-administration. Neuropsychopharmacology 30:1670–1680
Sulcova E, Mechoulam R, Fride E (1998) Biphasic effects of anandamide. Pharmacol Biochem Behav 59:374–352
Szabo B, Siemes S, Wallmichrath I (2002) Inhibition of GABAergic neurotransmission in the ventral tegmental area by cannabinoids. Eur J Neurosci 15:2057–2061
Tanda G, Pontieri FE, Di Chiara G (1997) Cannabinoid and heroin activation of mesolimbic dopamine transmission by a common μ1 opioid receptor mechanism. Science 276:2048–2050
Thiemann G, van der Stelt M, Petrosino S, Molleman A, Di Marzo V, Hasenöhrl RU (2008) The role of the CB1 cannabinoid receptor and its endogenous ligands, anandamide and 2-arachidonoylglycerol, in amphetamine-induced behavioural sensitization. Behav Brain Res 187:289–296
Tsou K, Brown S, Sañudo-Peña MC, Mackie K, Walker JM (1998) Immunohistochemical distribution of cannabinoid CB1 receptors in the rat central nervous system. Neuroscience 83:393–411
Wise RA (2005) Forebrain substrates of reward and motivation. J Comp Neurol 493:115–121
Wu X, French ED (2000) Effects of chronic Δ9-tetrahydrocannabinol on rat midbrain dopamine neurons: an electrophysiological assessment. Neuropharmacology 39:391–398
Xi Z-X, Gilbert JG, Peng X-Q, Pak AC, Li X, Gardner EL (2006) Cannabinoid CB1 receptor antagonist AM251 inhibits cocaine-primed relapse in rats: role of glutamate in the nucleus accumbens. J Neurosci 26:8531–8536
Xi Z-X, Spiller K, Pak AC, Gilbert J, Dillon C, Li X, Peng X-Q, Gardner EL (2008) Cannabinoid CB1 receptor antagonists attenuate cocaine’s rewarding effects: experiments with self-administration and brain-stimulation reward in rats. Neuropsychopharmacology 33:1735–1745
Zimmer A, Zimmer AM, Hohmann AG, Herkenham M, Bonner TI (1999) Increased mortality, hypoactivity, and hypoalgesia in cannabinoid CB1 receptor knockout mice. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 96:5780–5785
Acknowledgement
This research was supported by the Intramural Research Program of the National Institute on Drug Abuse, National Institutes of Health.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Li, X., Hoffman, A.F., Peng, XQ. et al. Attenuation of basal and cocaine-enhanced locomotion and nucleus accumbens dopamine in cannabinoid CB1-receptor-knockout mice. Psychopharmacology 204, 1–11 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00213-008-1432-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00213-008-1432-0