Abstract
Rationale
We have previously reported that selective antagonism of brain D3 receptors by SB-277011A or NGB 2904 significantly attenuates cocaine- or nicotine-enhanced brain stimulation reward (BSR).
Objective
In the present study, we investigated whether the selective D3 receptor antagonists SB-277011A and NGB 2904 and the putative partial D3 agonist BP-897 similarly reduce methamphetamine (METH)-enhanced BSR.
Materials and methods
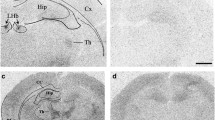
Rats were trained to respond for rewarding electrical self-stimulation of the medial forebrain bundle. To assess the degree of drug-induced changes in BSR, a rate–frequency curve shift paradigm was used to measure brain-reward threshold (θ 0).
Results
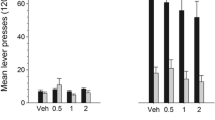
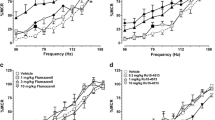
METH (0.1–0.65 mg/kg, i.p.) dose-dependently lowered (∼10–50%) BSR thresholds, producing an enhancement of BSR. Pretreatment with SB-277011A (12 mg/kg, but not 24 mg/kg, i.p.) significantly attenuated METH-enhanced BSR. NGB 2904 (0.1–1.0 mg/kg, but not 10 mg/kg) also attenuated METH-enhanced BSR. SB-277011A or NGB 2904 alone, at the doses tested, had no effect on BSR. Pretreatment with BP-897 (0.1–5 mg/kg) dose-dependently attenuated METH-enhanced BSR. However, when the dose was increased to 10 mg/kg, BP-897 shifted the stimulation–response curve to the right (inhibited BSR itself) in the presence or absence of METH.
Conclusions
Selective antagonism of D3 receptors by SB-277011A or NGB 2904 attenuates METH-enhanced BSR in rats, while the METH-enhanced BSR attenuation produced by BP-897 may involve both D3 and non-D3 receptors. These findings support a potential use of selective D3 receptor antagonists for the treatment of METH addiction.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Andreoli M, Tessari M, Pilla M, Valerio E, Hagan JJ, Heidbreder CA (2003) Selective antagonism at dopamine D3 receptors prevents nicotine-triggered relapse to nicotine-seeking behavior. Neuropsychopharmacology 28:1272–1280
Baldo BA, Jain K, Veraldi L, Koob GF, Markou A (1999) A dopamine D1 agonist elevates self-stimulation thresholds: comparison to other dopamine-selective drugs. Pharmacol Biochem Behav 62:659–672
Bauco P, Wise RA (1997) Synergistic effects of cocaine with lateral hypothalamic brain stimulation reward: lack of tolerance or sensitization. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 283:1160–1167
Caine SB, Koob GF (1993) Modulation of cocaine self-administration in the rat through D-3 dopamine receptors. Science 260:1814–1816
Campiani G, Butini S, Trotta F, Fattorusso C, Catalanotti B, Aiello F, Gemma S, Nacci V, Novellino E, Stark JA, Cagnotto A, Fumagalli E, Carnovali F, Cervo L, Mennini T (2003) Synthesis and pharmacological evaluation of potent and highly selective D3 receptor ligands: inhibition of cocaine-seeking behavior and the role of dopamine D3/D2 receptors. J Med Chem 46:3822–3839
Campos AC, Xi Z-X, Gilbert J, Ashby CR Jr, Heidbreder CA, Newman AH, Gardner EL (2004) Blockade of dopamine D3 receptors by SB-277011A, NGB 2904 or BP 897 attenuates nicotine-enhanced brain stimulation reward in rat. Abstracts of the 34th Annual Meeting of the Society for Neuroscience; 2004 November 23–27; San Diego, CA. 2004 Abstract Viewer/Itinerary Planner. Online. Society for Neuroscience, Washington, DC. Abstract 691.6
Cervo L, Carnovali F, Stark JA, Mennini T (2003) Cocaine-seeking behavior in response to drug-associated stimuli in rats: involvement of D3 and D2 dopamine receptors. Neuropsychopharmacology 28:1150–1159
Cervo L, Cocco A, Petrella C, Heidbreder CA (2007) Selective antagonism at dopamine D3 receptors attenuates cocaine-seeking behaviour in the rat. Int J Neuropsychopharmacol 10:167–181
Coulombe D, Miliaressis E (1987) Fitting intracranial self-stimulation data with growth models. Behav Neurosci 101:209–214
Di Ciano P, Underwood RJ, Hagan JJ, Everitt BJ (2003) Attenuation of cue-controlled cocaine-seeking by a selective D3 dopamine receptor antagonist SB-277011-A. Neuropsychopharmacology 28:329–338
Diaz J, Pilon C, Le Foll B, Gros C, Triller A, Schwartz J-C, Sokoloff P (2000) Dopamine D3 receptors expressed by all mesencephalic dopamine neurons. J Neurosci 20:8677–8684
Dillon C, Li X, Ashby CR Jr, Heidbreder CA, Gaál J, Xi ZX, Gardner EL (2007) The dopamine D3 receptor antagonist SB-277011A potentiates cocaine-induced increases in extracellular dopamine in the nucleus accumbens in rats. Abstracts of the 37th Annual Meeting for Society of Neuroscience; 2007 November 3–7 San Diego, CA
Duarte C, Lefebvre C, Chaperon F, Hamon M, Thiébot M-H (2003) Effects of a dopamine D3 receptor ligand, BP 897, on acquisition and expression of food-, morphine-, and cocaine-induced conditioned place preference, and food-seeking behavior in rats. Neuropsychopharmacology 28:1903–1915
Duaux E, Gorwood P, Griffon N, Bourdel M-C, Sautel F, Sokoloff P, Schwartz J-C, Ades J, Lôo H, Poirier M-F (1998) Homozygosity at the dopamine D3 receptor gene is associated with opiate dependence. Mol Psychiatry 3:333–336
Edmonds DE, Gallistel CR (1974) Parametric analysis of brain stimulation reward in the rat: III. Effect of performance variables on the reward summation function. J Comp Physiol Psychol 87:876–883
Fouriezos G, Bielajew C, Pagotto W (1990) Task difficulty increases thresholds of rewarding brain stimulation. Behav Brain Res 37:1–7
Gyertyán I, Gál K (2003) Dopamine D3 receptor ligands show place conditioning effect but do not influence cocaine-induced place preference. Neuroreport 14:93–98
Heidbreder CA, Gardner EL, Xi Z-X, Thanos PK, Mugnaini M, Hagan JJ, Ashby CR Jr (2005) The role of central dopamine D3 receptors in drug addiction: a review of pharmacological evidence. Brain Res Rev 49:77–105
Heidbreder CA, Andreoli M, Marcon C, Hutcheson DM, Gardner EL, Ashby CR Jr (2007) Evidence for the role of dopamine D3 receptors in oral operant alcohol self-administration and reinstatement of alcohol-seeking behavior in mice. Addict Biol 12:35–50
Ikemoto S (2007) Dopamine reward circuitry: two projection systems from the ventral midbrain to the nucleus accumbens–olfactory tubercle complex. Brain Res Rev (in press)
Joyce JN, Millan MJ (2005) Dopamine D3 receptor antagonists as therapeutic agents. Drug Discov Today 10:917–925
Kita K, Shiratani T, Takenouchi K, Fukuzako H, Takigawa M (1999) Effects of D1 and D2 dopamine receptor antagonists on cocaine-induced self-stimulation and locomotor activity in rats. Eur Neuropsychopharmacol 9:1–7
Kornetsky C (2004) Brain-stimulation reward, morphine-induced oral stereotypy, and sensitization: implications for abuse. Neurosci Biobehav Rev 27:777–786
Le Foll B, Goldberg SR (2005) Cannabinoid CB1 receptor antagonists as promising new medications for drug dependence. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 312:875–883
Levant B (1997) The D3 dopamine receptor: neurobiology and potential clinical relevance. Pharmacol Rev 49:231–252
McCann UD, Ricaurte GA (2004) Amphetamine neurotoxicity: accomplishments and remaining challenges. Neurosci Biobehav Rev 27:821–826
Micheli F, Heidbreder CA (2006) Selective dopamine D3 receptor antagonists: a review 2001–2005. Recent Pat CNS Drug Discov 1:271–288
Miliaressis E, Rompré P-P (1987) Effects of concomitant motor reactions on the measurement of rewarding efficacy of brain stimulation. Behav Neurosci 101:827–831
National Academy of Sciences (National Research Council, Commission on Life Sciences, Institute of Laboratory Animal Resources) (1996) Guide for the Care and Use of Laboratory Animals. National Academy Press: Washington DC
Newman AH, Cao J, Bennett CJ, Robarge MJ, Freeman RA, Luedtke RR (2003) N-{4-[4-(2,3-dichlorophenyl)piperazin-1-yl]butyl, butenyl and butynyl}arylcarboxamides as novel dopamine D3 receptor antagonists. Bioorg Med Chem Lett 13:2179–2183
Pak AC, Ashby CR Jr, Heidbreder CA, Pilla M, Gilbert J, Xi Z-X, Gardner EL (2006) The selective dopamine D3 receptor antagonist SB-277011A reduces nicotine-enhanced brain reward and nicotine-paired environmental cue functions. Int J Neuropsychopharmacol 9:585–602
Paxinos G, Watson C (1998) The rat brain in stereotaxic coordinates, 4th edn. Academic, San Diego
Pilla M, Perachon S, Sautel F, Garrido F, Mann A, Wermuth CG, Schwartz J-C, Everitt BJ, Sokoloff P (1999) Selective inhibition of cocaine-seeking behaviour by a partial dopamine D3 receptor agonist. Nature 400:371–375
Platt DM, Rowlett JK, Spealman RD (2002) Behavioral effects of cocaine and dopaminergic strategies for preclinical medication development. Psychopharmacology 163:265–282
Ranaldi R, Beninger RJ (1994) The effects of systemic and intracerebral injections of D1 and D2 agonists on brain stimulation reward. Brain Res 651:283–292
Reavill C, Taylor SG, Wood MD, Ashmeade T, Austin NE, Avenell KY, Boyfield I, Branch CL, Cilia J, Coldwell MC (2000) Pharmacological actions of a novel, high-affinity, and selective human dopamine D3 receptor antagonist, SB-277011-A. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 294:1154–1165
Riddle EL, Fleckenstein AE, Hanson GR (2006) Mechanisms of methamphetamine-induced dopaminergic neurotoxicity. AAPS J 8:E413–E418
Ross JT, Corrigall WA, Heidbreder CA, LeSage MG (2007) Effects of the selective dopamine D3 receptor antagonist SB-277011A on the reinforcing effects of nicotine as measured by a progressive-ratio schedule in rats. Eur J Pharmacol 559:173–179
Singh J, Desiraju T, Raju TR (1996) Dose-response functions of apomorphine, SKF 38393, LY 171555, haloperidol and clonidine on the self-stimulation evoked from lateral hypothalamus and ventral tegmentum. Indian J Physiol Pharmacol 40:15–22
Sokoloff P, Le Foll B, Perachon S, Bordet R, Ridray S, Schwartz J-C (2001) The dopamine D3 receptor and drug addiction. Neurotox Res 3:433–441
Sokoloff P, Diaz J, Le Foll B, Guillin O, Leriche L, Bezard E, Gross C (2006) The dopamine D3 receptor: a therapeutic target for the treatment of neuropsychiatric disorders. CNS Neurol Disord Drug Targets 5:25–43
Stanwood GD, Artymyshyn RP, Kung M-P, Kung HF, Lucki I, McGonigle P (2000) Quantitative autoradiographic mapping of rat brain dopamine D3 binding with [125I]7-OH-PIPAT: evidence for the presence of D3 receptors on dopaminergic and nondopaminergic cell bodies and terminals. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 295:1223–1231
Stemp G, Ashmeade T, Branch CL, Hadley MS, Hunter AJ, Johnson CN, Nash DJ, Thewlis KM, Vong AKK, Austin NE (2000) Design and synthesis of trans-N-[4-[2-(6-cyano-1,2,3,4-tetrahydroisoquinolin-2-yl)ethyl]cyclohexyl]-4-quinolinecarboxamide (SB-277011): a potent and selective dopamine D3 receptor antagonist with high oral bioavailability and CNS penetration in the rat. J Med Chem 43:1878–1885
Vorel SR, Ashby CR Jr, Paul M, Liu X, Hayes R, Hagan JJ, Middlemiss DN, Stemp G, Gardner EL (2002) Dopamine D3 receptor antagonism inhibits cocaine-seeking and cocaine-enhanced brain reward in rats. J Neurosci 22:9595–9603
Wicke K, Garcia-Ladona J (2001) The dopamine D3 receptor partial agonist, BP-897, is an antagonist at human dopamine D3 receptors and at rat somatodendritic dopamine D3 receptors. Eur J Pharmacol 424:85–90
Wise RA (1996) Addictive drugs and brain stimulation reward. Annu Rev Neurosci 19:319–340
Wood MD, Boyfield I, Nash DJ, Jewitt FR, Avenell KY, Riley GJ (2000) Evidence for antagonist activity of the dopamine D3 receptor partial agonist, BP 897, at human dopamine D3 receptor. Eur J Pharmacol 407:47–51
Xi Z-X, Gardner EL (2007) Pharmacological actions of NGB-2904, a selective dopamine D3 receptor antagonist, in animal models of drug addiction. CNS Drug Rev 13:1–21
Xi Z-X, Gilbert J, Campos AC, Kline N, Ashby CR Jr, Hagan JJ, Heidbreder CA, Gardner EL (2004) Blockade of mesolimbic dopamine D3 receptors inhibits stress-induced reinstatement of cocaine-seeking in rats. Psychopharmacology 176:57–65
Xi Z-X, Gilbert JG, Pak AC, Ashby CR Jr, Heidbreder CA, Gardner EL (2005) Selective dopamine D3 receptor antagonism by SB-277011A attenuates cocaine reinforcement as assessed by progressive-ratio and variable-cost–variable-payoff fixed-ratio cocaine self-administration in rats. Eur J Neurosci 21:3427–3438
Xi Z-X, Newman AH, Gilbert JG, Pak AC, Peng X-Q, Ashby CR Jr, Gitajn L, Gardner EL (2006) The novel dopamine D3 receptor antagonist NGB 2904 inhibits cocaine’s rewarding effects and cocaine-induced reinstatement of drug-seeking behavior in rats. Neuropsychopharmacology 31:1393–1405
Yuan J, Chen X, Brodbeck R, Primus R, Braun J, Wasley JWF, Thurkauf A (1998) NGB 2904 and NGB 2849: two highly selective dopamine D3 receptor antagonists. Bioorg Med Chem Lett 8:2715–2718
Acknowledgment
This research was supported entirely by the Intramural Research Program of the National Institute on Drug Abuse, National Institutes of Health, Department of Health and Human Services.
Conflict of interest statement
All authors hereby declare that, except for income received from their respective primary employers, no financial support or compensation has been received from any individual or corporate entity over the past 3 years for research or professional services. There are no personal financial holdings that could be perceived as constituting a potential conflict of interest.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Spiller, K., Xi, ZX., Peng, XQ. et al. The selective dopamine D3 receptor antagonists SB-277011A and NGB 2904 and the putative partial D3 receptor agonist BP-897 attenuate methamphetamine-enhanced brain stimulation reward in rats. Psychopharmacology 196, 533–542 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00213-007-0986-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00213-007-0986-6